The celestial body
The cluster of stars known as Taurus, found to the northwest of Orion’s belt, is one of the constellations in the zodiac. It can be observed in the night sky between Aries and Gemini. Currently, scientists have extensively researched this group of stars and have accumulated numerous intriguing details about Taurus through many years of observation.
The Legend of the Taurus Constellation
The Taurus constellation has been observed by humans since ancient times. The exact moment when astronomers identified the stars within it as a distinct cluster is uncertain. One of the earliest accounts of the constellation was recorded by the Greek scholar Eudoxus in the 3rd century BC, and later it was incorporated into Ptolemy’s Almagest.
Due to the abundance of stories surrounding the gods in ancient Greece, constellations were given names in their honor and often linked to fantastical creatures. Taurus followed this pattern, with three myths associated with the celestial cluster.
During that era, it was believed that Zeus embodied this constellation. To abduct Europa and confine her to the island of Crete, he transformed into a white bull and carried her away. Another legend suggests that the constellation represents the bull that Hercules battled on the same island, an encounter considered his seventh labor. A third myth proposes that the constellation was the fiery bull discovered and tamed by Jason in Colchis.
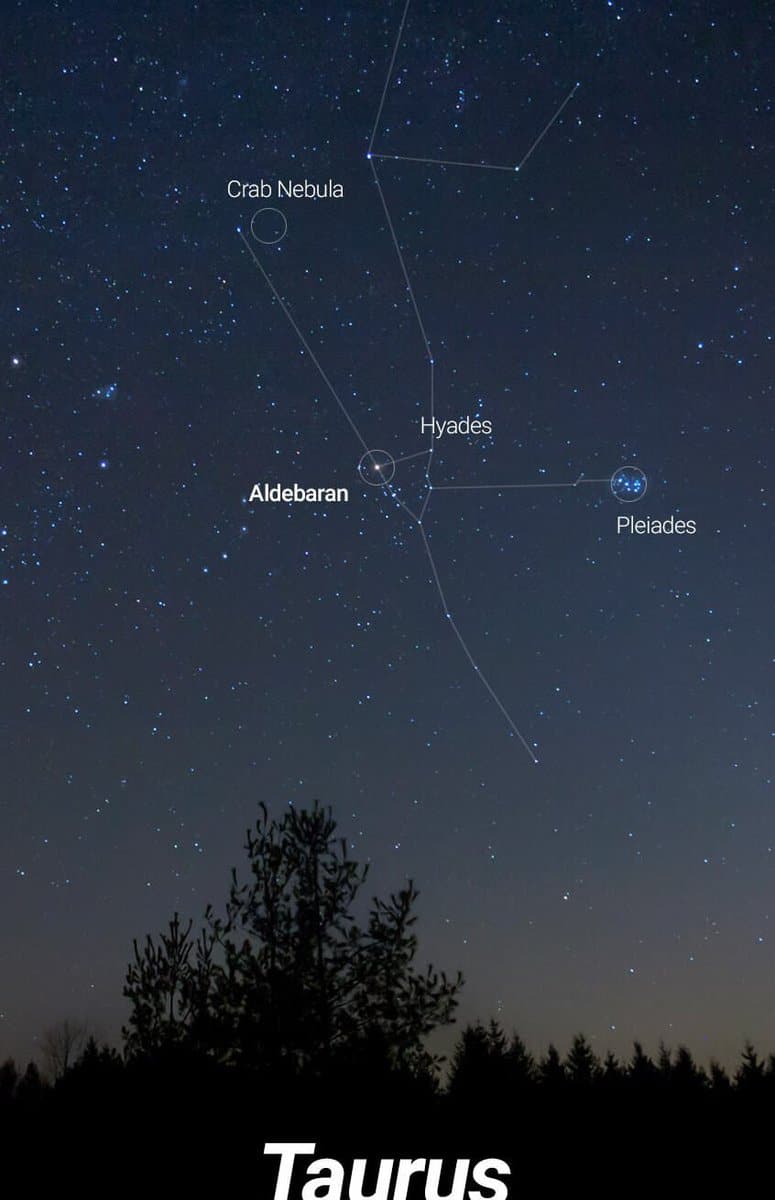
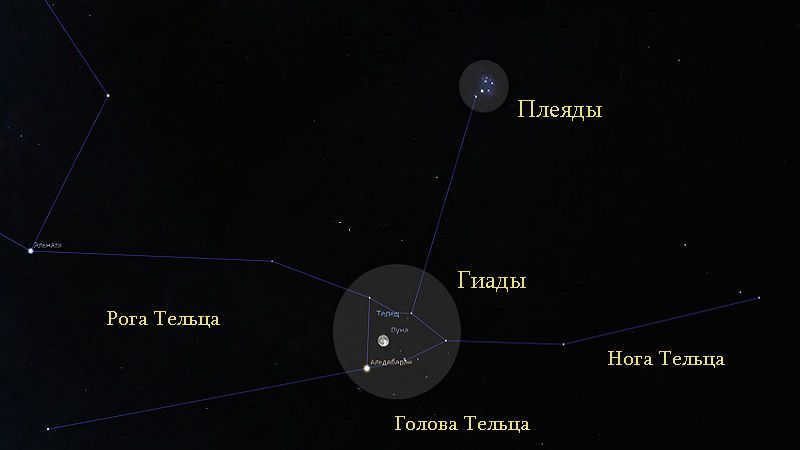
In the Taurus constellation, there are two star clusters that can be easily observed – the Pleiades and the Hyades. The Pleiades cluster is located 410 light-years away from Earth and consists of 500 stars. On the other hand, the Hyades cluster is situated 150 light-years away and contains 132 stars.
Did you know? The name “Hyades” has an interesting origin, as it translates from ancient Greek to “it’s raining”. This is because when these stars are close to the horizon, it signals the upcoming rainy season in certain regions.
Taurus also has its own myths and legends in Slavic culture. People from these countries often associate the constellation with the god of cattle, Veles. This connection is not surprising, considering that the Greek name for Taurus sounds similar to the word “turus”, which means bull.
Taurus, like any other constellation, has specific characteristics that were identified by astronomers in ancient times. With the advancement of modern equipment, more precise parameters were able to be determined:
- The constellation is known as Taurus in Latin, and is also abbreviated as Tau;
- The symbol of this star cluster is a bull;
- Direct ascension is observed between 3 hours 17 minutes and 5 hours 53 minutes;
- The declination angle ranges from -1 degree 45 minutes to +30 degrees 40 minutes;
- Taurus covers an area of 797 square degrees in the sky, making it the 17th largest constellation;
- The brightest stars in the cluster are Aldebaran (0.87m), Nat (1.65m), Alcyone (2.85m), and Tau (2.97m);
- The constellation is home to meteor streams called Turids and Beta-Taurids;
- The constellations Gemini, Orion, Eridanus, Aries, Cetus, Ascendant, and Perseus are situated near Taurus.
- The cluster can be best observed during November and December, when it can be seen from latitudes ranging from -59 degrees to +89 degrees.
Thanks to these parameters, locating Taurus in the night sky is easy, even for amateur astronomers. It can be found in the first quadrant of the northern hemisphere, spanning latitudes from -65 degrees to +90 degrees. Taurus is home to two Messier objects, M1 and M45, as well as five stars with orbiting planets.
The primary stars of the Taurus constellation
The Taurus constellation is comprised of a vast array of stars, however, there is a cluster of key stars that astronomers specifically identify. These stars possess significant luminosity, making them easily observable from our planet, yet they are situated at varying distances from the solar system.
Aldebaran
can be rephrased as
Aldebaran is a star in the constellation Taurus
.
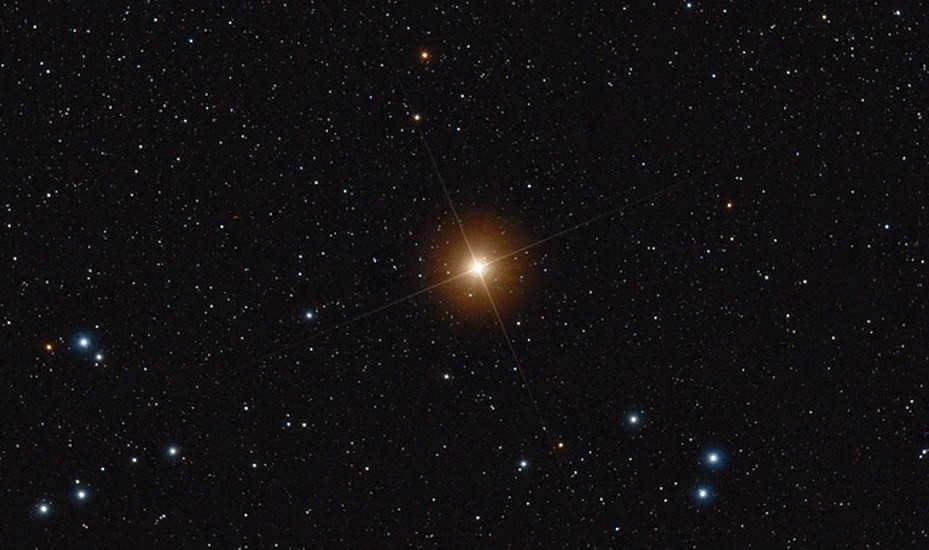

Situated in the improvised head of Taurus, the constellation, the brightest star can be found. It is classified as a normal giant with a reddish-orange luminosity. Due to its proximity of only 65 light years from Earth, it is easily observable in the night sky with the naked eye. Currently, Aldebaran is gradually expanding in size as a result of its helium burning process. At present, the star has a diameter 38 times larger than that of the sun.
Fascinating fact: Aldebaran is often referred to as the “eye of Taurus” as it is positioned directly below the “horns” of the constellation.
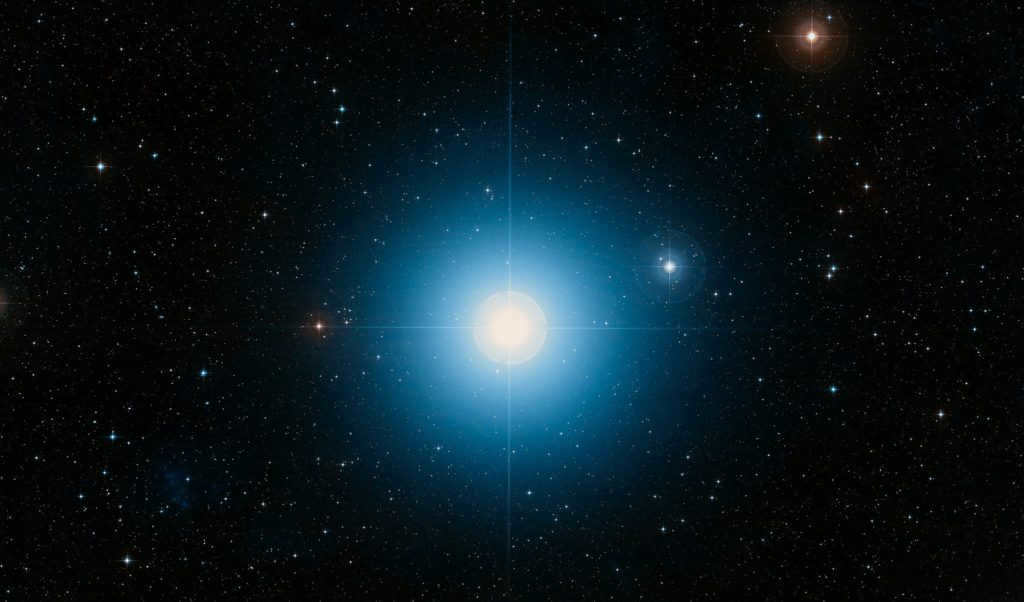

The second brightest star, five times larger than the Sun, is situated on the boundary with the Ascendant constellation, leading ancient astronomers to assign it to both constellations at different times.
Nat’s luminosity is amplified by a nearby companion, resulting in its classification as a “binary star.” Observations have indicated that Nat is currently undergoing a transition into a gas giant, although it still has a considerable distance to go before attaining this status.
Alcyone
Alcyone is a bright star in the Pleiades star cluster. It is also known as Eta Tauri and is located in the constellation of Taurus. Alcyone is the brightest star in the Pleiades and is visible to the naked eye. It is a blue-white star and is roughly 370 light-years away from Earth. Alcyone is one of the most well-known stars in the night sky and has been observed and studied by astronomers for centuries. Its unique properties and position in the sky make it a fascinating object of study.

These stars, known as A, B, C, and D, are located in close proximity to each other. Each star has its own unique characteristics and brightness. Among them, there are blue-white giants as well as yellow dwarfs. When viewed with a telescope that does not have a high magnification, Alcyone appears as a single star.
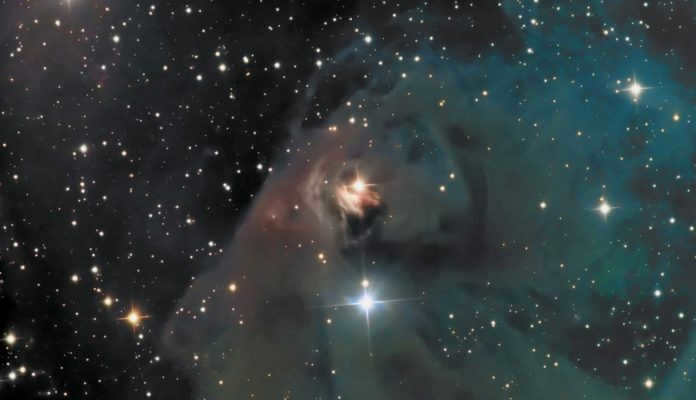

There is a young star located in the center of a massive hydrogen nebula. The core of the celestial body has a strong gravitational pull, causing the surrounding gas and dust to gradually come together and form a solid sphere.
Here’s an interesting fact: The total mass of the nebula is 1000 times greater than that of the Sun, making Taurus a significant and luminous object in its final stages of development.

