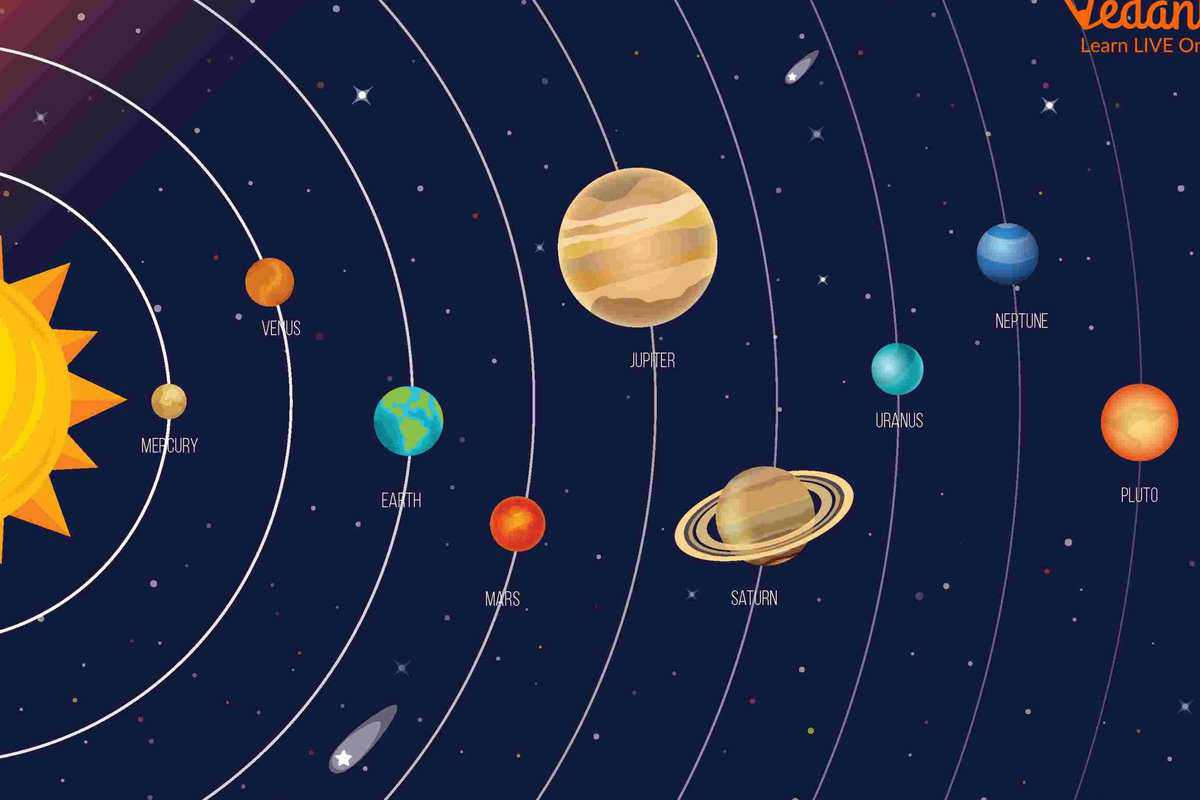
Goals: Identifying the planets in our solar system, providing information about them, expanding knowledge, developing attention, critical thinking, memory, information processing skills, and fostering an appreciation for our planet Earth.
Download:
Preview:
Municipal budgetary general educational institution
“Mukhtolovskaya basic school”
Ardatovsky district of Nizhny Novgorod region.
The lesson prospectus on the surrounding world
elementary school teacher
Lesson on the program “Planet of Knowledge”.
Lesson type: Introduction to new material
Lesson topic: “THE SOLAR SYSTEM”.
Purpose: Introduce students to the planets of the solar system
Objectives: Discover the planets that make up the solar system, provide an overview of them, expand knowledge, develop attention, thinking, memory, the ability to process information and draw conclusions, foster a sense of responsibility towards our home planet.
Create conditions for the formation of SDGs
1) Personal: motivation for learning, moral and ethical assessment (evaluating learned content based on social and personal values);
2) Cognitive: setting a cognitive goal, searching and selecting information, analyzing to identify features, synthesizing to create a whole from parts, selecting grounds for comparing objects, establishing cause-and-effect relationships;
3) Communicative: actively cooperating in searching and gathering information, evaluating partner’s actions;
4) Regulatory: setting goals, planning, controlling, correcting, evaluating, ability to mobilize strength and energy;
Equipment: educational presentation, projector, group work cards, self-assessment sheets.
– Hi! Please take a seat. Today, we will be exploring a variety of new and fascinating concepts.
- What is the term for self-luminous celestial bodies? (Stars)
- What is the color of the hottest stars? (White and blue)
- Which stars are considered “cooler”? (Yellow and red)
- What type of scientists study stars? (Astronomers)
- What factor determines the color of a star? (Temperature)
- What is the name for the world as seen by astronomers? (The universe or the cosmos)
- What tool is used to study the universe? (Telescope)
- Which is closer to the Earth: the Sun or the Moon? (Moon)
- The Moon is a… (Satellite)
- What is the brightest star in the night sky called? (Sirius)
- Which star can be used for navigation at night? (Polaris)
- What is the attire worn by astronauts? (A spacesuit)
- The gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth. (Atmosphere)
III. Definition of the lesson’s theme. Main stage
– Let’s solve the anagram
The subject of our lesson is the solar system.
Planets have a round shape
Which planet is the largest and which is the smallest?
Is there life on other planets?
