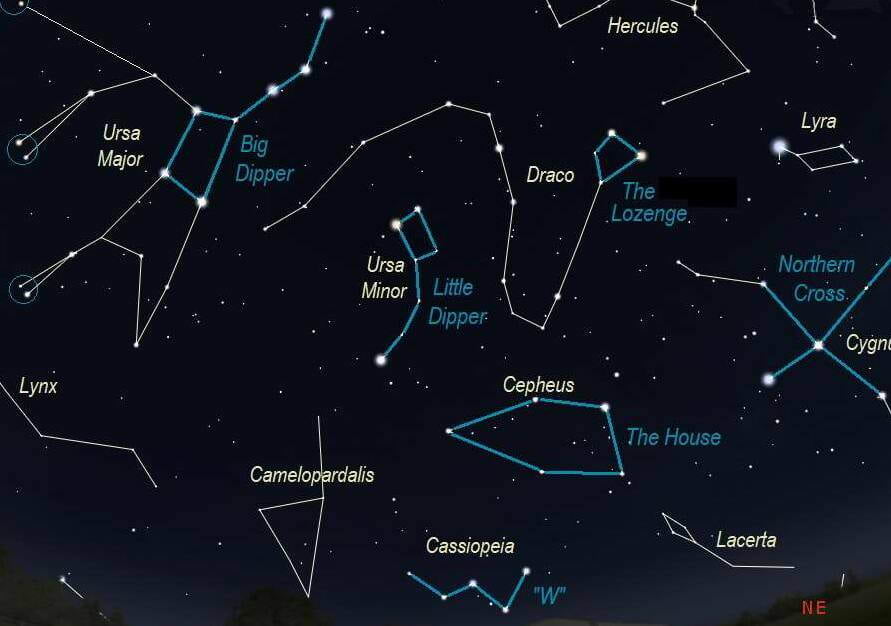
An asterism is a group of stars that form a recognizable pattern within a constellation. These patterns are often used as guideposts for astronomers to locate specific areas of the sky. Here are some examples of well-known asterisms:
- The Big Dipper, which is part of the Ursa Major constellation, is one of the most famous asterisms. It consists of seven bright stars that form the shape of a ladle or dipper.
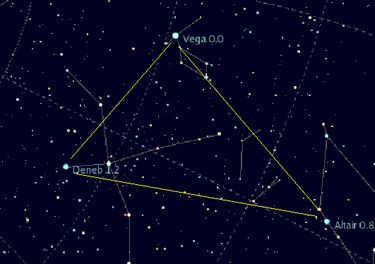
- The Summer Triangle is another popular asterism that is visible in the summer months. It is formed by three bright stars: Vega in the Lyra constellation, Altair in the Aquila constellation, and Deneb in the Cygnus constellation.
- The Pleiades, also known as the Seven Sisters, is a well-known asterism in the Taurus constellation. It is a cluster of stars that is visible to the naked eye and has been referenced in various mythologies and cultures throughout history.
These are just a few examples of the many asterisms that can be found in the night sky. They serve as both a source of wonder and a practical tool for astronomers.

Asterism is a term used to describe a specific group of stars in the night sky that is easily recognizable and has had a consistent name throughout history.
Basic details

The Big Dipper’s Bucket. Attempt to locate two galaxies that are well-liked among stargazers in this picture.
The term asterism is derived from the Greek word ἀστήρ, meaning star. Humans have long been fascinated by asterisms. References to these exquisite celestial formations can be found in ancient cultures worldwide. The most renowned asterism, which is likely known by nearly every individual on the planet, is the Big Dipper’s Bucket. The Bucket is a component of the Big Dipper constellation, which represents the body and tail of an animal.
In the 19th century, asterism was commonly used as a synonym for the astronomical term “constellation”. However, in 1922, the definitions of these terms were separated. Nowadays, the term “constellation” refers to a specific area of the sky, while “asterism” still refers to a specific group of stars.
Asterisms do not hold much scientific value in modern astronomy. Instead, they are more culturally and navigationally significant. Most asterisms consist of stars that are widely spaced apart, making them different from true star clusters. The Pleiades asterism and similar ones are the only exceptions, as they are actually star clusters.
Various Kinds of Constellations
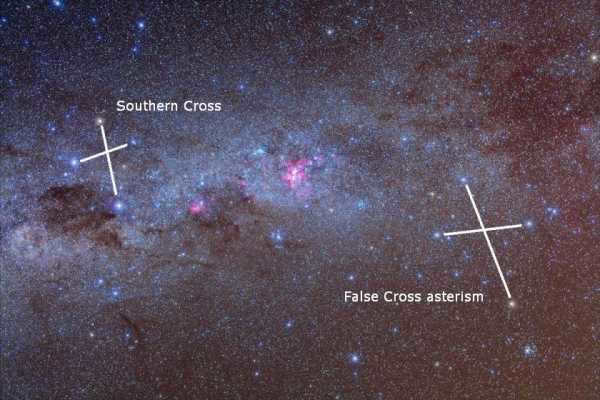

The Southern Cross (on the left) and the False Cross (on the right) are examples of asterisms.