There is a massive behemoth spinning at a velocity of 181 km/h, resulting in the release of a gaseous cloud into the vastness of space and a gradual loss of its mass. Additionally, the star experiences a stretching effect at its equator and a flattening at its poles due to its intense motion.
Merope

Merope, a subgiant star, has depleted its hydrogen fuel in its core. Nevertheless, there remains an adequate amount of hydrogen in its outer shell, causing it to emit light that is 630 times brighter than the Sun. Merope is situated within a nebula, yet its luminosity easily penetrates through and reaches Earth in just 360 years, a relatively short distance in the vastness of space.
The additional prominent stars in Taurus
Aside from the primary ones, there are various other significant stars that exist within the constellation:
- Taygeta. Represents a trinary star system. It is situated at a relatively close distance of 440 light years from the solar system. These luminaries possess their own satellites, which exert mutual gravitational attraction.
- Celeno. Positioned 430 light years away from Earth, it has a visual magnitude of 5.488, making it less easily observable in the night sky. In the past, it was referred to as the “Lost Pleiades” due to the challenge astronomers faced in spotting it amidst the starry expanse. Moreover, it necessitated aligning the stars correctly in space and observing them only during a specific time of the year.
- Maya. Another massive celestial body that belongs to the nebula with the same designation. It is situated at a distance of 360 light-years from Earth. Composed mainly of mercury and manganese, Maya emits a grayish-purple radiance that is 660 times more luminous than sunlight.
- Ro. This star bears a resemblance to our Sun in certain aspects. It surpasses the Sun in size by 88% and has a rotation period of 488 days. Ro’s brightness fluctuates by 1% every hour and a half, alternating between increases and decreases. From our vantage point on Earth, this star is located 152 light-years away, making it observable with semi-professional equipment. Astronomers classify Ro as a Delta Shield class star.
Taurus, a constellation in the night sky, is home to numerous stars that possess distinct characteristics.
Celestial entities within the Taurus constellation

The Taurus constellation is home to a variety of celestial objects, with several notable ones standing out:
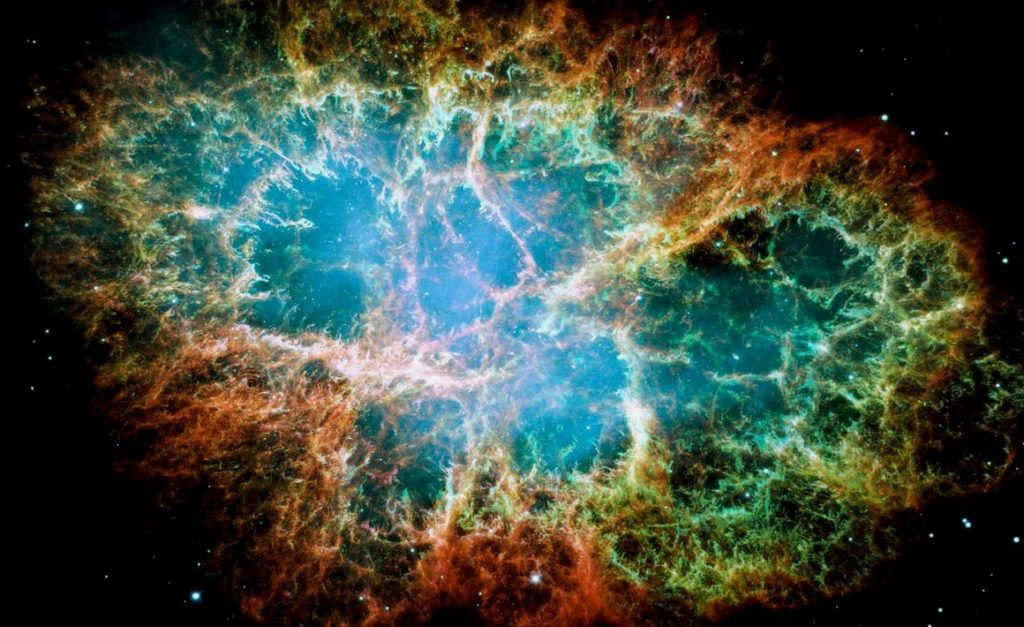
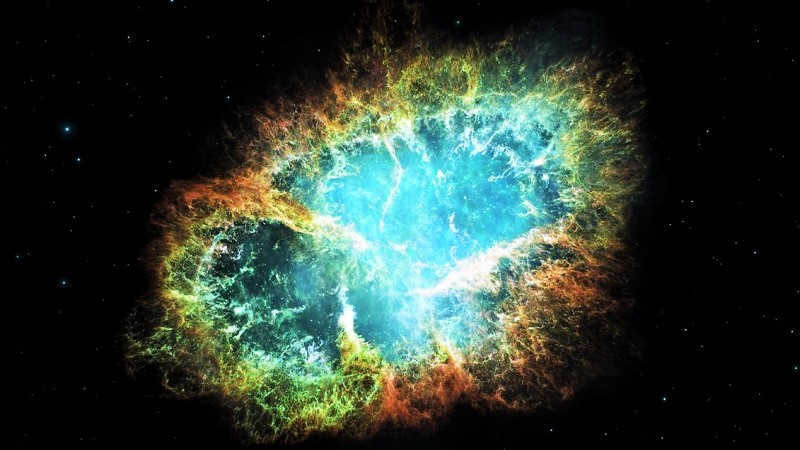
- The Crab Nebula. This nebula formed after a supernova explosion and is continuously fueled by the neutron star Pulsar, which exerts pressure on it with its winds. The nebula spans a size of 11 light-years.
- The Pleiades. This cluster of stars is the brightest and can be easily observed even with amateur equipment. It formed approximately 100 million years ago.
- The Hyades. This extensive cluster contains hundreds of stars and emerged 625 million years ago. It is located 153 light-years away from the Sun.
- The Hynde nebula was first identified by John Hynde in 1852, and it is characterized by its variable brightness. The nebula’s appearance changes regularly due to the pulsation of stars.
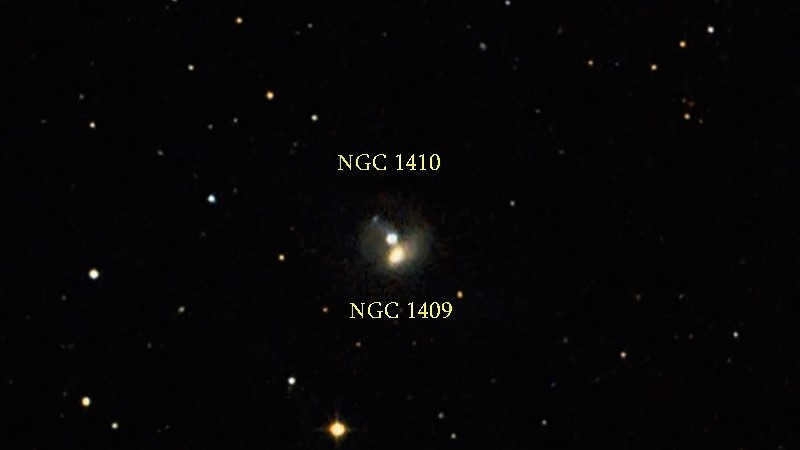
- MGC 1409 and NGC 1410 are two galaxies that are slowly moving towards each other under the influence of gravity. Currently, they are separated by a distance of 20,000 light-years.
- NGC 1514 is a planetary nebula located 800 light years away from the sun.
- The Crystal Ball Nebula, discovered in 1790, features a double star at its center.
- NGC 1746 is an asterism with a visual magnitude of 6.1. It was discovered by Henry Louis D’Arré in 1863.
- The Merope Nebula is the remnants of a supernova explosion and can be found in the Pleiades cluster.
- NGC 1647, 1807, 1817. These star clusters are situated in various regions of the constellation and are distinctive for their luminous collection of stars.
Fascinating trivia: Online platforms and software programs exist that enable users to explore each celestial object up close through immersive 3D space modeling.
Where can Taurus be spotted in the night sky?

If you are familiar with the arrangement of the constellations, it is not difficult to locate Taurus in the night sky. Gemini can be found to the east of it, while Keith and Aries are on the west side. Orion lies to the south, and Perseus to the north.
Did you know: On May 11th, the Sun enters the boundaries of Taurus and gradually moves across its expanse.
To enhance your viewing experience, you can utilize binoculars. Even with a 20x magnification, you will be able to clearly see many of the prominent features within the Taurus constellation.
Astrological significance of the Taurus constellation