1. Discussion. In ancient times, observers noticed that there were moving lights in the sky. They called them planets. Planets are cold celestial bodies that do not emit their own light. They are visible because they reflect sunlight. Planets are explored by automated interplanetary stations. These stations fly to the planets and capture close-up images of their surfaces. The sun and the planets together form the solar system. Only Earth has living beings in the solar system. There are no living creatures on the other planets.
The Solar System is a planetary system comprising of the central star, known as the Sun, and a collection of celestial bodies that revolve around it.
The Sun, which happens to be the nearest star to Earth, is an enormous, blazing celestial entity that perpetually radiates light and heat. Although the Sun appears diminutive when viewed from our planet, it is, in reality, so vast that Earth appears minuscule in comparison. To put it into perspective, if we were to liken the Sun to an orange, then the Earth would be akin to a tiny poppy seed.
There are nine enormous planets that orbit the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Each of these planets follows a unique path around the Sun, known as an orbit. The solar system is organized in order of distance from the Sun, with the first four places occupied by the Earth-group planets: Earth, Venus, Mars, and Mercury. These planets are primarily composed of rock and metal. The next four places are taken by the Jupiter group planets, also known as the giant planets. These planets differ significantly from the Earth-group planets in several aspects. Firstly, they are incredibly large and have immense masses but relatively small densities, similar to that of water. Secondly, their chemical composition is mainly made up of hydrogen and helium gases, which are characteristic of the Sun’s composition. Thirdly, each of the giant planets has numerous satellites, and lastly, they are all surrounded by thin rings. These planets include Saturn, Neptune, Jupiter, Uranus, and the dwarf planet Pluto. Although the other planets in the solar system have been extensively studied, Pluto remains a subject of debate and has not been fully explored. It is now classified as a “dwarf planet.”
3. Complete the ZHU table
The planets have a spherical shape
Which planet is the biggest and which is the smallest?
What defines the solar system?
There are nine planets. Jupiter is the largest planet and Pluto is the smallest one. The path a planet follows is called an orbit.
The solar system consists of the planets and the Sun.
4. The technique known as “Tangled Logic Chains”. Unravel the logic chain and write down the names of the planets in order of their distance from the Sun.
- Earth, Venus, Mars, Mercury, Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter, Pluto.
- Mercury, Earth, Uranus, Pluto, Venus, Jupiter, Mars, Saturn, Neptune.
Regarding the subject: systematic advancements, demonstrations, and written records
Summary of a class on our surroundings titled “Planets in the solar system”.
This particular class is the second installment in the 4th grade curriculum as part of the “School of Russia” program developed by A.A.Pleshakov.