While there are no official catalogs or records of asterisms maintained by astronomers, it is common to categorize these phenomena into various types. Asterisms are typically classified as seasonal (based on the time of year when they are visible), figurative (representing specific areas of constellations), paired (composed of two stars), telescopic (barely visible to the naked eye), and others.
Some of the well-known asterisms include
There are several notable asterisms that every astronomy enthusiast should be acquainted with. Among the most significant of these asterisms is the Great Wagon, situated within the Ursa Major constellation. Nowadays, it is highly unlikely to find someone who is not familiar with this particular asterism.
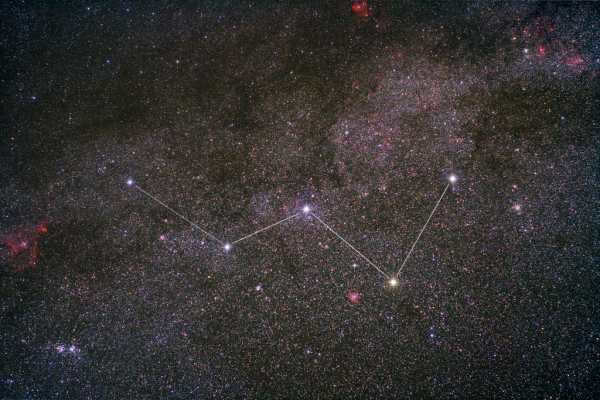

The asterism known as the “W” in the constellation Cassiopeia is widely recognized as one of the most prominent features in the night sky of the Northern Hemisphere. Its name pays homage to its striking resemblance to the letter “W” in the Latin alphabet. This particular asterism can be observed across the vast expanse of Russia. Another well-known asterism in the Northern Hemisphere is the Summer-Fall Triangle, which consists of three notable stars: Altair, Vega, and Deneb. The name of this asterism stems from its optimal visibility during the summer and fall seasons in the mid-latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere.


Orion’s Belt consists of three stars: Alnitak (ζ of Orion), Alnilam (ε of Orion), and Mintaka (δ of Orion), which are located in the center of the image.
There are several other well-known asterisms, such as the Scorpion’s Tail, the Pleiades, the Hyades, Kemble’s Cascade, the False Southern Cross in the Centauri constellation, the Egyptian Cross, and the Little Bucket, which includes Polaris in its tail. While asterisms may not have much practical significance in modern scientific astronomy, they hold great cultural and aesthetic value, making them important in the history of astronomy and humanity as a whole.
- An asterism (from the Greek word ἀστήρ “star”) is a distinct group of stars that has a historically recognized name. An asterism is not considered to include all the prominent stars of a constellation, such as the Dolphin, the Northern Crown, the Hair of Veronica, or the Southern Cross. However, in the original understanding of a constellation as a group of stars, these concepts are closely related and sometimes interchangeable. For example, in early ancient texts, the seven-star constellation “Bucket” was synonymous with the Big Dipper constellation, and Cassiopeia is equivalent to the “W” asterism.
In the Russian tradition, asterisms are distinguished from scattered star clusters that can be seen with the naked eye.
The idea of asterism is not strictly scientific, but rather a nod to tradition; there is no official record of asterisms. With the growth of amateur astronomy, enthusiasts have created catalogs of asterisms made up of stars that can be observed with non-professional telescopes.
Related concepts
Orion (Greek Ὠρίων) is a constellation located near the celestial equator. It is named after the hunter Orion from Greek mythology.
Capricorn (Latin. Capricornus, Sarga – goat, Cornu – horn) is a zodiacal constellation found in the southern hemisphere of the sky, situated between Aquarius and Sagittarius. The best time for observing this constellation is in July and August. It can be seen in the southern and central regions of Russia.
Taurus is a constellation in the zodiac, located between Gemini and Aries, to the northwest of Orion. The most notable stars in Taurus include Aldebaran with an apparent sidereal magnitude of 0.87, Nat with a magnitude of 1.65, Alcyone with a magnitude of 2.85, and ζ Taurus with a magnitude of 2.97. Within the constellation of Taurus, there are several star clusters, namely the Hyades and Pleiades, as well as the Crab Nebula, which contains the pulsar PSR B0531+21.