Taurus, the second sign of the zodiac, comes after Aries. It occupies a portion of the sky that spans from 30 to 60 degrees. This astrological sign is associated with the time period between April 21 and May 20.
Individuals born during this time display remarkable perseverance, efficiency, and a strong drive to provide for themselves and their loved ones. They are also known for their unwavering loyalty and ability to form lifelong partnerships.
Many science fiction authors often mention the constellation Taurus in their works, especially in those where the main characters embark on a journey through the vast cosmos. However, one of the most notable examples of Taurus in literature can be found in Stanislav Lem’s book series “The Star Diaries of Ion Tycho.”
In the fourteenth journey of the book series, the events take place on Enteropia, a planet located near a double star that is part of the Taurus constellation. In the continuation of the novel, the protagonist travels to the planet Enzia, which is in close proximity to Enteropia.
In ancient times, Taurus held even greater significance in literature. Greek authors often composed myths and tales that featured the constellation, and it would often personify specific characters.
A fascinating video about the constellation Taurus
If you happen to come across any inaccuracies, kindly select the specific text segment and hit Ctrl+Enter.
The ancient zodiacal constellation of Taurus is steeped in myths and legends. Modern scientists are drawn to Taurus due to its abundance of fascinating objects.
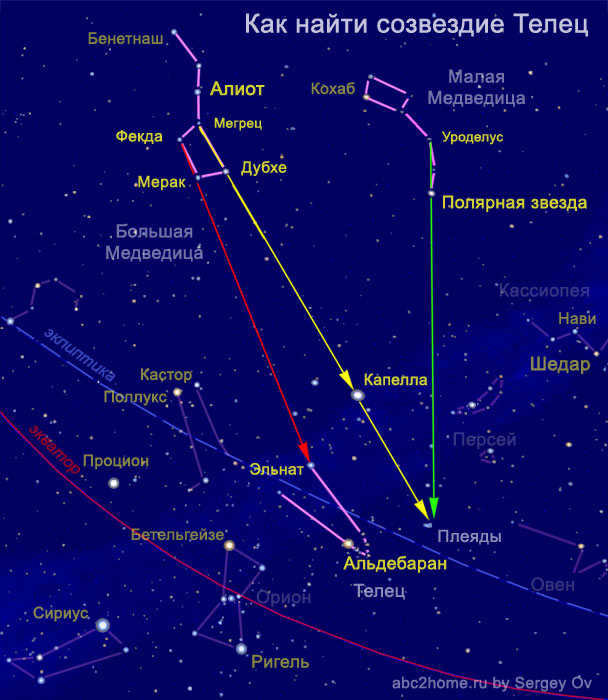
Locating Taurus in the Night Sky
Finding the constellation of Taurus in the night sky is a relatively simple task. The Sun passes through Taurus starting from May 11th. The optimal time for observation is from November to January.
The fiery cluster of stars known as the Pleiades and the reddish-hued Aldebaran serve as excellent reference points. To the east, one can spot the bright constellation Gemini. To the south, closer to the horizon, lies the distinctive Trapezium pattern of the constellation Orion. Taurus is bordered by the circlet of stars in Perseus to the north, and by the less prominent constellations Aries and Whale to the west.
The origin and mythology behind the name
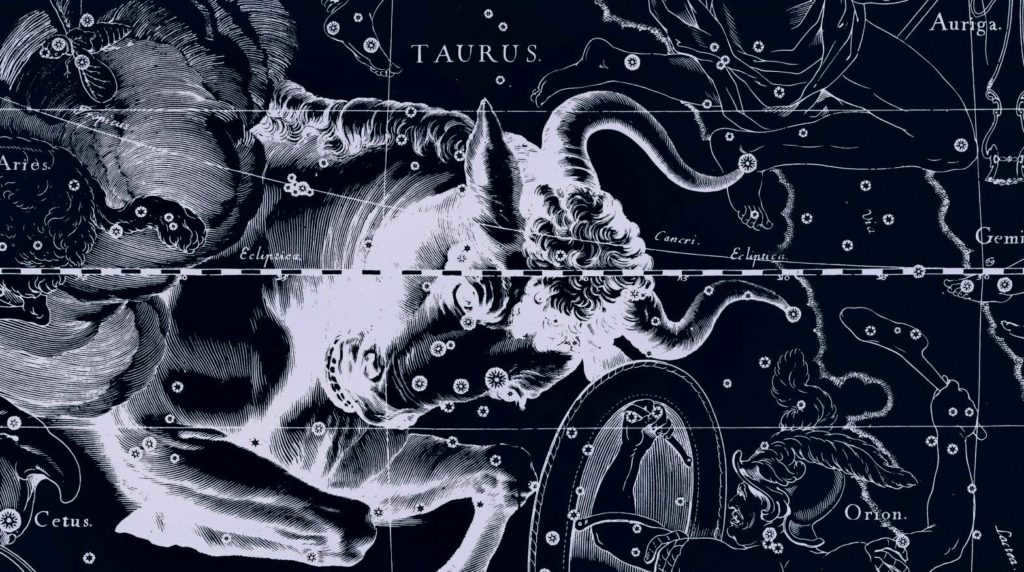
The constellation of Taurus was initially described by Eudoxus of Cnidus, an ancient Greek mathematician and astronomer, in his work Phenomena. Taurus is featured in the Almagest catalog of Claudius Ptolemy. In this catalog, the star Aldebaran is referred to as Lamparus or Lighthouse.
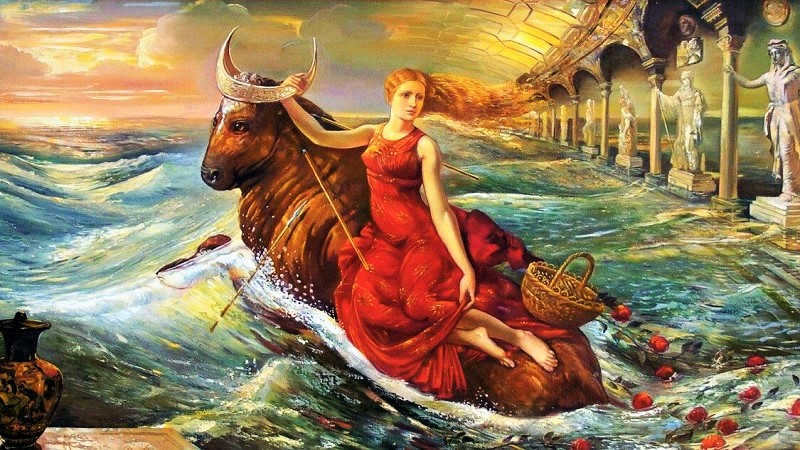
The Taurus constellation is connected to the ancient Greek myth of Zeus and Europa. King Agenor had a daughter named Europa, who was considered the most beautiful girl on earth. She was only second in beauty to the goddesses. One day, Europa was playing with her friends in a meadow.
Noticing her from the peak of Olympus, Zeus made the decision to abduct the young woman. To avoid alarming Europa and her companions, Zeus transformed into a majestic white bull and seamlessly integrated himself among King Agenor’s herds. In this cunning disguise, Zeus successfully seized the enchanting Europa and transported her to the island of Crete. It was there, in the guise of Zeus, that he revealed himself to Europa and she became his cherished lover, ultimately giving birth to three sons.
Another account suggests that Taurus manifested in the heavens following Heracles’ epic confrontation with the bull.
Description
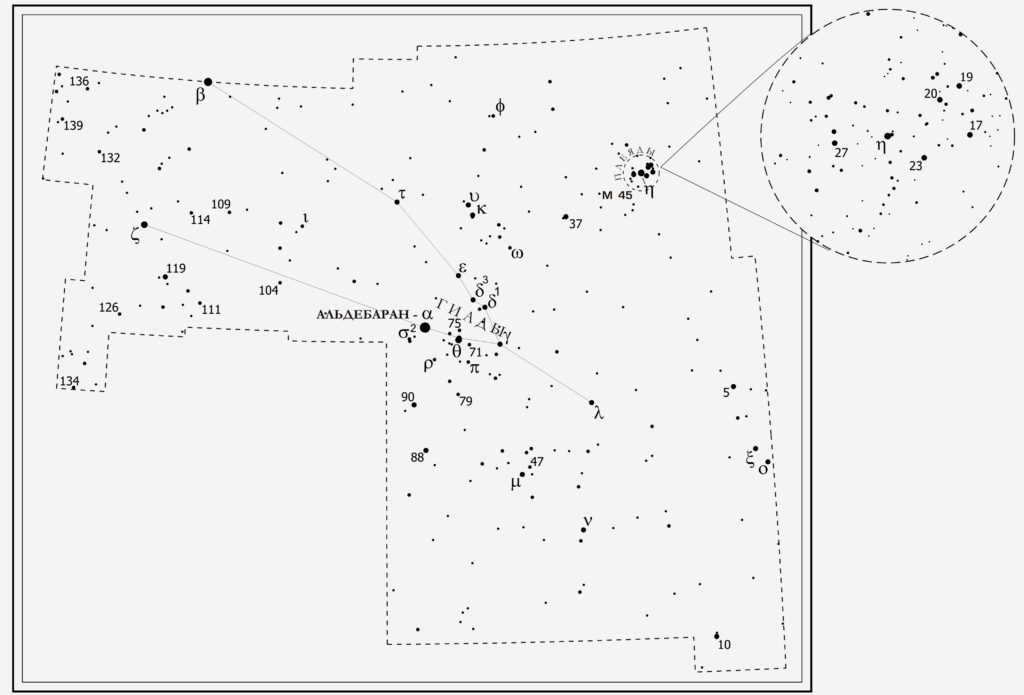
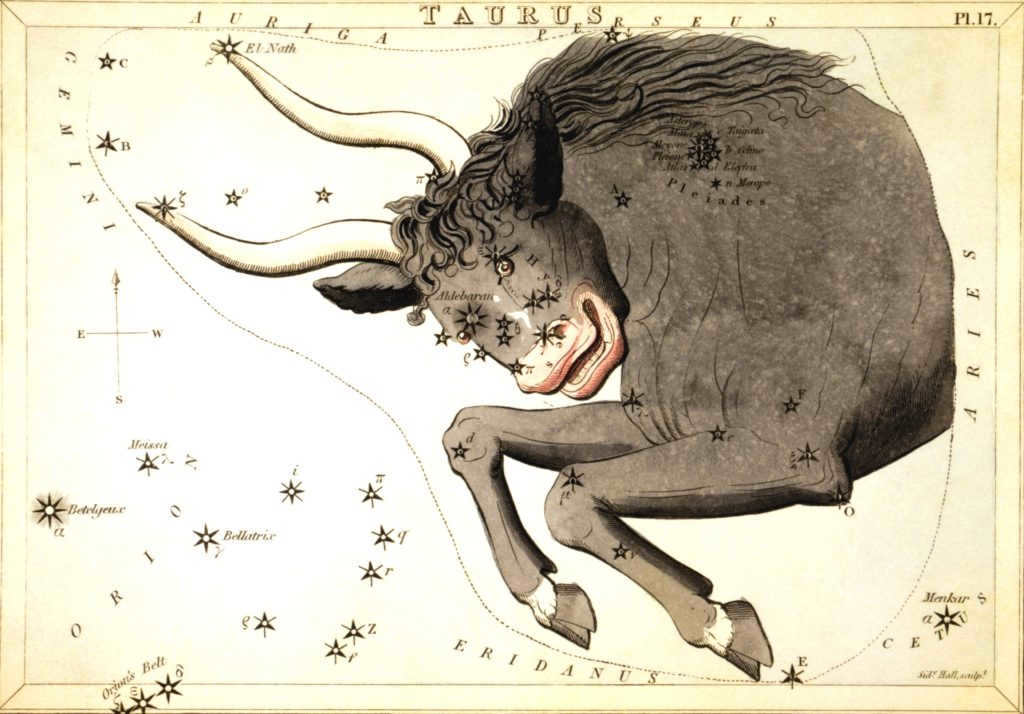
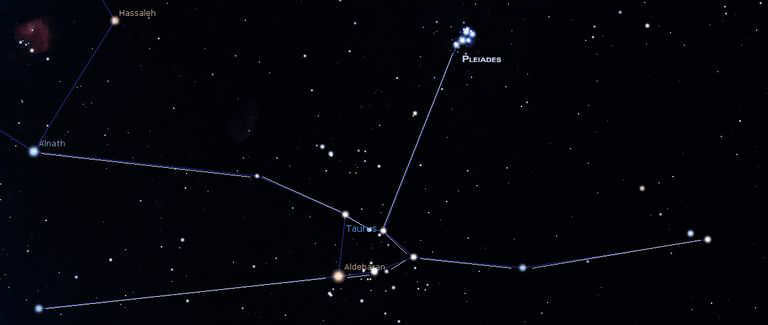
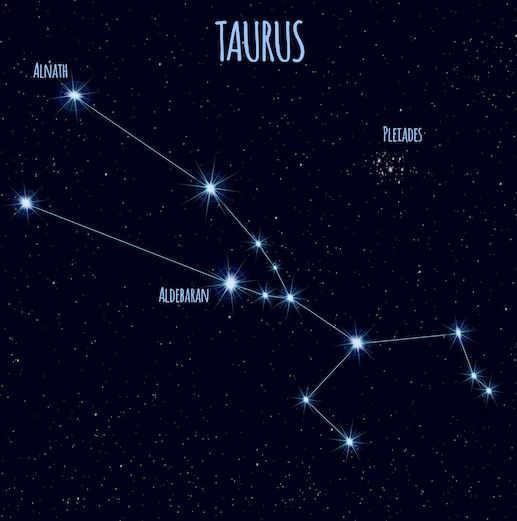
Taurus is the Latin name for Taurus. This constellation is home to 216 stars that can be seen with the naked eye at night. Taurus covers an area of 797 square degrees, making it the 17th largest constellation. The most prominent stars in Taurus include Aldebaran, Nat, Alcyone, Zeta Taurus, Electra, and Merope.
Located on the eastern border of the Giyads lies a star with a distinctive reddish-orange hue that catches the eye in the nighttime sky. Interestingly, this star is not directly associated with the Giyads, but rather goes by the name Aldebaran, which translates to “pursuing” in Arabic. Aldebaran seems to trail behind the Pleiades, almost as if it’s following them. It has earned the nicknames “ox’s eye” and “bull’s eye” due to its position just below the horn of the constellation.
Among all the stars discovered in the vast expanse of the Universe, Alpha Taurus holds the 13th position in terms of brightness. It falls into the spectral class K5 III and its luminosity can vary between 0.78 and 0.93 stellar magnitude. This star, an orange giant, is reaching the end of its lifespan.
The star is 38 times larger than our Sun in terms of diameter. It emits a brightness that is 150 times greater than our Sun. Despite having the same mass as the Sun, which is 1.988 x 1030 kg, the star is located at a distance of 65 light years from us. Aldebaran is an interesting celestial object as it is a double star. It consists of a main star and a companion, which is a red dwarf.
Nat, Beta
El-Nat, or Nat, is the Arabic term for “horns of the bull.” Beta Taurus is located on the border of the Ascendant constellation and is the second most luminous star in the Taurus constellation. It falls under the B7 III classification and has a stellar magnitude of 1.65 units.
This star is located approximately 131 light-years away from Earth. It is currently moving away from us at a velocity of 9km/s. Nat is around 5-6 times larger than our Sun and has a mass that is 4.5 times greater than that of the Sun.
Nat is a blue giant star that is expanding in size and is expected to eventually surpass Aldebaran in size and brightness. Additionally, Nat has a companion star.
T of Taurus
The T of Taurus.
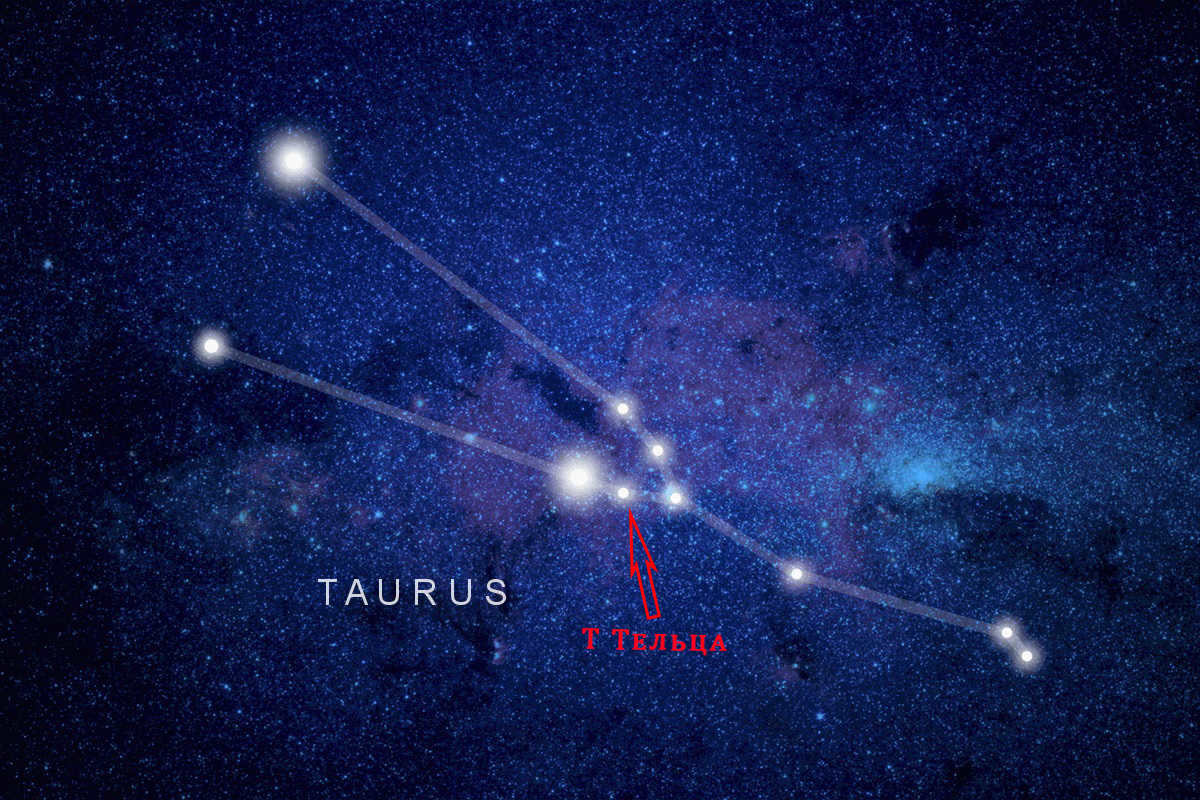
This particular celestial body falls into the category of variable stars. Taurus was first identified in 1852 by John Haydn and is currently in the process of formation. At its core, hydrogen undergoes a reaction that transforms it into a protostar. It is comprised of a cloud of gas and dust that gradually contracts to give rise to a new entity. The mass of T Taurus is 1,000 times greater than that of the Sun. The object is located approximately 400 light years away. It is believed that the system consists of a minimum of 3 stars.
The star is not named, but it is intriguing due to its distance of 417 sv years and its brightness which is 5,700 times greater than that of our Sun. Its stellar magnitude is 2.97. Zeta Taurus completes an orbit around Taurus in 133 days.
Alcyone, Aeta.
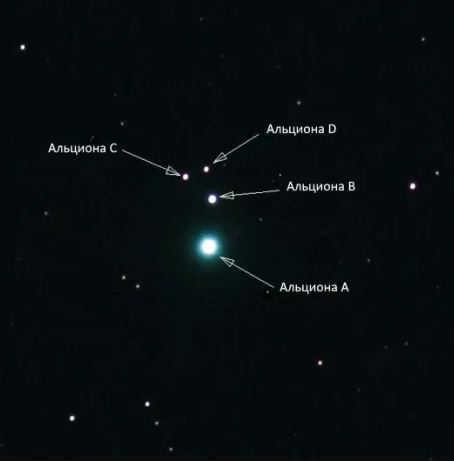
Alcyone is a member of the multiple star class. Its overall stellar magnitude is 2.87. It is situated within the Pleiades cluster.
The primary star in the system, Alcyone A, is positioned at the center and has a spectral class of B7III. It rotates at an incredible velocity and possesses an oblong shape resembling a rugby ball.
Additionally, the system contains the stars Alcyone B and C. Both stars belong to the A0 class, with Alcyone C being a variable star that regularly alters its brightness. Through a telescope, it is possible to observe Alcyone D, a white-yellow dwarf with a spectral class of F2.
Electra
Electra is a massive blue-white giant star situated in the Pleiades cluster. With an apparent stellar magnitude of 3.75, it shines incredibly bright, being 1,225 times more luminous than the Sun. The distance to Electra is estimated to be around 370 sv years, and it has a mass that is five times that of our Sun. Additionally, its radius is six times larger than the Sun’s radius.
Merope
Merope can be observed within the Pleiades cluster and is located at a distance of 440 sv years from our position. This celestial body belongs to the category of blue-white Class B giants and possesses a stellar magnitude of 4.14. In terms of brightness, Merope surpasses the Sun by a factor of 630. Furthermore, its radius is four times larger than that of our star, while its mass reaches 4.5 times the mass of our Sun.

Star clusters and nebulae
Apart from the mentioned constellation, Taurus is abundant in other fascinating celestial objects. In Taurus, one can observe dispersed groups of stars called Giyads and Pleiades.
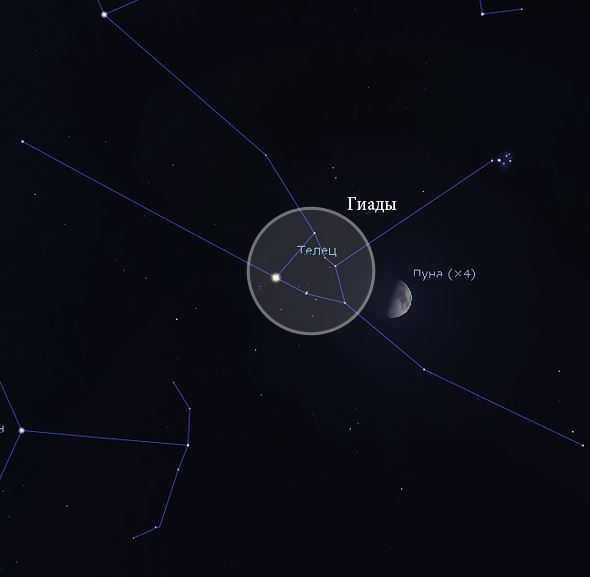
Coming even closer to us, at a distance of 130-150 light years, we find the Hyades. This cluster boasts a remarkable 132 stars that shine brighter than the 9th magnitude. In fact, we have knowledge of around 700 stars that are part of this breathtaking gathering.
These celestial wonders, known as the Hyades, gracefully glide through space at an astonishing speed of 44km/s. It is fascinating to note that approximately 800 thousand years ago, they approached the center of our system, coming within a mere 60 light years. As for their age, the Hyades have been gracing our skies for an impressive 650 million years.
In Greek mythology, the Hyades were revered as the daughters of Atlante and Ephra. These sisters were known for their profound grief over the tragic death of their beloved brother, Gias, who perished while hunting. Overwhelmed with sorrow, the sisters eventually succumbed to their own grief.
To honor their immense sorrow, Zeus immortalized the Hyades by placing them in the sky for all to see. Interestingly, the exact number of sisters varies from one source to another. Some speak of a group of five, while others insist there were seven sisters in total.
According to one version, there is a belief that Atlanteus and Ephra had a total of 15 daughters. Out of these, seven daughters named Gias were unable to cope with the loss and were transformed into Giyads. The remaining daughters became known as the Pleiades.
Pleiades
The Pleiades are also known as the “Seven Sisters” in honor of the daughters of the titan Atlas and the oceanid Pleione: Alcyone, Taygete, Merope, Celaeno, Electra, Sterope, and Maia. In Greek mythology, the Pleiades were attacked by the hunter Orion, and Zeus concealed them in the sky. However, Orion himself has also become a constellation and is now situated nearby, keeping a watchful eye on them.