Teaching about the globe: "The celestial bodies revolving around the sun" (second grade).
Teaching materials based on the Federal State Educational Standards for second grade, following the developmental system of L.V. Zankov, in the subject of "Environment", with the topic of "Celestial Bodies of the Solar System".

Planets of the Solar System: Lesson Plan for 2nd Graders
This lesson plan provides an overview of the topic “Planets of the Solar System” for 2nd grade students. It includes various supplementary materials such as poems and riddles to enhance the learning experience.

Creating a Lesson on the Celestial Bodies “Planets of the Solar System”
The goals and objectives of the lesson are as follows:
- Educational:
- To introduce students to the planets of the solar system.
- To help students understand the reasons behind day and night cycles, as well as seasonal changes on Earth.
- To familiarize students with the scientific research and exploration of the planets.
Outline of a lesson on the topic “Planets of the Solar System”
Lesson outline for the School of Russia, Grade 4. The main objective of this lesson is to create an environment where children can become familiar with the different planets in our solar system. The specific objectives of this lesson include:
Lesson plan for exploring the universe: “The Planets in our Solar System”
Lesson overview for exploring the world around usProgram: Russian SchoolClass: 4Lesson topic: “The Planets in our Solar System”Objective: to provide an opportunity for children to become acquainted with the various planets in our solar system.
Planets of the Solar System Lesson Outline
Lesson outline for the World Around Program:
Program: School of Russia
Class: 4
Lesson topic: “Planets of the Solar System”
Objective: To provide an opportunity for children to become familiar with the planets of the Solar System.

At present, there are a total of 58,742 educational establishments that are providing extra reductions ranging from 2% to 25%. In order to ascertain the specific discount applicable to all staff members of your educational institution, kindly access your personal Infoworks account.


Enroll in our professional retraining course
Theory and methodology of teaching in elementary classes of compensatory and correctional-developing type
We have the option to apply your educational institution’s discount to our current discount offer (the amount depends on the number of your colleagues who have completed Infowork courses).
Currently, there are additional cumulative discounts available (ranging from 2% to 25%) for 58,742 educational institutions. To determine the specific discount applicable to all employees of your educational institution, please log in to your personal Infoworks account.


We offer a professional development course that focuses on the theory, methodology, and practice of teaching chess to elementary school students in accordance with the FSES LEO framework.
Discounts are available!
In addition to the discounts we offer, your educational institution may also provide a discount based on the number of colleagues who have taken Infowork courses. The exact discount amount can be determined by logging into your personal Infoworks account.
Currently, 58,742 educational institutions are eligible for discounts ranging from 2% to 25%. To find out the discount applicable to all employees of your educational institution, please log in to your personal Infoworks account.


Managing Envy among Middle School Students – Effective Strategies
Slide-by-Slide Presentation Description:

Slide 1: How many planets orbit the sun?


Slide 2: The solar system is composed of a total of eight planets and more than 63 satellites that are continuously being discovered. Additionally, there are several dozen comets and a significant number of asteroids. Each celestial body follows its own distinct trajectory as it orbits around the Sun, which is 1,000 times more massive than all the other bodies in the solar system combined.

Slide 3: The Origins of the Planets
Approximately 5-6 billion years ago, one of the disk-shaped gas-dust clouds within our expansive galaxy, the Milky Way, initiated a gradual collapse towards its center, eventually giving rise to the Sun as we know it today. Moreover, as proposed by a particular hypothesis, the immense gravitational forces at play caused a multitude of dust and gas particles orbiting the Sun to coalesce into spherical formations, which would later become the planets. Alternatively, another theory suggests that the gas-dust cloud rapidly fragmented into distinct clusters of particles that subsequently underwent compression and consolidation, ultimately shaping the current planetary bodies. At present, the 8 planets continue to orbit the Sun in a perpetual dance.