References mentioned in the literature
It is not unusual for amateur astronomers to have a better understanding of the constellations than professional scientists. What captures the interest of sky enthusiasts is not the size of a constellation, but rather the arrangement of bright stars that form a recognizable shape. These distinctive patterns are known as asterisms. The term “asterism” has ancient origins and was once used in the early 17th century to refer to a constellation. However, the term “constellation” eventually replaced “asterism” in this context, and asterisms came to refer to smaller groups of stars that are part of constellations or form distinct shapes. One well-known asterism is the Big Dipper, which resembles a bucket. Other familiar asterisms include Orion’s Belt, the letter “M” in Cassiopeia, and the Summer Triangle composed of Vega, Deneb, and Altair. Some asterisms are made up of dim stars, such as the Pleiades in the Taurus constellation. If a constellation lacks bright stars or a clear pattern, it tends to go unnoticed by the general public.
Continuation of Related Concepts
Constellations – divisions of the celestial sphere in modern astronomy that aid in easily navigating the starry sky. In ancient times, constellations were recognizable figures formed by bright stars.
The Eagle constellation, also known as Aquila in Latin, is located in the equatorial region. It is positioned in the eastern part of the Milky Way, just south of the Arrow constellation. The total area covered by the Eagle constellation is 652.5 square degrees, and it contains 70 stars that are brighter than the 6th magnitude.
The Ascendant constellation, also referred to as Auriga in Latin, can be found in the northern hemisphere of the sky. The brightest star in this constellation is Capella, which has a visual magnitude of 0.1. The best conditions for observing the Ascendant constellation are in December and January, and it is visible throughout Russia.
Cepheus (Latin. Cepheus) is a constellation located in the Northern Hemisphere of the sky, taking the shape of an irregular pentagon. The southern region of this constellation can be found along the Milky Way. It covers a total area of 587.8 square degrees in the sky and contains a count of 148 stars that can be seen with the naked eye.
Ara is a constellation situated in the southern hemisphere of the sky. It spans an area of 237.0 square degrees and features 60 stars that are visible to the naked eye. In the southern part of Russia (south of latitude 44° 30′), a small portion of this constellation, void of any bright stars, emerges very close to the horizon during the months of May and June. The star α Sacristan (with a magnitude of 2.95) is not observable in Russia, but under favorable conditions, it can be seen near the horizon line in southern cities of the former Soviet Union located below latitude 40° 08′ (such as Bukhara, Samarkand, Nakhichevan).
Zayats (Latin: Lepus) is a star pattern located in the sky’s southern hemisphere. It covers an area of 290.3 square degrees and contains 72 stars that can be seen without the use of a telescope. It is commonly observed in the central and southern regions of Russia, with the best viewing conditions occurring in December.
Aries is a well-known constellation in the zodiac, even though it does not have any stars brighter than a second magnitude. The three main stars, Hamal (referred to as the “head of the ram”), Sheratan (meaning “mark” or “sign”), and Mezartim (designated as α, β, and γ of Aries respectively), are easily identifiable as they lie to the south of the Triangle. The star Mesartim, which has a magnitude of four, was one of the first double stars to be discovered using a telescope (by Robert Hooke in 1664).
Serpens is a constellation located near the celestial equator. It covers an area of 636.9 square degrees in the night sky and includes 106 stars that can be seen with the naked eye. The best time to observe Serpens is in June, and it can be seen throughout Russia. What makes this constellation unique is that it consists of two distinct parts that are not connected. The northwestern part is known as “The head of the serpent,” while the eastern part is called “The tail of the serpent.”
Perseus, on the other hand, is a constellation found in the northern part of the sky. It is named after the Greek hero who famously defeated the Gorgon Medusa. Perseus is one of the 48 constellations identified by Ptolemy and is recognized as one of the 88 modern constellations by the International Astronomical Union. Notable features of Perseus include the variable star Algol (β Per) and its association with the annual Perseid meteor shower.
The constellation Grus, also known as Crane, can be observed in the southern hemisphere of the sky. In Russia, it is partially visible in the southern regions below 53° N. One of the notable stars in Crane is Alnair, which has a sidereal magnitude of 1.7. Alnair is located 100 light-years away and is used for astronavigation. Crane is situated between the constellations South Fish in the north and Tucana in the south. It covers an area of 365.5 square degrees in the sky and contains 53 stars that can be seen without the aid of a telescope.
Serpentine (also known as Ophiuchus) is a large constellation that spans the equator and intersects with the ecliptic. It is often referred to as the 13th sign of the zodiac, although it is not officially part of the zodiacal circle in European astrology. This is because the signs of the zodiac in European astrology do not perfectly align with the constellations, as there has been a gradual shift in the Sun’s passage through the constellations over time.
Sails (sometimes spelled Sails) is a constellation located in the southern hemisphere of the sky. It is known for its proximity to the Milky Way, with its southern border running along some of the richest areas of the galaxy. Sails covers an area of 499.6 square degrees in the sky and contains 195 stars that can be seen with the naked eye.
Cancer is a zodiac constellation that is not easily noticeable and can only be seen on a clear night between the constellations of Leo and Gemini. The brightest star in Cancer, known as β Cancer, has an apparent magnitude of 3.53m.