The dispersed group, which is one of the nearest to us, is located at a distance of 410 light-years. The primary stars of the group are massive white giants that emit a strong luminosity. These stars are in their early stages of development, just beginning to gain strength. The age of the group is approximately 100 million years, which is relatively young in terms of the vastness of the universe.
The Crab Nebula, also known as the M1 object, is a remarkable phenomenon located in the Taurus constellation.
It is the result of a supernova star explosion that took place in 1054 A.D. The explosion was so powerful that it could be observed from Earth for a continuous period of 23 days, both during the day and night. Additionally, the remnants of the supernova were visible only at night for the following 2 years. It is worth noting that the light from this explosion actually reached Earth 6500 years after the event occurred in 1054 AD.
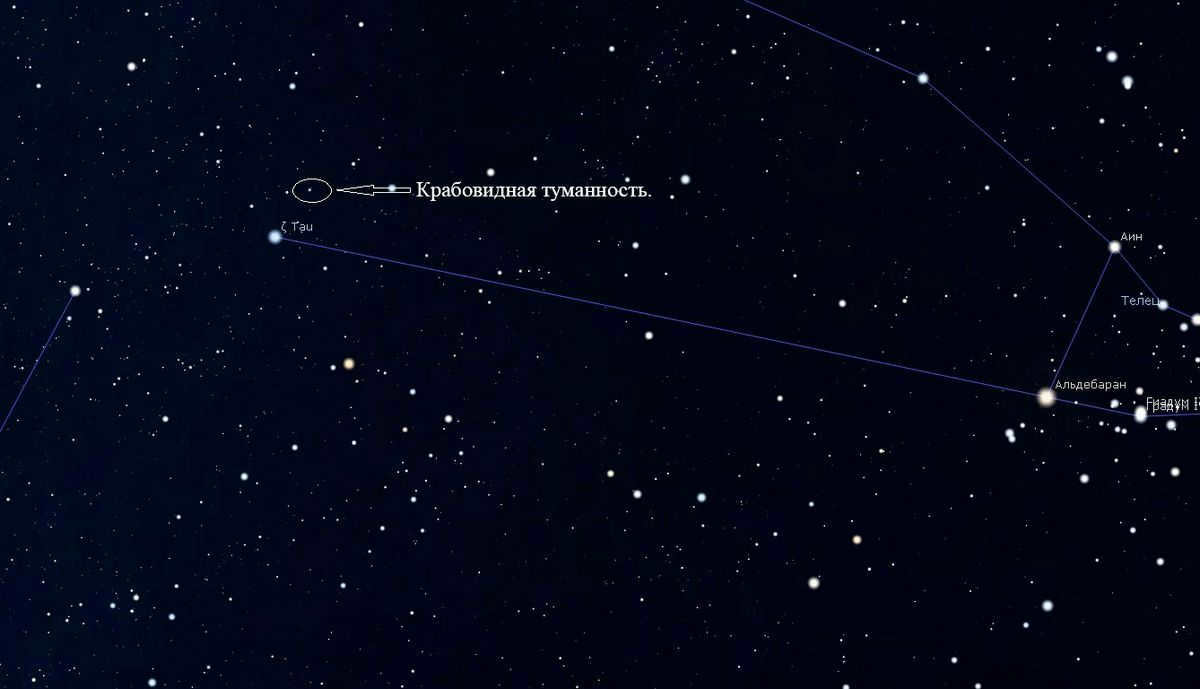
Charles Messier took an interest in this celestial object and added it to his collection as M1. The Crab Nebula can be observed near the Zeta Taurus star. It has an apparent brightness of 8.4 magnitude. This nebula is expanding and constantly changing its structure. It is located 6300-6500 light years away from us and emits powerful X-ray radiation.
The pulsar PSR B0531+21 can be found at the center of the M1 object, emitting periodic pulses of electromagnetic radiation. The pulsar is incredibly small, measuring only 30 km in size, but it has a mass 2.5 times that of the Sun. This star rotates at an astonishing speed of 30 revolutions per second.
Aside from the ones already mentioned, there are numerous other fascinating entities within the confines of the Taurus constellation:
Taurus is a highly conspicuous constellation in the celestial sphere and presents itself as an enticing subject for exploration. It encompasses a plethora of extraordinary and enigmatic phenomena, captivating the attention of scientists and avid stargazers alike.
Answers to questions
One parsec is equivalent to 3.2616 light-years.
Spectral classification is primarily based on the luminosity and temperature of stars. Stars are arranged in order of decreasing temperature from blue giants to red dwarfs: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. The luminosity class is denoted by Roman numerals from I to VII.
A neutron star with a strong magnetic field is known for its inclined axis rotation and its emission of radio, gamma, and X-ray radiation.
A light-year represents the distance that light travels in a vacuum within one year. It is commonly accepted to be 9,460,730,472,580,800 meters or 63,241 astronomical units.
The parallax angle refers to the change in a star’s coordinates caused by the Earth’s motion in its orbit. The farther a star is, the less noticeable its displacement relative to our planet will be.
Scientific Facts Video Review
The Taurus constellation is one of the most star-rich among the zodiacal constellations. It is situated in the Northern Hemisphere and is most visible during the months of November to January.
The ancient bull in the celestial sphere
It is remarkable that even without the aid of optical instruments, an individual can observe a staggering 216 stars within this constellation. Taurus occupies an impressive 800 square degrees of the sky.

When using a planetarium program, you can observe the constellation Taurus.
Geographically, Taurus is positioned between the constellations Aries and Gemini, to the northwest of the constellation Orion. Additionally, nearby Taurus, you can find the constellations Eridanus, Whale, Perseus, and Ascendant. This particular constellation is visible throughout Russia, and in the middle latitudes, it can be seen almost year-round, except for the second half of spring and the first half of summer. The Sun is located in Taurus from mid-May (the 14th) to mid-June (the 19th).
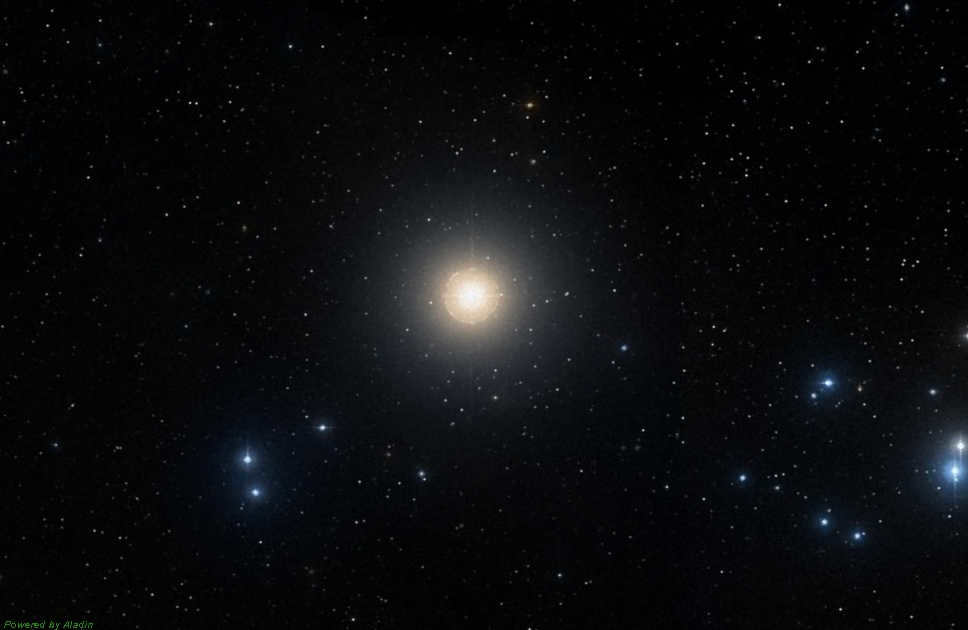

Image of Aldebaran, the brightest star in the Taurus constellation and one of the most prominent stars in the night sky, captured from the DSS catalog.
Aldebaran, also known as the alpha star of Taurus, shines with a magnitude of 0.85m, making it the brightest star among all 12 zodiac constellations. Positioned at the head of the constellation, it has often been referred to as the “eye of Taurus.” The star is also known by other names such as Lamparus or Palilius.
With a spectral class of K5 III, Aldebaran is classified as a normal giant and displays a warm orange color. Orbiting around Aldebaran at a distance of several hundred astronomical units is a companion star, a red dwarf of class M2. Aldebaran is located approximately 65 light years away from Earth.

Aldebaran is currently in an active phase of burning helium, which has resulted in an expansion of its size. The diameter of Alpha Taurus has now increased to 38 times that of the Sun. Aldebaran possesses a mass equivalent to 2.5 times that of our Sun and emits a luminosity 150 times greater than that of the Sun. Alpha Taurus is a variable star that experiences irregular and insignificant changes in its luminosity. The amplitude of the variation in stellar magnitude is only 0.2m.
Runner-up in luminosity, runner-up in the alphabetical order

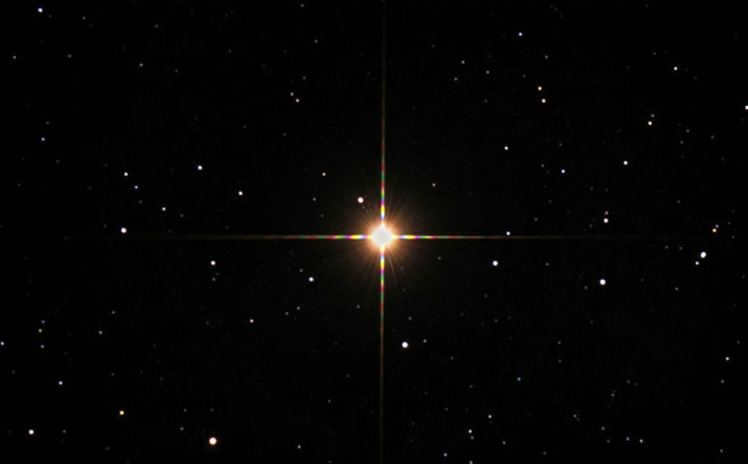
Star Nat or Beta Taurus Photo
Another notable star in the Taurus constellation is the Nat or beta Taurus star, which has a magnitude of second (1.65m). This star is commonly known as El-Nat, derived from its Arabic name meaning “bull’s horns”. It is located in close proximity to the Ascendant constellation. Ptolemy mentioned this star in his Almagest, noting that it belonged to both Taurus and Ascendant constellations simultaneously.
This constellation, known as Zeta “horned”, is
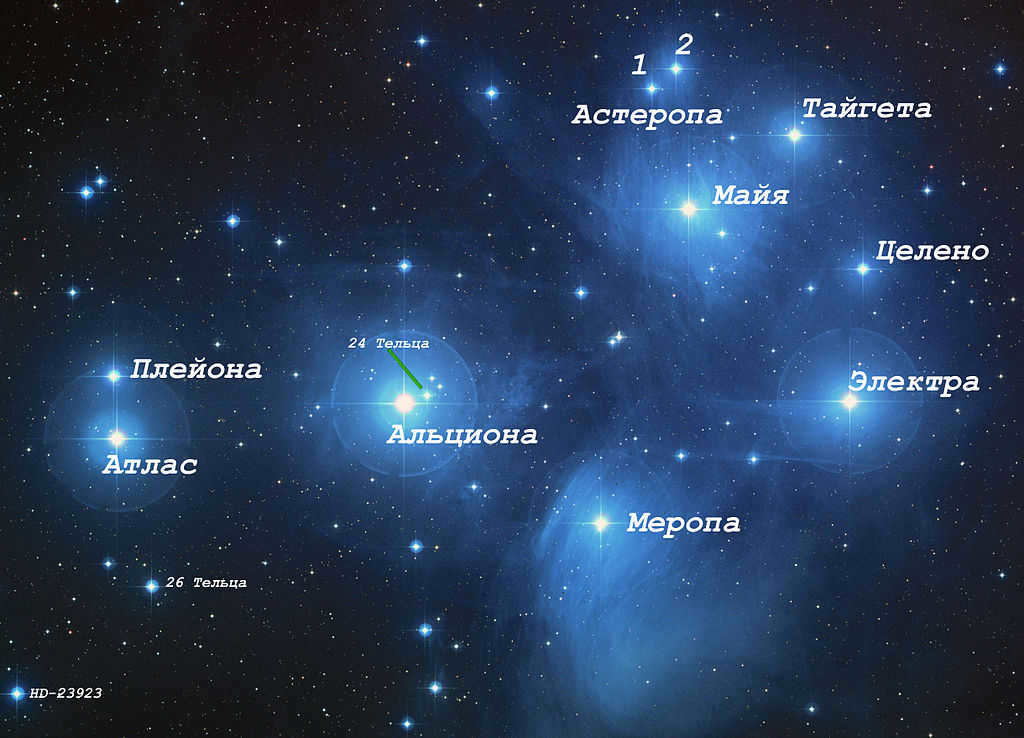
The Pleiades cluster is known for its scattered stars.
Taurus is fascinating because it contains two stars with similar names, thanks to the Latin alphabet. One of them is named Eta Taurus or Alcyone. This star is part of a multiple stellar system, consisting of four components: A, B, C, and D. The first component, Alcyone A, is a Ve star, meaning its shape is ellipsoidal due to its rapid rotation. Alcyone A is classified as a blue-white giant star with a spectral class of B7IIIe and an apparent magnitude of approximately 2.87m.
Components B and C are stars of the main-sequence in class A0, with magnitudes of 6 and 8, respectively. On the other hand, Alcyone C is a variable star that undergoes changes in its luminosity of approximately 0.05m every hour and a half. Lastly, Alcyone D, the final component, is a star classified as a white-yellow dwarf of spectral class F2. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.7m. All four stars within the Eta Taurus system can be easily observed with a telescope.
Zeta Taurus
Rewrite the text to make it unique, using the English language and preserving the HTML markup:
Zeta Taurus

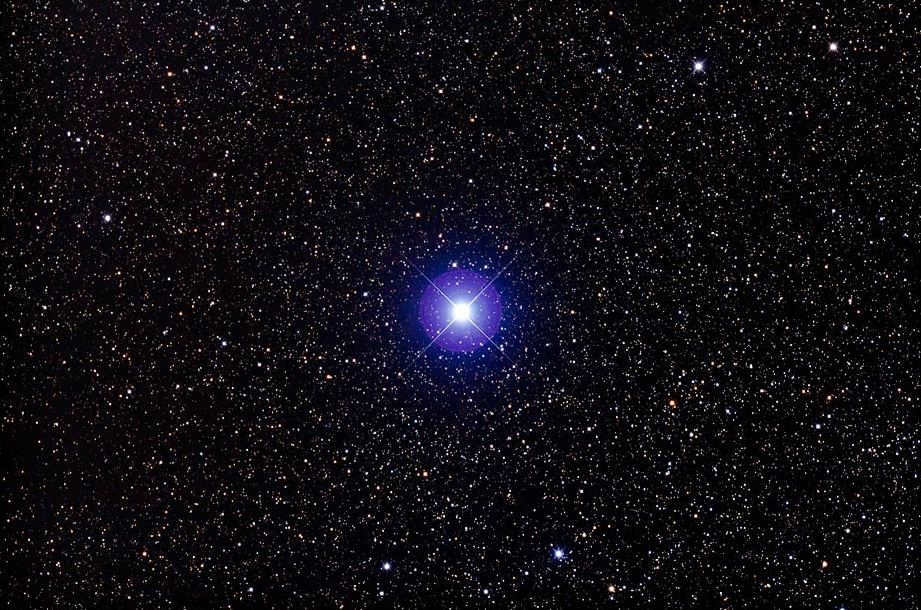
Zeta Taurus is situated 417 light-years distant from our location. This binary system is also an exemplar of Ve stars in Alcyon A. Zeta Taurus does not possess a conventional designation. It possesses a third stellar magnitude (2.97m) and is classified as B4IIIpe/G8III on the spectrum. A brilliant blue-white giant within the Taurus zeta binary system, Taurus showcases an exceptionally robust luminosity that surpasses the Sun’s by as much as 5,700 times.