Slide 4
The Sun is at the center of the solar system, around which the planets revolve. The planets themselves do not emit heat or light, but instead reflect the sunlight. Currently, there are officially recognized to be 8 planets in the solar system. To briefly list them in order of distance from the Sun, we have:

In addition to the Moon, the solar system also contains natural satellites orbiting other planets. All planets, except Mercury and Venus, have their own natural satellites. There are currently more than 60 known satellites in the solar system. Many of the satellites of the outer planets were discovered through the analysis of photographs taken by automated spacecraft. For instance, Leda, the smallest satellite of Jupiter, measures only 10 kilometers in diameter.

Slide 7
The Sun is a celestial body that is crucial for the existence of life on our planet Earth. It provides us with vital energy and heat. According to the stellar classification system, the Sun is classified as a yellow dwarf. It has an estimated age of approximately 5 billion years. The Sun’s equatorial diameter measures around 1,392,000 km, which is 109 times larger than the diameter of our planet Earth. The Sun rotates at a rate of 25.4 days at the equator and 34 days at the poles. It has a mass of approximately 2×10 to the power of 27 tons, which is about 332,950 times the mass of Earth. The core of the Sun has an incredibly high temperature of around 15 million degrees Celsius, while the surface temperature is about 5500 degrees Celsius. In terms of composition, the Sun is primarily composed of 75% hydrogen and the remaining 25% consists of other elements, with helium being the most abundant. Now, let’s delve into the fascinating topic of the number of planets orbiting the Sun within our solar system and explore the unique characteristics of each planet.
Mercury, as the initial planet in the solar system, is the eighth slide.

Slide 9: Mercury is one of the four inner planets that orbit closest to the sun. The other three inner planets are Venus, Earth, and Mars. Unlike the four giant planets, these inner planets have solid surfaces. Mercury is the fastest moving planet, experiencing extreme temperature changes due to being burned by the sun’s rays during the day and freezing at night.
Here are some characteristics of Mercury:
– Period of orbit around the Sun: 87.97 days.
– Diameter at the equator: 4878 km.
– Rotation period (revolution around the axis): 58 days.
– Surface temperature: 350 degrees during the day and -170 degrees at night.
– Atmosphere: very rarefied, primarily composed of helium.
– Number of satellites: 0.
– Major satellites of the planet: 0.


Venus is the second planet in the solar system in terms of importance.


Slide 11 provides insight into the characteristics of Venus. This planet has a revolution period around the Sun of 224.7 days and a diameter at the equator measuring 12104 km. It takes Venus 243 days to complete one rotation around its axis. The average surface temperature on Venus is a scorching 480 degrees. Its atmosphere is dense and predominantly composed of carbon dioxide. Venus has no satellites or major satellites orbiting around it.


Earth is believed to have originated from a cloud of gas and dust, similar to other planets. Over time, the collision of gas and dust particles caused the planet to gradually grow. The surface temperature of Earth once reached a scorching 5,000 degrees Celsius before cooling down and developing a solid rocky crust. However, even to this day, the temperature in the planet’s interior remains remarkably high at 4,500 degrees Celsius. The rocks within the interior are in a molten state, and when volcanoes erupt, they release this molten material onto the surface. Unlike other planets, Earth has the unique feature of having water on its land, which is crucial for supporting life. This is possible because Earth is positioned at an ideal distance from the Sun, receiving the necessary heat and light without being burnt up.


In slide 14, we can see the characteristics of the Earth:
The time it takes for the Earth to orbit around the Sun is 365.3 days.
The diameter at the equator is 12756 km.
The time it takes for the Earth to rotate around its axis is 23 hours and 56 minutes.
The average surface temperature is 22 degrees Celsius.
The Earth’s atmosphere is mostly composed of nitrogen and oxygen.
The Earth has 1 satellite.
The main satellite of the Earth is the Moon.