Swan is a constellation located in the northern hemisphere of the sky. The bright stars in this constellation form a distinct cross-shaped pattern, known as the Northern Cross asterism, which stretches along the Milky Way. In ancient times, people associated this constellation with flying birds, with the Babylonians referring to it as the “forest bird” and the Arabs calling it a chicken.
This list includes the brightest stars that can be observed from Earth in the optical range, based on their apparent stellar magnitude. For multiple stars, the total stellar magnitude is provided.
Lyra, also known as લેયરા in Gujarati and Latin Lyra or Lyr, is a small constellation located in the northern hemisphere. It lies between the constellations of Hercules and Swan.
Foxglove (Latin: Vulpecula, Vul) is a faint constellation found in the northern part of the celestial sphere, situated within the boundaries of the Summer Triangle.
Zodiacal constellations (derived from the Greek word ζωδιακός, meaning “animal”) are a group of 13 constellations positioned along the ecliptic, which is the Sun’s apparent yearly path across the stars. These constellations are named after various animals, a tradition that has been followed since ancient times.
Pheonix (Latin: Phoenix, Phe) is a constellation located in the southern hemisphere of the night sky. It covers an area of 469.3 square degrees and contains 68 stars that can be seen with the naked eye.
Monoceros is an equatorial constellation known as the Unicorn in Latin and derived from the Greek word μονόκερως. It covers an expansive area of 481.6 square degrees in the night sky and boasts 146 stars that are visible to the naked eye. While Monoceros lies within the Milky Way, it lacks any prominent or bright stars. However, its location can be easily identified as it resides within the winter triangle formed by the brilliant stars Sirius, Procyon, and Betelgeuse. As one of the 15 constellations crossed by the celestial equator, Monoceros is visible in the central and southern regions.
Camelopardalis, also known as the Giraffe in Latin, is a sizeable but faint polar constellation found in the northern hemisphere. The most luminous star in this constellation is β Giraffe, which possesses a stellar magnitude of +4.03m. In Russia, Camelopardalis can be observed throughout the year, with the best viewing conditions occurring in January and February.
Naugolnik is the name given to a group of stars in the southern part of the sky. It is located to the southwest of Scorpius and to the north of the Southern Triangle. The constellation is also in contact with Circulus. The Milky Way can be seen passing through Naugolnik. However, despite this, the region is not rich in bright stars. In fact, there are no stars in Naugolnik that are brighter than 4.0 visual sidereal magnitude. Nevertheless, there are still 42 stars in the constellation that can be seen with the naked eye. The area of the sky occupied by Naugolnik measures 165.3 square degrees. The best time to observe this constellation is in May and June. It is partially observable in southern Russia, specifically south of 48 N.
Tucan is another constellation in the southern hemisphere of the sky. Its Latin name is Tucana, and it is commonly referred to as Tuc. Tucan spans an area of 294.6 square degrees in the sky. It contains 44 stars that are visible to the naked eye.
Bayer designations – designations of stars with Greek alphabet letters, which were proposed by Johann Bayer in the star atlas Uranometria (published in 1603). These designations are still widely used today, although there are now other systems for naming stars that cover a much larger number of stars.
Dolphin (Latin: Delphinus) is a small constellation in the northern hemisphere of the sky. Its three brightest stars have luminosities of 3.7, 3.8, and 4.0 sidereal magnitudes. The best time for observing this constellation is from June to September, except in the circumpolar regions of Antarctica. It is visible throughout Russia. Dolphin is a kite-like constellation located near the summer-fall triangle, close to Altair:114.
A group of three or more stars that appear to be close to one another when viewed from Earth is known as a multiple star. This closeness can be due to mere visibility, where stars at different distances appear close in the line of sight, making the star optically multiple. Alternatively, the stars may be physically close and bound together by gravity, making the star physically multiple. Physically multiple stars are a specific type of multiple star system.
Voron (also known as corvus in Latin) is a small constellation located in the southern hemisphere of the sky. It is situated between the constellations Virgo and Hydra. The brightest star in Voron has a stellar magnitude of 2.6m. The best visibility conditions for this constellation are during the months of March and April. Voron can be observed from the middle latitudes and southern regions of Russia.
The Blue Giant is a type of star known as a spectral class O or B. These stars are young, hot, and massive, and can be found in the main sequence region of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Blue giants typically have masses ranging from 10 to 20 times that of the Sun, and their luminosity is thousands to tens of thousands of times greater.
Triangulum, also known as the Triangle constellation, is located in the northern hemisphere of the sky. It covers an area of 131.8 square degrees and contains 25 stars that can be seen without the aid of a telescope.
The Pigeon constellation, also known as Columba, is located in the southern hemisphere of the sky. It covers an area of 270.2 square degrees and contains 71 stars that can be seen without the aid of a telescope. This constellation is fully visible in the southern regions of Russia during the months of December and January. The brightest star in the Pigeon constellation is called Fact.