The Taurus Constellation
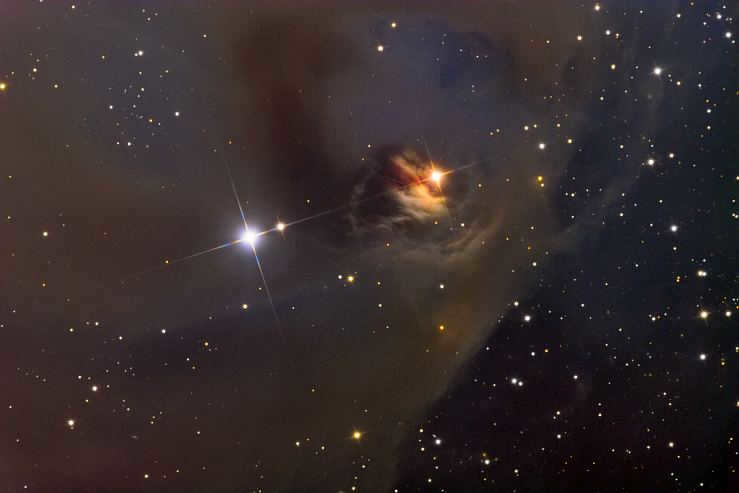

The photograph depicts T Taurus, a variable star located within the constellation Taurus.
T Taurus is a well-known variable star that serves as the model for other stars of its kind. This particular star is in an early stage of development, as its stellar matter precipitates from a slowly rotating circumstellar disk and forms a star. Within its core, hydrogen condenses into a protostar. A protostar refers to the central region of a massive cloud consisting of gas and dust, which weighs approximately 1000 times that of the Sun and gradually contracts under its own gravitational force.
In prehistoric times, two scattered clusters of celestial lights were discovered within the Taurus constellation.
Known as the Hyades
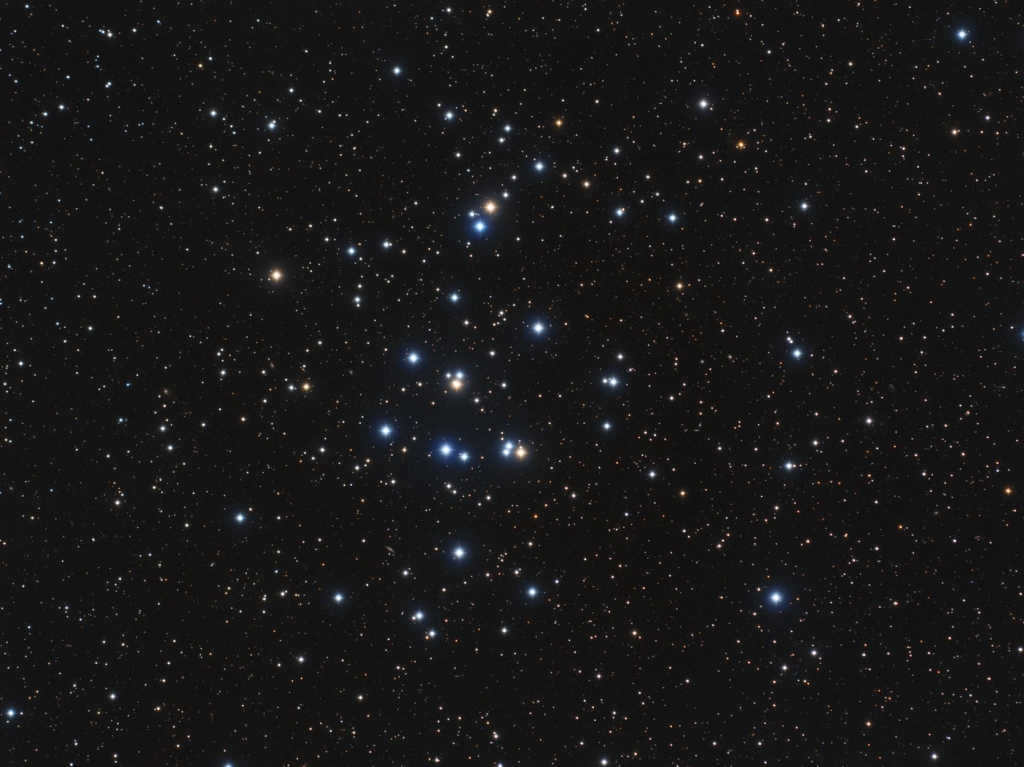

The first of these constellations is known as the Hyades. It can be easily observed with the naked eye, as the brightest member of Taurus, the star Aldebaran, is situated within the densely populated region. The alpha star of the constellation is not actually part of the cluster, but is only projected onto it. In total, around two hundred stars can be found in this constellation, with approximately four dozen being considered the brightest.
The Hyades cluster has an estimated diameter of about 70 light-years, and it is located approximately 130 light-years away from Earth. The cluster is believed to be around 620-650 million years old. The brightest stars within the cluster include Epsilon, Gamma, Theta, and Delta Taurus.
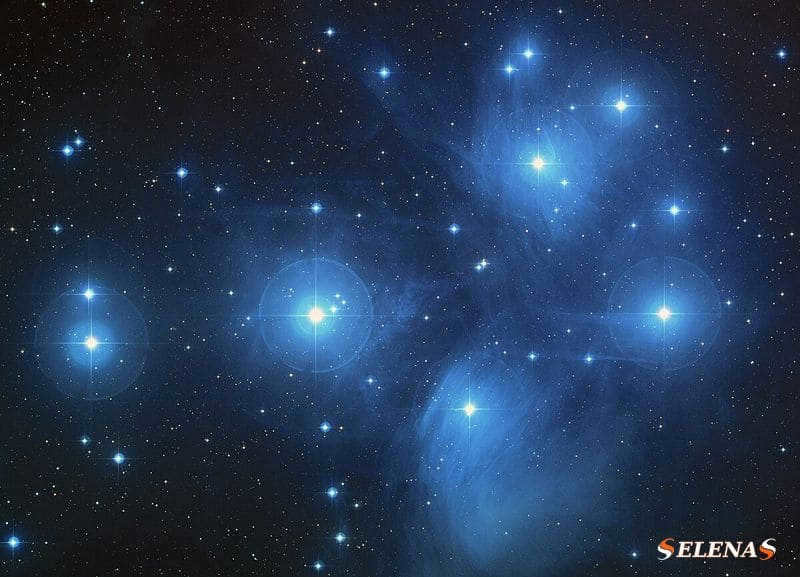
The Seven Sisters
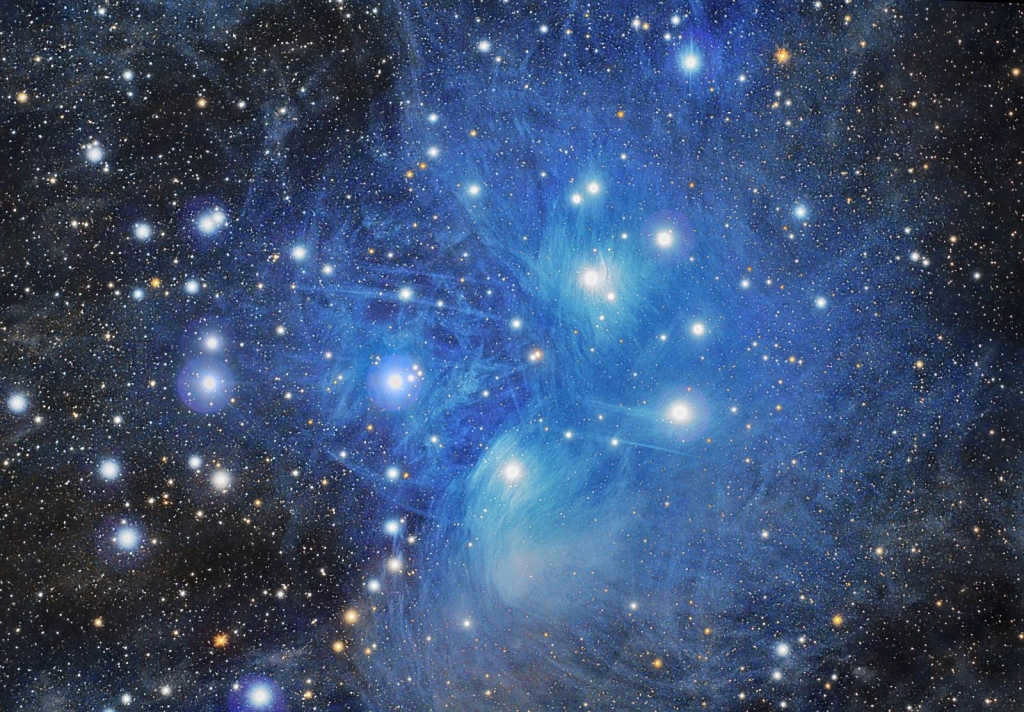

The Pleiades, also known as M45, is another interesting star cluster located in the Taurus constellation. This cluster is easily visible in the night sky, even without the need for binoculars, thanks to its composition of hot and luminous blue stars. It is situated approximately 440 light-years away from Earth and consists of around 1000 individual stars.
The Crab Nebula
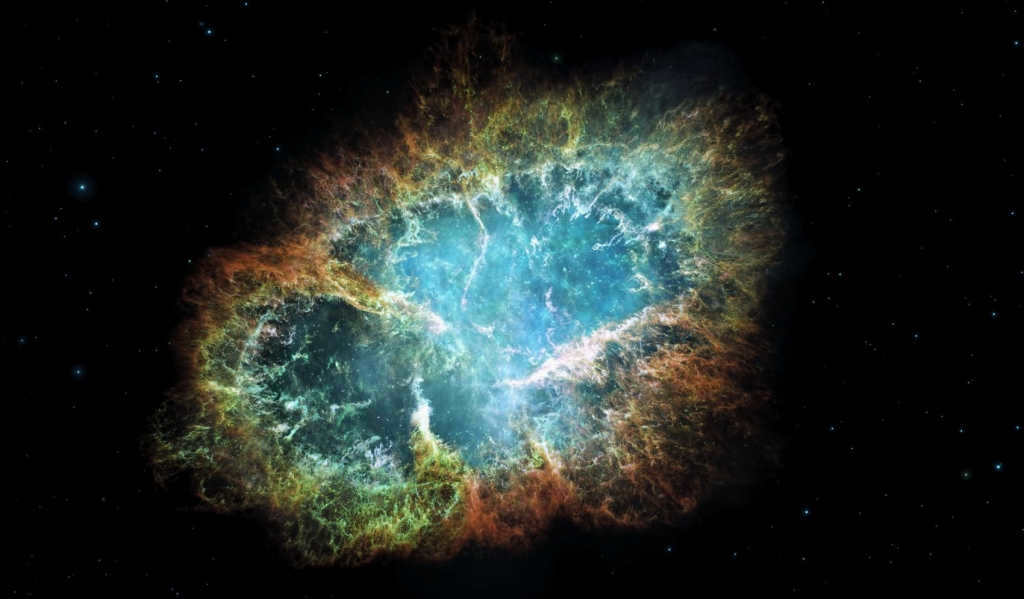
Image of the renowned Crab Nebula captured in exceptional detail
An exquisitely vibrant nebula formed as a result of the cataclysmic explosion of a supernova referred to as SN 1054. This spectacular nebula is commonly known as the Crab Nebula. In the realm of astronomical catalogues, it is recognized as a Messier object denoted by the number one – M1.
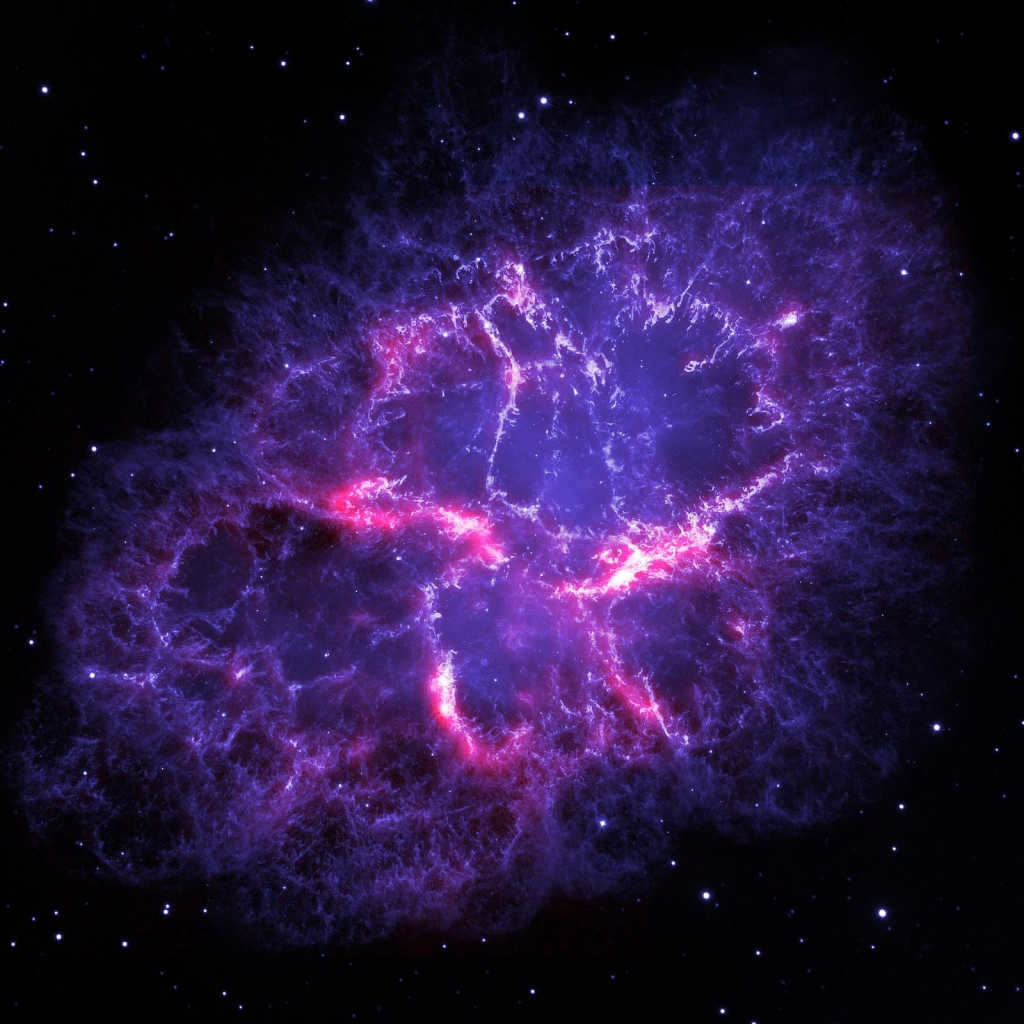