The planet Mars, which holds the fourth position in the solar system, is a celestial body with distinct features.


Slide 16: Due to its similarities with Earth, there was speculation about the existence of life on Mars. However, a spacecraft that touched down on the planet’s surface discovered no evidence of life. Mars is the fourth planet from the sun and has several notable characteristics:
Orbital period: 687 days
Equatorial diameter: 6794 kilometers
Rotation period: 24 hours and 37 minutes
Average surface temperature: -23 degrees Celsius
Atmosphere: Mostly composed of carbon dioxide and is sparsely populated
Satellites: Mars has two satellites, Phobos and Deimos.

In the solar system, Jupiter is positioned as the fifth planet, according to the 17th slide.

Slide 18
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are composed of hydrogen and other gases. Jupiter’s diameter is over 10 times larger than Earth’s, its mass is 300 times greater, and its volume is 1,300 times larger. It is also more than twice as massive as all the other planets in the solar system combined. To become a star, Jupiter would need to increase its mass by 75 times!
Here are some characteristics of Jupiter:
Orbit period around the Sun: 11 years 314 days.
Equatorial diameter: 143,884 km.
Rotation period (spin around its axis): 9 hours 55 minutes.
Average surface temperature: -150 degrees Celsius.
Atmosphere: primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. Number of moons: 16 (+ rings).
The major moons of Jupiter in order of distance from the planet are: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.

Saturn, the 6th planet in our solar system, is the 6th largest planet in terms of size.


Saturn, the second largest planet in the solar system, is famous for its stunning ring system composed of ice, rock, and dust that orbits the planet. This ring system gives Saturn a unique appearance and makes it stand out among other planets. The rings consist of three main components and have an outer diameter of 270,000 km, but they are relatively thin, with a thickness of about 30 meters.
Here are some key characteristics of Saturn:
- Period of orbit around the Sun: 29 years and 168 days
- Diameter of the planet at the equator: 120,536 km
- Rotation period (revolution around the axis): 10 hours and 14 minutes
- Surface temperature: -180 degrees Celsius (on average)
- Atmosphere: primarily composed of hydrogen and helium
- Number of satellites: 18 (including the rings)
- Major satellite: Titan

Uranus, the seventh planet in the solar system, is ranked as the 21st slide in order of appearance.


Neptune is known as the 8th planet in our solar system, consisting of 23 slides.

Slide 24 Currently, Neptune holds the distinction of being the final planet within our solar system. Its discovery was made through mathematical calculations, followed by observations through a telescope. In the year 1989, Voyager 2 embarked on a journey that allowed for captivating images to be captured, showcasing Neptune’s blue surface as well as its largest moon, Triton.
Neptune possesses a range of distinctive characteristics:
Orbital period around the Sun: 164 years and 292 days.
Equatorial diameter: 50,538 kilometers.
Rotation period (revolving around its axis): 16 hours and 7 minutes.
Average surface temperature: -220 degrees Celsius.
Composition of the atmosphere: primarily hydrogen and helium. Number of satellites: 8.
Prominent satellites: Triton.