Pisces (Latin. Pisces) is a large constellation in the zodiac, located between Aquarius and Aries. It is commonly divided into “northern Pisces” (positioned under Andromeda) and “western Pisces” (situated between Pegasus and Aquarius).
Peacock (Latin: Pavo) is a constellation found in the southern hemisphere of the celestial sphere, named after the stunning peacock bird. It can be fully observed in the entirety of the Southern Hemisphere and partially in the tropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere. However, no part of it can be seen from Russian territory. The constellation was one of the 12 introduced by P. Plancius during the analysis of observations of the night sky in the Southern Hemisphere conducted by P. D. Keyser. The presence of Peacock was first documented on a 14-inch star globe produced in Amsterdam in 1598 by Plancius and J. Hondius.
Pegasus (Latin: Pegasus) is a constellation situated in the northern part of the celestial sphere. It can be found in the southwest region of Andromeda. Pegasus covers a vast area of 1120.8 square degrees in the sky and is home to 166 stars that can be seen with the naked eye.
Fly (Latin. Musca, Mus) is another constellation that can be observed in the southern hemisphere of the sky. It is positioned within the Milky Way, south of the Southern Cross constellation. Fly occupies an area of 138.4 square degrees in the sky and boasts 60 stars that are visible without the aid of any optical device.
Lizard (Latin: Lacerta) is a constellation present in the northern part of the sky. It lies between Swan and Andromeda. Despite its location in the Milky Way, Lizard does not have any prominent stars. The brightest star within this constellation has a visual sidereal magnitude of 3.8. Lizard encompasses an area of 200.7 square degrees in the sky and contains 63 stars that can be seen without the need for any astronomical equipment.
The constellation known as Indian (Latin: Indus) is a lengthy but faint group of stars located in the southern part of the sky. It can be found below the constellations Microscope and Crane, stretching all the way to Octanthus. Indian is bordered by Toucan to the west, Telescope to the east, and Peacock to the southeast. Covering an area of 294 square degrees, it contains 38 stars that can be seen with the naked eye. In regions of southern Russia (below latitude 44° 30′), the northernmost section of Indian can be observed low on the horizon during late summer and early fall. In the southern part of Dagestan, under optimal conditions.
Octanthus (Latin: Octans) is a small and extremely faint constellation located in the southern hemisphere of the sky. It includes the South Pole of the world.
A spectral double is a binary star system that can be detected through spectral observations. These systems typically consist of two stars that are located very close to each other and have velocities large enough that they cannot be resolved as separate entities using modern telescopes. As the stars orbit around their common center of mass, one star moves towards us while the other moves away, resulting in unequal radial velocities along the observer’s line of sight.
The Shield constellation, also known as Scutum (Sct) in Latin, is a celestial formation located in the southern hemisphere near the celestial equator. It spans an area of 109.1 square degrees in the sky and contains 28 stars that can be seen without the aid of a telescope.
The constellation known as Flying Fish, or Volans in Latin, can be found in the southern hemisphere of the sky. It covers an area of approximately 141.4 square degrees and contains a total of 31 stars that can be seen with the naked eye. It should be noted that this constellation is not visible from Russia.
On the other hand, Hydra, which takes its name from the creature of Greek mythology, is also a constellation in the southern hemisphere of the sky. Its brightest star, Alfard, has a visual magnitude of 2.0. The best time to observe this constellation is during the months of February and March. While it can be seen in its entirety in the southern regions of Russia, it is only partially visible in the rest of the country.
- Asterism is an infrequently employed typographic symbol made up of three stars arranged in a triangle (⁂). It is commonly utilized to bring attention to a narrative or to differentiate subsections or episodes in a book. In Unicode, this character is represented by the code U+2042.
Oftentimes, this symbol appears as three (or occasionally more) asterisks or dots in a row, or increased indentation is utilized between paragraphs to organize the same separation of subsections from one another. Asterism or its equivalents can be utilized in conjunction with additional indentation to denote sections that are smaller than subchapters.
Similar concepts
A top dash is a typographic symbol consisting of a horizontal line drawn immediately above the text. In mathematical notation, the line above is commonly used as a vinculum to combine certain symbols. Additionally, the sign is utilized with Roman numerals to indicate the multiplication of a digit by a thousand, as well as in medieval abbreviations (sigla). The act of marking one or more words with a solid line above the letters is referred to as strikethrough.
Japanese punctuation (Jap. 約物 yakumono) refers to the various punctuation marks and rules governing their usage in the Japanese language.
Braille is a symbol represented by a thin straight line slanting to the right (i.e. forward when writing from left to right).
The vertical dash is a character in ASCII with the code 0x7C (hex), 124 (dec). UNIX users refer to this character as “pip”, derived from the English term “pipeline”. In the initial editions of V. E. Figurnov’s books, during the Soviet era, the term “pipe” was translated as “pipeline symbol”.