Crab Nebula M1 Image
The Crab Nebula, also known as M1, was first observed in 1731. It is located approximately 6500 light-years away from Earth. Currently, it has a diameter of around 11 light-years and is continuously expanding at a rate of about 1.5 thousand kilometers per second. The nebula is often referred to as a pulsar due to the presence of a pulsar at its center. This pulsar is a type of neutron star that emits radio waves, gamma rays, and stellar wind, which nourish the entire nebula.
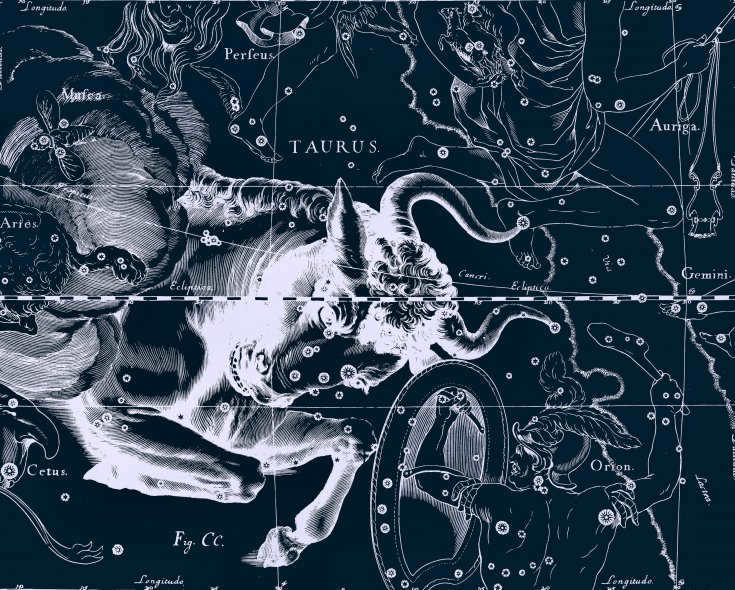

The constellation Taurus, depicted in a drawing by Jan Hevelius in his atlas of constellations, has a long history. While it was once believed to have been discovered by the mathematician Eudoxus, it is more likely that he was simply the first to describe the constellation. Taurus is also included in the Almagest catalog by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy. According to Greek mythology, Taurus represents the bull that Zeus transformed into in order to abduct Europe. He then carried the goddess across the sea to the Greek island of Crete.
The zodiacal cluster encompasses the expansive Taurus constellation, situated between Aries and Gemini. Additionally, it is flanked by Ascendant, Whale, Orion, Perseus, and Eridanus.
Ranking 17th in size amongst the entirety of celestial regions, Taurus covers an impressive 797 square degrees.
Notably, Taurus is not only renowned for its substantial size, but also for its widespread popularity. The bull is referenced in the traditions of numerous cultures worldwide.
However, the primary one is commonly believed to be the ancient Greek legend in which Zeus abducted the stunning Europa. He transformed into a bull and concealed himself among her father Agenor’s herd. The girl became fascinated by the magnificent bull and climbed onto its back. Zeus then transported her to the island of Crete, where he revealed his true identity. As a consequence, they had three sons together. Ever since, the constellation Taurus has symbolized the head of the bull.

In the 2nd century, the area was officially included in Ptolemy’s star catalog of the sky.
This constellation indicates the location of the Sun during the vernal equinox.
The most brilliant star among them all, as is often the case, is Alfa – Aldebaran. In fact, it holds the distinction of being the thirteenth brightest star in the entire sky. It is a massive orange star, with a visible brightness of 0.68. The name translates to “follower.”
Coming in as the second brightest is Beta – a massive blue star with a visible brightness of 1.86. The name El-Nat means “bumping.”
In the third position, we have This one — Alcyone, which represents the daughter of Atlanteus. It is a binary star system consisting of a massive star and a dwarf star. Together, they emit a total luminosity of 2.87.
Following closely is Zeta with a visible brightness of 3.01. Similar to This Taurus, it is also a double star system.
Lambda is a triple star system with a visible brightness of 3.47.
Epsilon is the second eye of the bull, known as Ain. It is an orange giant with a luminosity of 3.53.
Gamma is a yellow giant that represents the first Hyades. It has a luminosity of 3.65.
A xy is a multiple system consisting of main-sequence dwarf components. Its average visibility is 3.73.
Now let’s talk about the designation Delta in the constellation, which refers to three different systems.
Firstly, Delta 1 or the second Hyades is a triple star system with a giant as its main object.
Secondly, Delta 2 is represented by a main-sequence dwarf.
Lastly, Delta 3 is a multiple system where the main variable is a subgiant. The apparent magnitudes are 3.77, 4.8, and 4.3, respectively.
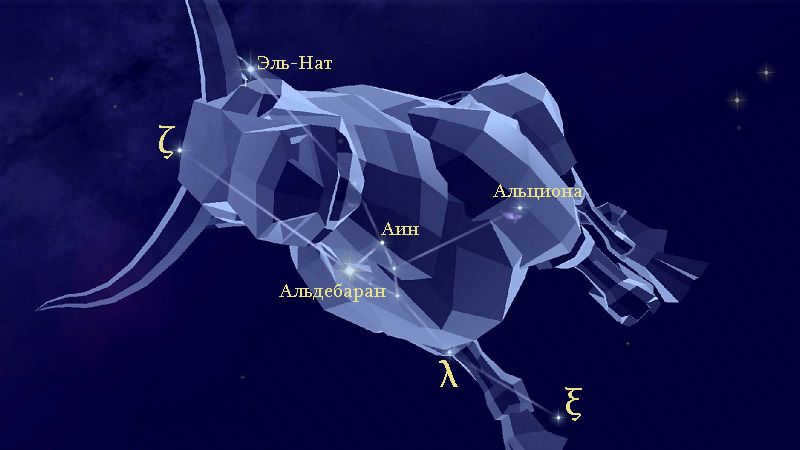
Theta is a binary star system consisting of giant stars. Its total visual magnitude is 3.84.
Nu is a white dwarf with a stellar magnitude of 3.91.
Tau, Kappa, and Ypsilon are multiple star systems with brightnesses of 4.26 and 4.21-5.27 and 4.28, respectively.
Mu is a blue subgiant with an apparent magnitude of 4.27.
Omicron belongs to the group of yellow giant stars and has an apparent magnitude of 4.86.
Taurus’s T is the prototype for the classification of variable stars. These stars exhibit optical variability and have strong chromospheric lines. They are also larger in mass and have a larger radius than main sequence stars.
Of course, we have only mentioned the primary stars of Taurus, but that is not all. As you can observe, the main components of the section are highly luminous and easily noticeable in the celestial sphere.
Which celestial objects are included in the constellation Taurus
As a matter of fact, there are numerous remarkable astronomical objects situated in this area. Many of them are widely renowned.
First and foremost, there are two of the most well-known open star clusters within this region:
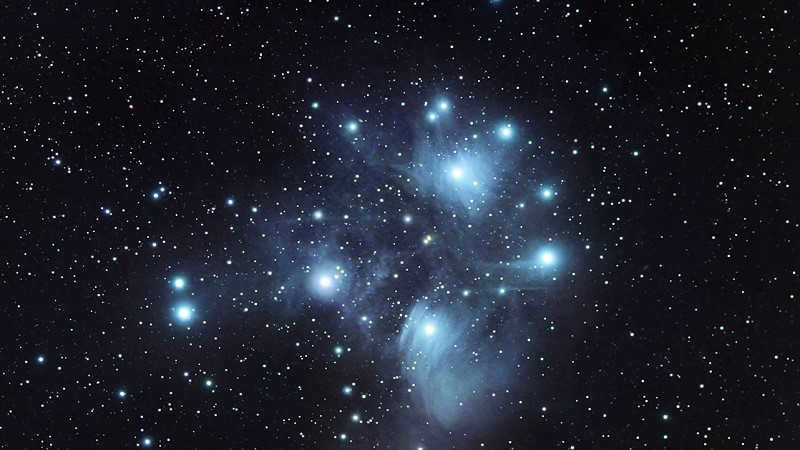
- The Pleiades, also known as the Seven Sisters, were initially discovered by Charles Messier and are designated as M45 in his catalog. This celestial cluster consists of hot and luminous stars and is located in close proximity to our solar system, making it easily observable from Earth. With an apparent magnitude of 1.6, it shines brightly in the night sky. In addition to its astronomical significance, the Pleiades are steeped in ancient Greek mythology. According to the myth, the Pleiades are the seven daughters of Atlas, who held the sky on his shoulders. Orion, the mighty hunter, pursued the beautiful sisters, but Zeus intervened and transformed them into doves, and later, into stars. Thus, the Pleiades star cluster came into existence.
- The Hyades is the nearest star cluster to our solar system. It consists of numerous shining celestial bodies and has a visual magnitude of 0.5. The term “Hyades” also refers to a group of five daughters of Atlas. Additionally, the Hyades cluster includes four of the most brilliant stars (Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Theta) that form a distinctive pattern resembling the letter V. This pattern represents the head of the Taurus constellation, which resembles a bull.

Hidden Nebulae in the Taurus Constellation
It should be noted that there is another Messier object concealed within the Taurus constellation, namely the M1 Crab Nebula. In reality, it is a gaseous medium that contains remnants of a supernova from the year 1054. Its visual magnitude is 8.4.
It has been discovered that the M1 Crab Nebula emits powerful radio and X-rays. Within it lies a neutron star known as PSR B0531+21.
Additionally, there have been observations of nebulae in the vicinity:
- The Crystal Ball – a massive planetary interstellar medium with a luminosity of 9.43.
- Merope – a reflective nebular region with an apparent magnitude of 13. It received its name from the star that illuminates it.
- The Hynde Nebula is a variable nebula that also reflects light from T Taurus. As a result, its brightness measures 9.43.


Currently, there is an intriguing phenomenon occurring where two galaxies, NGC 1409 and NGC 1410, are in the process of merging. These galaxies are connected by a gas arc, creating a visually captivating sight. The combined brightness of these galaxies has an average apparent magnitude of 15.4.

Moreover, there are dispersed star formations with luminosities ranging from 6.4 to 7.7. These include: NGC 1647, NGC 1807, and NGC 1817.
The Taurus constellation possesses meteor showers – the Taurids and Beta Taurids. The former occurs in November while the latter takes place in June-July.
Being located within the latitude range of +89 to -59, the celestial site is completely accessible to individuals residing in Russia.
Astronomers have determined that the Sun traverses the constellation of Taurus from May 14 to June 19, resulting in its temporary concealment from observers during this period. However, it can be easily spotted in the night sky at other times. The most optimal conditions for observing the Sun are typically observed in November and December.
Continuing with the discussion of zodiacal constellations, today we will explore the Taurus constellation!
Taurus is a prominent constellation located in the northern sky and is one of the oldest known constellations.
Its name is derived from the Latin word for “bull” and it is represented by the head of a bull.
Taurus is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac and was originally documented by the ancient Greek astronomer Claudius Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD.
However, its origins can be traced back to the Bronze Age.
In Greek mythology, Taurus is associated with Zeus, who transformed into a bull to approach and abduct Europa.

Three of the most prominent stars in the Taurus constellation are Aldebaran, Elnath, and Alcyone.
Additionally, the Taurus constellation is famous for two clusters of open stars that are closest to Earth – Messier 45, also known as the Pleiades, and the Hyades.
Overall, there are 17 officially named stars and two Messier objects within the Taurus constellation.
History and mythology of the constellation Taurus
The constellation Taurus has been documented and recognized since ancient times, specifically during the early Bronze Age when it served as a marker for the Sun’s position during the vernal equinox.
Taurus is most commonly associated with the representation of a bull in various cultures, notably in Greek and Egyptian mythologies.
Rock art discovered at Lascaux, dating back to 15,000 BC, showcases carvings and depictions of Taurus.
In Greek mythology, Taurus is linked to Zeus, the king of the gods, who transformed into a bull in order to approach Europa, the stunning daughter of the Phoenician king Agenor, and abduct her.
Zeus cleverly disguised himself among the king’s herd, and due to his remarkable beauty as a bull, he managed to capture Europa’s attention.
Once Europa mounted his back, Zeus swiftly rose and began the journey towards the sea.
In an alternate retelling, Europa was also charmed by Zeus, who subsequently transformed into a bull to evade Hera’s imminent discovery.

Position of Taurus Constellation
Taurus is among the largest constellations in the night sky, covering an impressive area of 797 square degrees.
It is situated in the first quadrant of the northern hemisphere (NQ1) and can be observed at latitudes ranging from +90° to -65°.
Its right ascension is 4.9 hours and its declination is 19°.
The optimal time to view Taurus is in January at 9 pm.
Starting from May 13 to June 21 since 2008, the Sun has been appearing in the Taurus constellation.
Taurus is classified as one of the zodiac constellations, alongside Aries, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, and Pisces.
Its neighboring constellations include Aries, Auriga, Cetus, Eridanus, Gemini, Orion, and Perseus.
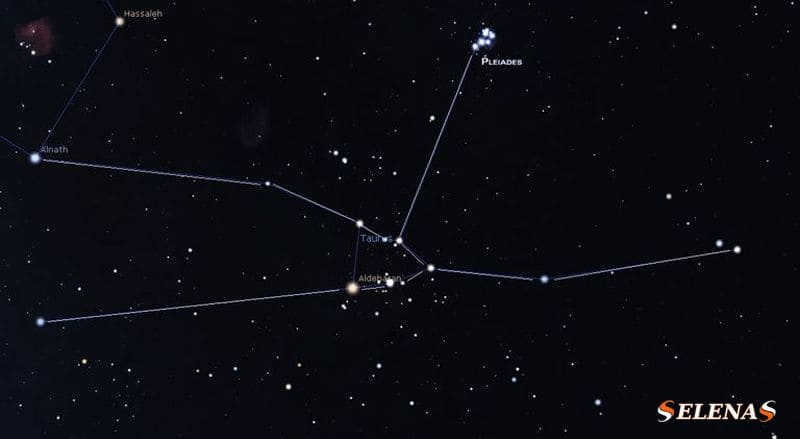
Famous stars in Taurus
Taurus is home to numerous notable stars.
Among them are Aldebaran, Elnath, and Alcyon, which are the three brightest stars in this constellation.
Aldebaran
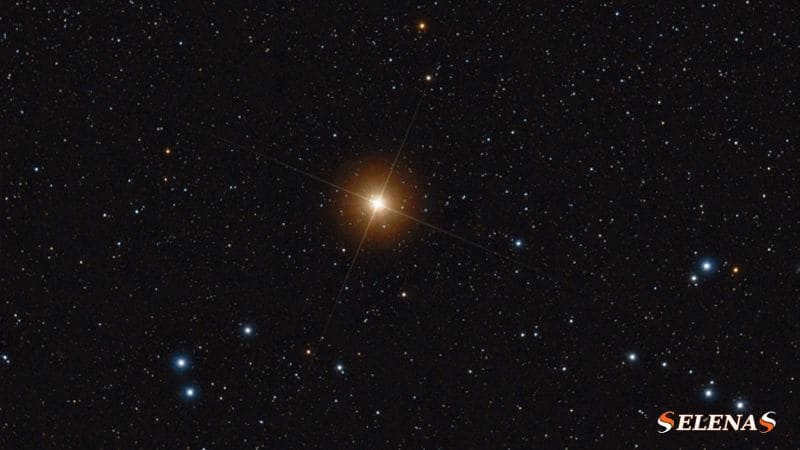

Aldebaran, also known as Alpha Taurus, is the most prominent star in the Taurus constellation and the thirteenth brightest star in the celestial sphere.
It is an orange giant with a visual magnitude that ranges from 0.75 to 0.95.
This celestial body acquired its name, which means “follower,” due to its apparent movement following the Pleiades cluster, also known as the Seven Sisters, across the sky.
Aldebaran has been classified as a K5III star and is situated approximately 65.1 light-years away from our planet.
It is categorized as a slow irregular variable of the LB type.
The star’s brightness fluctuates by around 0.2 magnitudes.
It possesses a diameter that is 44.2 times larger than that of the Sun and is approximately 425 times more luminous.
This particular star can be easily located in the night sky due to its proximity to the constellation Orion. In fact, if you follow the three prominent stars that make up Orion’s belt, they will point you directly towards this star.
Interestingly, this star also serves as a helpful guide for locating the Hayden cluster. While it is not officially a part of the constellation, it falls within the same line of sight and can assist in identifying the cluster’s location.
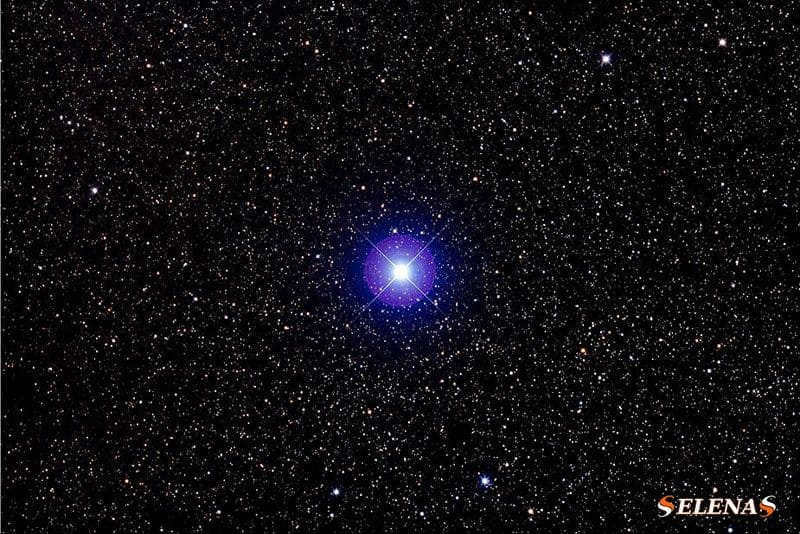

Elnath, also called Beta Taurus, holds the position of being the second most radiant star in the constellation Taurus with a visual magnitude of 1.68.
This colossal celestial object falls under the stellar classification of B7III and is situated roughly 131 light-years away from us.
With its luminosity measuring 700 times that of the Sun, Elnath dazzles in the night sky.
Its title is derived from the Arabic term “an-naţħ,” which translates to “battering,” a direct reference to the bull’s iconic horns.
Alcyon
Rewrite the text, making it unique, using the English language and preserving the HTML markup:
Alcyon
.
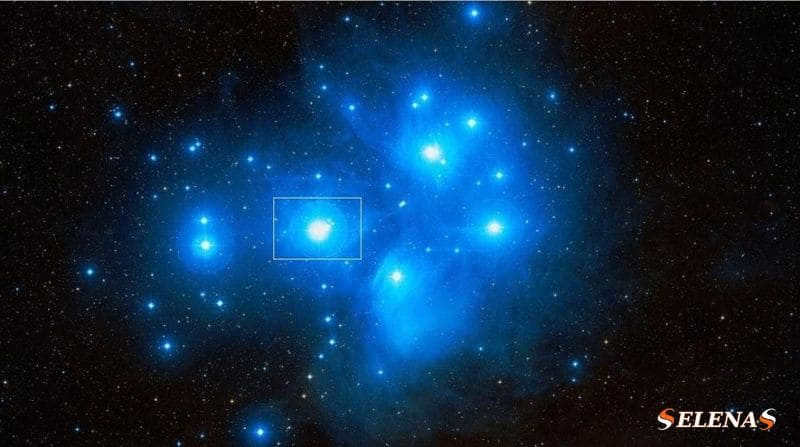

Alcyon, which is also known as Eta Taurus, stands as the third most radiant star in the Taurus constellation and the most brilliant member of the Pleiades cluster.
With an observable magnitude of 2.873, Alcyon rests approximately 370 light-years away from the Sun.
Alcyon is, in truth, an eclipsing binary system that consists of two stars with a separation of 0.031 seconds of arc.
Alcyon A, a blue-white giant of spectral class B7IIIe, serves as the primary star in the system.
This host star possesses a visual stellar magnitude of 2.87 and a radius that is ten times larger than the radius of the Sun.
Notably, Alcyon A also boasts a brightness that is about 2,400 times greater than that of the Sun.
Additionally, Alcyon A is recognized as a fast rotator, with a projected rotation speed of 215 km/s.
Within the Alcyon system, Alcyon A has three companions, namely Alcyon B, Alcyon C, and Alcyon D.
Zeta Tauri: An Interesting Spectroscopic Double Star
Zeta Tauri is an intriguing double star system, characterized by its stellar classification of B2 IIIpe.
Situated approximately 440 light-years away, this celestial object boasts a visual magnitude of 3.010, making it visible to the naked eye.
The primary star in this system is quite remarkable, with a mass equivalent to 11 times that of our Sun and a radius that is 5-6 times larger.
One of the most fascinating aspects of Zeta Tauri is its fast rotation, spinning at an impressive projected speed of 125 km/s.
In comparison, the companion star is slightly less massive than our Sun.
Together, these two components orbit each other in a mesmerizing dance, completing one revolution every 133 days.
Theta Tauri.
Theta Tauri is a binary star located in the Hayden cluster.
The two stars in the system, Theta-1 Taurus and Theta-2 Taurus, are separated by 5.62 minutes of arc.
Theta-1 Taurus is situated 154.4 light-years away from our solar system, while Theta-2 Taurus is positioned 150.4 light-years away.
Theta-1 Taurus is classified as an orange giant of the K spectral type, whereas Theta-2 Taurus is a white giant belonging to the A7 III spectral class.
Theta-1 Taurus is the fainter of the two stars, with a visual magnitude of 3.84, while the other has an apparent magnitude of 3.40.
Pectus Taurus (Pectus Tauri).
Pectus Tauri, which is also referred to as Lambda Taurus, represents a triple star situated in the Taurus constellation.
The name of this celestial object originates from the Latin language and signifies “breast of the bull”.
The overall visual magnitude of Pectus Taurus amounts to 3.47, while its distance from our planet is estimated to be approximately 480 light-years.
The key component of Pectus Taurus consists of an internal pair of stars known as Lambda Tauri AB. These stars revolve around each other every 3.95 days, creating an eclipsing double star system.
Their combined apparent magnitude ranges from 3.37 to 3.91, and they belong to the spectral class B3 V.
Lambda Taurus AB possesses a mass exceeding seven times that of the Sun and a radius more than 6.4 times larger than that of the Sun.
Moreover, it is approximately 5801 times brighter than the Sun and is characterized by a high rotational speed of 85 km/s.
The secondary star is a fast rotator, spinning at a velocity of 76 km/s.
With a spectral type of A4 IV, the secondary star is a subgiant that is approximately 1.9 times more massive than our Sun and shines 128 times brighter.
The third star, which is about twice as massive as the Sun, revolves around the inner pair with a period of 33.025 days.
Ain (Oculus Borealis).
Ain, also referred to as Oculus Borealis and Epsilon Taurus, is categorized as an orange giant with a stellar classification of K0 III.
It possesses an apparent stellar magnitude of 3.53 and is located approximately 147 light-years away.
The designations Ain and Oculus Borealis hold the meaning of “eye”.
Epsilon Taurus is a constituent of the Hayden cluster and is estimated to be around 625 million years old.
This celestial body holds the distinction of being the first planet ever discovered in an open cluster, and it remains the only known planet within the Hayden cluster.
Hyadum I I (Hyadum I).
Hyadum I, also referred to as Gamma Taurus, is a member of the Hayden cluster.
It is a giant star that falls into the spectral class III.
Positioned approximately 154 light-years away from the Sun, its apparent stellar magnitude is 3.654.
With a radius 13.4 times that of the Sun, it shines 85 times brighter.
Gamma Taurus is estimated to be around 430 to 530 million years old.
In Latin, its name translates to “First Hyades”.
Ushakaron, also referred to as Xi of Taurus, is a trinary star system comprising of three blue-white main-sequence dwarfs with spectral type B.
Out of the three stars, two are closely orbiting each other, completing one orbit every 7.15 days, while the pair orbits the third star in the system every 145 days.
Xi Taurus has a stellar magnitude ranging from 3.70 to 3.79 and is located approximately 222 light-years away from the Sun.
Delta Tauri
Delta Tauri is situated within the Hayden cluster and is comprised of three star systems.
The primary star system within Delta 1 of Taurus has a total apparent stellar magnitude of 3.77.
It is positioned roughly 153 light-years away from the Sun.
The main element of Delta-1 Taurus is an orange giant with a stellar classification of K0 III.
It is 74 times more luminous than the Sun and possesses a radius that is 11.6 times greater.
Taurus Delta-2 is a main-sequence dwarf star classified as A7V, with an apparent stellar magnitude of 4.80 and an approximate distance of 146 light-years.
Delta-3 Taurus is also a triple star system with an apparent stellar magnitude of 4.30.
It is roughly 148 light-years distant from the solar system.
The primary component of Delta-2 Taurus is a white subgiant star classified as A2 IV.
Kappa Tauri.
Kappa Tauri is located within the Hayden cluster and is composed of two A-type stars that orbit each other.
One of the stars is a subgiant and has a visual stellar magnitude of 4.21, while the other is a dwarf star with a stellar magnitude of 5.27.
Kappa Tauri in the constellation of Taurus is situated approximately 148 light-years away from the Sun.
Taurus Upsilon (Upsilon Tauri)
Taurus Upsilon is a triple star located in the constellation Taurus and is part of the Hayden cluster.
With an apparent magnitude of 4.28, Taurus Upsilon is approximately 155 light-years away.
The main component of Taurus Upsilon is a main-sequence dwarf star of spectral type A, whose brightness varies between 4.28 and 4.31 every 3.56 hours.
This star system is a spectroscopic double star, with its components separated by a distance of 0.02 arc seconds.
Additionally, Taurus Upsilon has a third component, a 12th magnitude star located 110 angular seconds away from the main pair.
119 Taurus, with a diameter 600 times that of the Sun, is among the largest stars ever discovered.
Additionally, it is one of the most reddish stars visible in the night sky, boasting a color index of 2.07.
This colossal star is classified as a red giant, falling under the stellar classification of M2 Iab-Ib, and has an apparent stellar magnitude of 4.32.
Remarkably, this celestial body is located approximately 1,802 light-years away from our planet.
The constellation 119 Taurus resides close to the ecliptic and may sometimes be concealed by the presence of the Moon.
On rare occasions, it can also be obscured by planets.
Rho Tauri (Rho Tauri).
Rho Tauri, an A8V spectral class star, is a main-sequence star of white color that is a member of the Hayden cluster.
With a mass 1.88 times that of the Sun, Rho Tauri has a visual stellar magnitude of 4.65.
It is situated approximately 152 light-years away from our location.
Rho Taurus is characterized by rapid rotation, with a projected rotation speed of 117 km/s and an estimated rotation period of 488.5 days.
111 Taurus (111 Tauri).
A binary star system known as 111 Taurus is characterized by its two stellar components.
The primary star belongs to the spectral type F8V, while the secondary star is classified as K5 V.
When observed together, these stars have an apparent magnitude of 5.1149 and are situated approximately 46.9 light-years from Earth.
In addition to their visible light emissions, this stellar duo is also recognized as a source of X-rays.
Omicron Tauri (Omicron Tauri)
Omicron Tauri is a massive binary star system classified as G6 III Fe-1.
With a visual magnitude of 3.61, it is located approximately 212 light-years away from our planet.
This celestial object completes an orbit around its center of mass every 533 days and boasts a radius 18 times larger than the Sun, as well as a mass three times that of our host star.
Moreover, Omicron Tauri shines 155 times brighter than our Sun.
T Tauri, discovered by the English astronomer John Russell Hind in October 1852, is a variable star.
It is situated in close proximity to Epsilon Taurus, which is part of the Hayden cluster, but it is actually located about 420 light-years further away.
The T variables in the Taurus constellation are stars that fall into the spectral classes F, G, K, and M and are somewhat larger than main-sequence stars with the same mass, resulting in a greater brightness.
Within the Taurus constellation, there are at least three stars, but only one is visible in the optical wavelength range, while the other two can be observed in the infrared.
These stars are found near the NGC 1555 reflection nebula and have a visible magnitude of 10.27, suggesting they are approximately 600 light-years distant from Earth.
RV Taurus (RV Tauri).
RV Tauri is a yellow supergiant star with a stellar classification of G2eIA-M2Ia.
Over a period of 78.5 days, the brightness of RV Tauri fluctuates between 9.5 and 13.5 magnitudes.
Scientists believe that RV Tauri is currently in the final stages of its life cycle.
In the near future, it will shed its outer layers and transform into a planetary nebula, eventually collapsing into a white dwarf.
Located approximately 7100 light-years away from Earth, RV Tauri is quite a distance from us.
HD 37124
HD 37124 belongs to the G4V spectral type and is classified as a yellow dwarf.
With an apparent stellar magnitude of 7.68, HD 37124 is located approximately 110 light-years away from Earth.
Further observations in 2005 confirmed the presence of three exoplanets in orbit around HD 37124.
Atlas
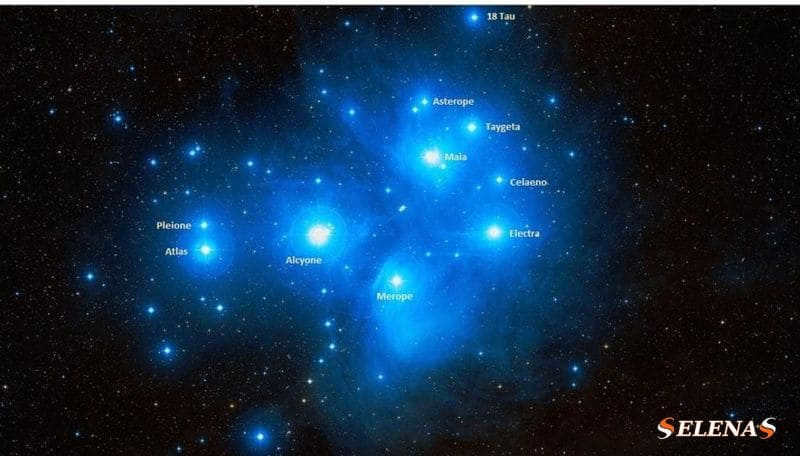