References in literary works
It is not unusual for amateur astronomers to possess a superior understanding of constellations compared to professional scientists. For enthusiasts of the night sky, the appeal of a constellation is not determined by its size, but by the arrangement of bright stars that form a distinctive figure. These unique figures are known as asterisms. “Asterism” is an ancient term; in the early 17th century, it was still in usage and referred to as a “constellation,” but over time, it was replaced by the term “constellatio” in that context. Asterisms, on the other hand, typically refer to smaller groups of stars that are part of constellations or form distinct patterns with bright stars. The Big Dipper’s handle is a well-known asterism. Other familiar examples include Orion’s Belt, the “letter M” in Cassiopeia, and the Summer Triangle composed of Vega, Deneb, and Altair. Some asterisms consist of dim stars, such as the Pleiades in the Taurus constellation. If a constellation lacks bright stars or fails to form a clear pattern, it does not capture the public’s attention.
A space serves as a delimiter between characters, indicating word boundaries in various writing systems. In terms of functionality, a space is classified as a punctuation mark.
A division symbol, which can take the form of a colon (∶), obelus (÷), or slash (∕), is utilized in mathematics to denote a division operation.
In programming, a string type (referred to as “string”) is a data type that consists of a sequence of alphabetical characters. Each instance of this type (known as a string variable) can be stored using a fixed number of bytes or have a variable length.
Unicode (commonly known as Unicode) is a standard character encoding system that encompasses characters from nearly all written languages worldwide. It currently stands as the prevailing standard for the Internet.
A backslash, also known as a backslash or backslash (in computer jargon – backslash or backslash from English. backslash), is a special symbol (\) that is spelled in the opposite direction of the usual slash symbol (/) (sometimes referred to as “forward slash”).
The Gould designations for stars are similar to Flemsteed’s in that they assign numbers to the stars in a constellation in ascending order of direct ascension. Each star is given an integer (starting at 1), followed by the letter “G.” (or sometimes immediately followed by the letter “G” without a space or dot), and then the Latin genitive of the constellation in which it is located (see List of constellations and their Latin name (genitive)).
The currency symbol or sign (¤) is a typographic character that belongs to the C1 Controls and Latin-1 Supplement group of the Unicode Standard. Its original name is Currency sign in English, and its code is U+00A4. The HTML mnemonic for it is ¤. This symbol is used in cases when a specific currency sign is not available or missing in a computer font.
An asterisk (Greek: ἀστέρισκος) is a typographic mark in the form of a small asterisk (*) with usually five or six points. It can be placed in a line or raised above the line.
Aperture refers to the area of a letter that is completely or partially enclosed by the shape of the letter or symbol. The Latin alphabet letters with closed apertures include A, B, D, O, P, Q, R, a, b, d, e, g, o, p, and q. Letters with open apertures include c, f, h, i, s, and so on. The digits 0, 4, 6, 8, and 9 also have apertures.
Run-length encoding (RLE) is an algorithm for data compression that replaces repeated characters or series with a single character and the number of repetitions. A series is defined as a sequence of identical characters. During encoding (compression), a series of identical characters is replaced with a string that includes the repeated character and the number of repetitions.
A list marker, such as a bullet (-), is a typographic character that is used to indicate list items, as demonstrated in the example below.
A wildcard character (also known as a joker character) is a character that is used to substitute for other characters or sequences of characters, resulting in character patterns. Regular expressions are an extension of wildcard characters.
Control characters are characters in the encoding that do not have a visual representation but are used to control devices, organize data transfer, and serve other purposes.
Backus-Naur Form (BNF) is a formal system for describing syntax in which certain syntactic categories are defined sequentially using other categories. BNF is commonly used to describe context-free formal grammars. There is an extended version of Backus-Naur that includes more concise constructions.
An empty string, in the field of computer science, refers to a string value that does not contain any characters (i.e., it has a length of zero).
Caret notation is a method used to represent control characters in ASCII encoding. This notation involves combining a caret character (^) with an uppercase letter, where the letter corresponds to the ASCII code of the character based on its position in the English alphabet. For instance, the end-of-transmission character, which has a value of 4, is denoted as ^D since D is the fourth letter in the alphabet. Similarly, the null character is represented as ^@ because @ comes before A in the ASCII table. The DEL character, with a value of 127, is commonly written as ^? since the ASCII character ? comes before @.
The concept of the author’s mark, which serves as one of the key components of the output information in a printed publication, was introduced by librarian Lyubov Borisovna Khavkina in 1916.
In Russian typography, the symbol No. is utilized to indicate the ordinal number of an object (assuming that the numerical value is mandatory) among other homogeneous objects – the number. In the United States of America, the number is denoted by the grid sign – #.
Mono-wide, or non-proportional font is a typeface where all characters (specifically, kegel sites of characters) possess equal width. This differs from a proportional typeface, where the letters vary in width from one another.
In typography, a hyphenation refers to the division of a part of text (such as a word, formula, etc.) when its beginning appears on one line and its end on another.
Mathematical notations, also known as the “language of mathematics,” are a complex system of graphical symbols used to represent abstract mathematical concepts and statements in a way that can be understood by humans. This system is a significant component of the various non-verbal communication systems employed by humanity, due to its intricacy and diversity. While this article primarily focuses on the internationally recognized sign system, it is important to note that different cultures throughout history have developed their own unique mathematical notations, some of which are still in limited use today.
The symbol commonly known as the lattice sign (#) has various other names, such as lattice, octothorpe (derived from the Latin term “octothorpe” meaning “eight ends”), hash, number sign, diez, and sharpe (the latter two due to the visual resemblance of these symbols). In cases where a system lacks the technical capability to input the pound symbol, the lattice sign is often used as a substitute.
Dash (French: tiret, derived from the verb tirer – to stretch) is a punctuation mark that is used in various languages. In Russian writing, the dash was introduced by the writer and historian N. M. Karamzin. The rules for its usage and the name of this symbol were not immediately established. It was initially referred to as “molchanka” in A. A. Barsov’s “Russian Grammar”, then as “trait”, and later as “thought-separating sign” in A. H. Vostokov’s “Abridged Russian Grammar”.
Obelus, also known as obel (÷) (derived from the Latin word “obelus” which comes from the Greek word ὀβελός, the same root as obelisk) is a non-letter symbol that resembles a combination of the minus and colon signs.
Typography refers to a collection of fonts, available in various sizes and styles, that share a cohesive design and consist of specific typographic characters. Generally, a typeface includes alphanumeric and punctuation characters, as well as special symbols. Some typefaces are solely comprised of non-alphabetic characters, such as those used for mathematical or cartographic purposes. It’s important to note that the term “typeface” is often mistakenly used interchangeably with “font,” despite their distinct meanings.
A font, derived from the German word “Schrift” meaning “to write,” is a visual arrangement of letterforms and characters that form a unified stylistic and compositional system. It represents a set of symbols of a particular size and style. In the realm of typography, a font specifically refers to a collection of typographic letters intended for use in typing.
The typographic symbol known as the colon sign (₡) is part of the Currency Symbols group in the Unicode standard. Its original name is the colon sign and its code is U+20A1. This symbol is primarily used to represent the currency units known as “colon” in Costa Rican and Salvadoran currencies.
Shinjitai, which translates to “new forms of signs” in Japanese, refers to the forms of kanji that have been used in Japan since the Toho kanji list was established in 1946. The older forms of kanji are referred to as kyujitai, meaning “former forms of signs.” While some of the new forms in shinjitai resemble the simplified Chinese characters, they have undergone fewer extensive modifications. As a result, modern Japanese kanji are more similar to traditional Chinese characters.
The Natural Area Code (NAC), also known as the NAC in Russian transliteration, is an innovative geocoding system that allows for precise determination of areas or volumes anywhere on our planet. Unlike traditional latitude and longitude coordinates, the NAC code utilizes a combination of thirty alphanumeric sequences, resulting in a shorter and more efficient code.
Colon (:), a punctuation mark consisting of two dots placed vertically, serves the purpose of connecting two parts of a text in a causal, explanatory, or other semantic relationship.
Fifty-nine icosahedrons, also referred to as The Fifty-Nine Icosahedra, is a captivating book authored and illustrated by Harold Coxeter, Patrick du Val, H. T. Flaser, and J. F. Petrie. This remarkable publication showcases various star shapes of regular convex (Platonic) icosahedra, meticulously constructed using a set of rules proposed by J. C. P. Miller.
Regular expressions (also known as regex) are a formal language used for searching and manipulating substrings in text. They rely on the use of metacharacters, which are wildcard characters that represent patterns. The pattern string, often referred to as a “template” or “mask,” is used for searching and consists of symbols and metacharacters that define the search rule. Additionally, a replacement string can be specified for text manipulation, which may contain special characters.
Variable stars are given special designations if they haven’t already been assigned a letter from the Greek alphabet. These designations follow the Bayer designation format and are combined with the name of the constellation in the genitive case, indicating the star’s location (see List of constellations and their Latin names in the genitive case).
A block (portion of a sheet of stamps) is a term used to refer to a section of a stamp sheet that contains two or more stamps that are connected and not separated from each other.
An emoticon (also known as an emotion icon or emoticon) is a pictogram that represents an emotion and is typically made up of typographic characters.
Free fonts PT (short for “Peter” font system; PT stands for Public Type) is a project aimed at creating freely available fonts with an open license that support all languages spoken by small ethnic groups in the Russian Federation (see the list of languages). Currently, the font family consists of three sets.