Atlas, also known as 27 Taurus, is a triple star system named in honor of the titan Atlas, who is the father of the Pleiades. It is important to note that this Atlas is not to be confused with Saturn’s moon of the same name.
With a visual stellar magnitude of 3.62, Atlas is located approximately 381 light-years away from the Sun.
The main component of the system is Atlas A, which is a blue-white giant star classified as B8 III. It has visual stellar magnitudes of 4.1 and 5.6. Atlas B, its companion, has an apparent stellar magnitude of 6.8.
Electra, also known as 17 Taurus, is a blue-white giant star classified as B6 IIIe.
Being the third most luminous star in the Pleiades cluster, Electra shines brightly.
Located approximately 600 light-years away from our planet, Electra displays an apparent magnitude of 3.705.
Electra rotates rapidly, with a projected speed of 181 km/s.
At times, its visibility is hindered by the presence of the Moon or occasionally by planets.
Maya (Maia).
Maia, also identified as 20 Taurus, is a B8 III spectral class blue giant.
It is part of the Maia Nebula (NGC 1432), which is situated in the Pleiades cluster.
Maya has a visual stellar magnitude of 3.871 and is positioned approximately 360 light-years away.
Its mass is four times that of our Sun, and its radius is 5.5 times greater.
Furthermore, it is 660 times more luminous than the Sun.
Merope
can be rephrased as “Merope is able to be paraphrased.”

Merope, also known as 23 Taurus, is a subgiant star in the B6IVe spectral class. It has a blue-white color and is situated approximately 360 light-years away from Earth.
With a brightness that is 630 times greater than the Sun and a visual stellar magnitude of 4.113, Merope shines brightly in the night sky. Its mass is equivalent to 4.5 times that of the Sun, and its radius is four times larger as well.
Enveloped by the Merope Nebula, this star and its surrounding nebulous cloud create a stunning celestial sight.
Taygeta, also known as 19 Taurus, is a star system with three stars that is positioned approximately 440 light-years away from our solar system.
With an apparent magnitude of 4.30, Taygeta is visible to the naked eye.
The primary star in the system, Taygeta A, consists of two stars that orbit each other and are classified as a spectroscopic double star. Taygeta A is a blue-white subgiant with a stellar classification of B6IV. The two stars in Taygeta A have magnitudes of 4.6 and 6.1, and they have a separation of 0.012 arc seconds. They complete one revolution around each other every 1313 days.
Pleione Star
Pleione, also known as 28 Taurus or BU Tauri, is a binary star located in the Pleiades cluster. It has a stellar classification of B8Ivpe.
With a visual magnitude of 5.048, Pleione is approximately 392 light-years away from Earth.
Due to its proximity to the brighter Atlas star, Pleione is not easily visible to the naked eye.
Pleione shines with a brightness that is about 190 times greater than that of the Sun.
This star was named after Pleione, a figure from Greek mythology. Pleione was the daughter of Tefia and Oceanus, and the mother of Gias, the Hyades, and the Pleiades.
Calaeno (Celaeno)
Celaeno, also known as Celaeno or 16 Taurus, is a subgiant star that emits a blue-white light and has been classified as B7 IV.
With a magnitude of 5.448, this star is visible from a distance of approximately 430 light-years away from our solar system.
Calaeno possesses a radius that is four times larger than that of the Sun and exhibits a projected rotation speed of 185 km/s.
Among the Seven Sisters of the Pleiades, Calaeno stands out as the most challenging one to observe, as it can only be seen without the aid of binoculars when the conditions are optimal and the skies are clear.
Asterope
Asterope, which is also referred to as 21 and 22 Taurus, consists of two stars that are positioned 0.04° apart and are both located approximately 440 light-years away.
Situated in the Pleiades cluster, 21 Taurus is classified as a B8 V main-sequence dwarf star, while 22 Taurus is categorized as an A0Vn main-sequence dwarf star.
With a stellar magnitude of 5.76, 21 Taurus shines slightly brighter than 22 Taurus, which has a visual stellar magnitude of 6.43.
Deep sky entities
Taurus constellation contains numerous deep sky entities, such as Messier objects and nebulae.
Below, we will explore these remarkable celestial objects.
The Nebula of the Crab.
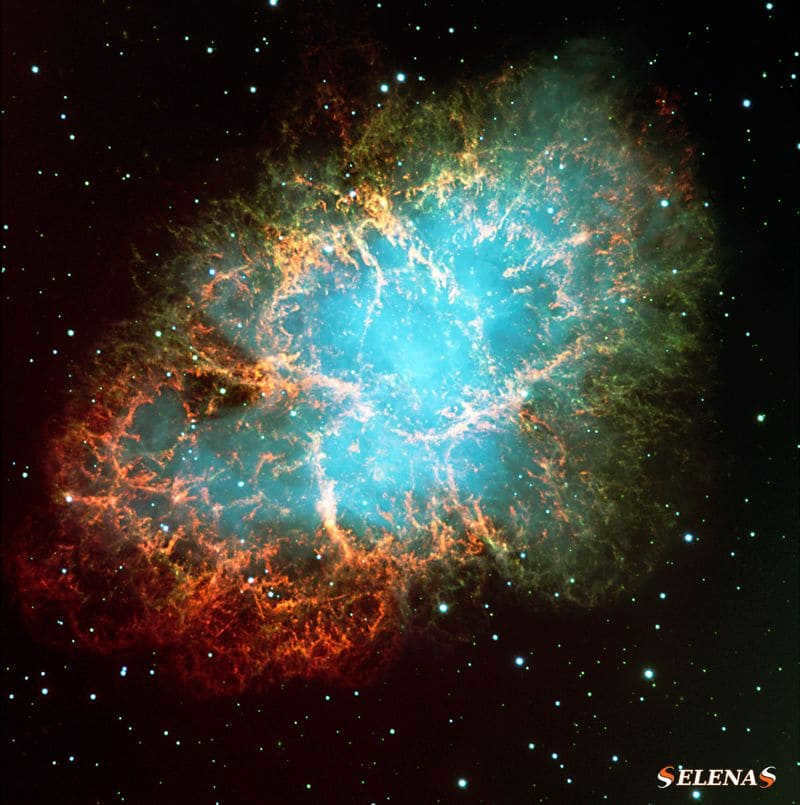

The Crab Nebula, also referred to as Messier 1, is a leftover from a supernova explosion.
John Bevis, an English physician and astronomer, initially spotted Messier 1 in 1731, and it was the first celestial object to be included in Messier’s catalog in 1758.
Messier 1 is a nebula with a pulsar, typically found within the remnants of supernovae.
The apparent brightness of the Crab Nebula is measured at 8.4 magnitudes.
It spans approximately 11 light years in diameter and is expanding at a velocity of 1,500 kilometers per second.
Scientists estimate its distance from the Sun to be around 6,500 light-years.
A crab pulsar is a neutron star located at the core of the SN 1054 supernova remnant.
This pulsar was initially detected in 1968.
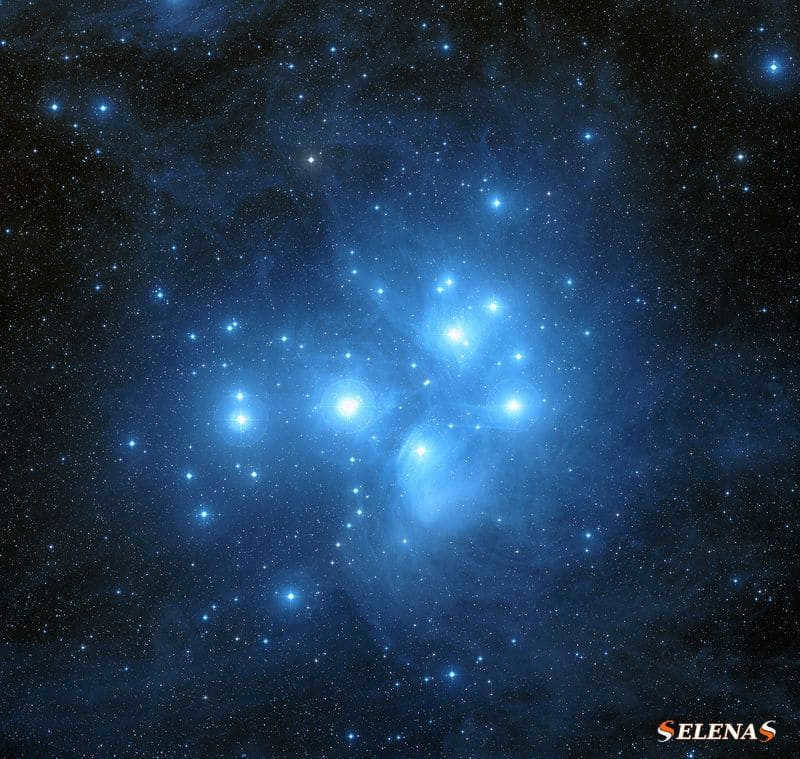
The Pleiades, also known as The Seven Sisters, is a prominent star cluster in the constellation of Taurus (The Bull).

Messier 45, also known as the Pleiades, is a cluster of hot, luminous Class B stars that have formed within the past 100 million years.
Due to its brightness, the Pleiades is one of the most easily identifiable star clusters in the night sky.
With an apparent stellar magnitude of 1.6, the Pleiades is located approximately 390 to 460 light-years away from our solar system.
The Pleiades cluster is named after the Pleiades, the seven sisters in Greek mythology – Altion, Calaeno, Electra, Maia (the mother of the god Hermes), Merope (the wife of Sisyphus), Sterope, and Taygeta – as well as their parents, the sea nymph Pleione and the titan Atlas.
Messier 45 will continue to exist for approximately 250 million more years, at which point the gravitational interactions with neighboring objects will result in the dispersion of the stars.
This cluster has been recognized in numerous cultures throughout history and is believed to have been first observed during the Bronze Age.
The Hyades Cluster

The Hyades Cluster, which is also referred to as Caldwell 41, Melotte 25, or Collinder 50, is an open cluster that contains numerous stars.
It is estimated to be approximately 625 million years old and is the nearest open star cluster to the Sun, making it the most extensively studied.
The most luminous stars in the Hyades cluster consist of Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Theta of Taurus, and they create a V-shape along with the brightest star in the Taurus constellation, Aldebaran.
Aldebaran is not part of this cluster, but it lies in the same line of sight.
In fact, it is much closer to us than the Hyades Cluster.
Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Theta of Taurus form the Bull’s head and collectively contribute to the apparent stellar magnitude of 0.5 for the Hyades Cluster.
They are situated approximately 153 light-years away.
Hind’s Variable Nebula (NGC 1555)
The Hind’s Variable Nebula, also called NGC 1555, is a type of nebula that changes in brightness. It is classified as a reflection nebula.
This nebula is situated in close proximity to the star T Taurus, which provides the illumination for its appearance.
John Russell Hind was the first to spot this nebula on October 11, 1852.
NGC 1410 and NGC 1409
NGC 1409 and NGC 1410 form a pair of colliding galaxies that are linked by a boundary spanning over 20,000 light-years.
As a result of this interaction, NGC 1410 has witnessed the formation of numerous stars.
In the future, the gravitational forces between these two galaxies will cause them to merge into a single entity.
Combined, these galaxies have a visible magnitude of 15.4 and are located 300 million light-years away from the Sun.
Crystal Ball Nebula (Crystal Ball Nebula)
The Crystal Ball Nebula, which is also called NGC 1514, is a massive planetary nebula with a visible stellar magnitude of 9.43.
Scientists believe that it revolves around a binary star system with an orbital period of approximately 10 days.
Renowned astronomer William Herschel was the first to spot it in November 1790.
NGC 1746 is a group of stars with a visual brightness of 6.1.
Heinrich Louis d’Arrest discovered it in 1863.
Merope Nebula (NGC 1435)
The Merope Nebula, also known as NGC 1435, is a diffuse reflection nebula.
It surrounds the star Merope and is located in the Pleiades star cluster.
It is illuminated by starlight and has a visual brightness of 13.0.
NGC 1435, which is about 440 light-years away from the solar system, was discovered by Wilhelm Tempel, a German astronomer.
NGC 1647
NGC 1647 is a star cluster that was found and has a visual brightness of 6.4.
This cluster can be found positioned in between the horns of a bull.
NGC 1817
NGC 1817 is a different open star cluster that has a visual brightness of 7.7.
It was discovered by William Herschel on the 19th of February, 1784.
NGC 1807
NGC 1807 is also a star cluster that is open in nature.
It possesses a stellar magnitude of 7.0 and was initially discovered by John Herschel on January 25, 1832.
Additional details
- The constellation of Taurus was referred to as MUL.APIN or “Heavenly Bull” by Babylonian astronomers;
- In Buddhism, it is believed that Gautama Buddha was born during the full moon in Vaishakha, which corresponds to Taurus;
- The festival of Vesak, or Vesakkha, is celebrated to mark Buddha’s birthday and takes place on the first or second full moon when the Sun is in Taurus;
- Taurus held significant religious importance among the Druids, who celebrated a religious festival in Taurica when the Sun passed through the constellation.