A nibble, also known as a half-byte, tetrad, or hexadecit (short for hexadecimal digit), is a unit of measurement for information. It is equal to four binary digits (bits) and is convenient because it can be represented by a single hexadecimal digit. In other words, it is exactly one hexadecimal digit. A nibble can have 16 different values, as there are 16 possible combinations of four binary digits. In the Russian language, the term “tetrada” is used as a synonym for a nibble.
The Nassi-Shneiderman diagram is a graphical representation of structured algorithms and programs. It was developed in 1972 by American graduate students Ben Shneiderman and Isaac Nassi.
In typography, a list is a method of organizing various types of enumerations. Each element in a list begins with a list marker or number, and the text of the list should not extend beyond the left margin.
A corridor in typography refers to the arrangement of several spaces in adjacent lines, forming a vertical or slanted row. Corridors are considered a layout defect as they distract the eye from the horizontal flow of the text, negatively impacting readability. One way to identify corridors in printed text is by turning it upside down, while blurring can be used for text displayed on a monitor.
Indentation style, also known as indentation, is a set of rules for formatting source code. It involves properly indenting program blocks to enhance readability.
In typography, a superscript or super script refers to a character that is written above the main line. This is commonly used in mathematical and chemical formulas.
Asterism (from the Greek word ἀστήρ meaning star) refers to a group of stars that is easily recognizable and has an independent name with historical significance. It’s important to note that groups of stars that encompass all the major stars of a constellation, such as Dolphin, the Northern Crown, Veronica’s Hair, or the Southern Cross, are not considered asterisms. However, in the original understanding of a constellation as a group of stars, these concepts are closely related and sometimes even interchangeable. For example, in early ancient texts, the seven-star “Bucket” was synonymous with the Big Dipper constellation, and Cassiopeia is equivalent to the asterism “W”.
In the Russian tradition, certain scattered star clusters that are visible to the naked eye are also classified as asterisms.
There are several commonly encountered asterisms including:
- The Summer and Fall Triangle;
- The Winter Triangle and Winter Circle;
- The Spring Triangle;
- The Big Square in the constellation Pegasus (including α Andromeda);
- The Big Bucket in the constellation Big Dipper;
- The Small Bucket in the constellation of the Little Dipper;
- The Dragon’s Head in the constellation Dragon;
- The W asterism in the constellation Cassiopeia;
- The Jug in the constellation Aquarius;
- Orion’s Belt and
- The Sword of Orion in the constellation Orion;
- The Sheaf in the constellation Orion;
- The Northern Cross in the constellation Swan;
- The False Southern Cross in the constellation Centaurus;
- The Sickle in the constellation Leo;
- The Gorgon’s Head in the constellation Perseus;
- The Scorpius constellation has a tail.
- In the Pisces constellation, there are North Fish and West Fish.
- In the Cancer (cluster) constellation, there are Crèche and Donkey.
- In the Taurus constellation, there are Pleiades and Hyades (clusters).
- In the Ascendant constellation, there are The Goat and Goats.
- In the Foxy constellation, there is Hanger (scattered cluster Cr 399).
- In the Giraffe constellation, there is Kemble’s Cascade.
- The Egyptian Cross is a figure made up of the brightest stars from several constellations.
Related articles
Citations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Discover the definition of “Asterism (astronomy)” in different dictionaries:
- Asterism – Wiktionary?… Wikipedia
- Pleiades (astronomy) – Pleiades Scattered cluster Pleiades, Scattered cluster History of study Discoverer Date of discovery Designations M45 Observable data (Epoch J2000.0) Class… Wikipedia
- Hyades (mythology) – This term has other meanings, see Hyades. Asterism of the Hyades in the constellation Taurus The Hyades (dr. Greek Ὑάδες rain) in Greek mythology… Wikipedia
- Vega – Vega Star Position of Vega in the constellation Lyra History of study Designations Vega, α Lyr, 3 Lyr, HIP 91262[1], GCRV 11085… Wikipedia
- Vega (star) – The position of Vega in the constellation Lyrae has been studied throughout history. It is also known by its designations Vega, α Lyr, 3 Lyr, HIP 91262[1], GCRV 11085 … according to Wikipedia.
- Vega – The term “Vega” has other meanings, which can be found in the article about Vega (meaning). Vega Star … according to Wikipedia.
- Scorpius (constellation) – The term “Scorpius” has other meanings, which can be found in the article about Scorpio (meaning). It should not be confused with the zodiac sign Scorpio. Scorpio … according to Wikipedia.
- Leo (constellation) – The term “Leo” has other meanings, which can be found in the article about Leo (meaning). Leo … according to Wikipedia.
- Cancer (constellation) – The term “Cancer” has other meanings, which can be found in the article about Cancer. It should not be confused with the zodiac sign Cancer. Cancer … according to Wikipedia.