Slide 25: Now, if you’re asked, answer confidently – there are 8 planets in our solar system. This has been officially recognized since 2006. Arranging the planets of the solar system in order from the sun, refer to the provided image. Do you think maybe removing Pluto from the list of planets was a result of scientific bias?
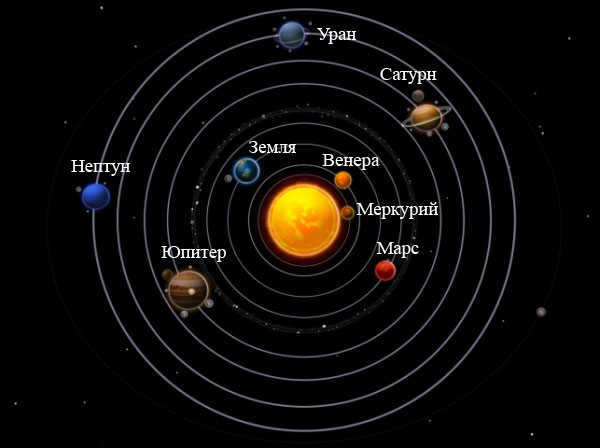
The solar system consists of a collection of celestial bodies that revolve around a radiant star known as the Sun. This celestial body serves as the primary source of both light and heat within the solar system.
It is widely believed that the formation of our planetary system can be attributed to the explosive aftermath of one or more stars, an event that occurred roughly 4.5 billion years ago. Initially, the solar system existed as a conglomerate of gas and dust particles, but as time progressed and as a result of its own gravitational pull, the Sun and other planets gradually took shape.
The celestial bodies in the solar system
Located at the heart of the solar system is the Sun, around which revolve eight celestial bodies: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Up until the year 2006, Pluto was also a member of this assembly of celestial bodies. Originally considered the 9th celestial body from the Sun, it was eventually reclassified as a dwarf planet due to its substantial distance from the Sun and diminutive size. Specifically, it is one of several dwarf planets situated within the Kuiper belt.
All of the aforementioned celestial bodies are generally classified into two broad categories: the terrestrial group and the gas giants.
The terrestrial group encompasses the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These celestial bodies are characterized by their relatively small size, rocky surfaces, and their proximity to the Sun.
The Sun
All the planets and satellites in the solar system revolve around the Sun, which is a star composed of hydrogen and helium. The Sun, which is currently 4.5 billion years old, is in the middle of its life cycle and is gradually increasing in size. At present, the diameter of the Sun is 1,391,400 kilometers. In the future, this star will expand and reach the Earth’s orbit.
The Sun serves as the source of heat and light for our planet. Its activity fluctuates every 11 years, increasing or decreasing.
Studying the Sun in detail is challenging due to the extremely high temperatures on its surface. However, ongoing efforts to send a specialized spacecraft as close to the star as possible are being made.
The group of planets known as Earth
Mercury
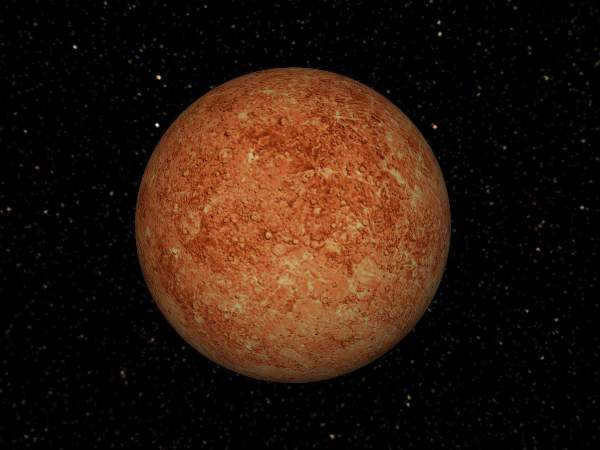

This particular planet, known as Mercury, is one of the smaller celestial bodies found within the vast expanse of the Solar System. With a diameter measuring at approximately 4,879 kilometers, it holds the distinction of being the closest planet to the Sun. This close proximity to the Sun has led to a significant discrepancy in temperature. During the daytime, the average temperature on Mercury can reach a scorching +350 degrees Celsius, while plummeting to a frigid -170 degrees Celsius during the night.
In terms of its orbit around the Sun, Mercury completes a full revolution in just 88 Earth days. Interestingly, a single day on Mercury spans a duration of 59 Earth days. Furthermore, it has been observed that this particular planet has the ability to periodically alter its rotational speed around the Sun, as well as its distance and position in relation to it.
Studying Mercury in depth is quite challenging because of its close proximity to the Sun. Occasionally, Mercury can be observed from Earth without the aid of a telescope.
There is a theory suggesting that Mercury was previously a moon of Venus, although there is still no conclusive evidence to support this hypothesis. Unlike many other planets, Mercury does not have any natural satellites.
Venus, the second planet from the Sun
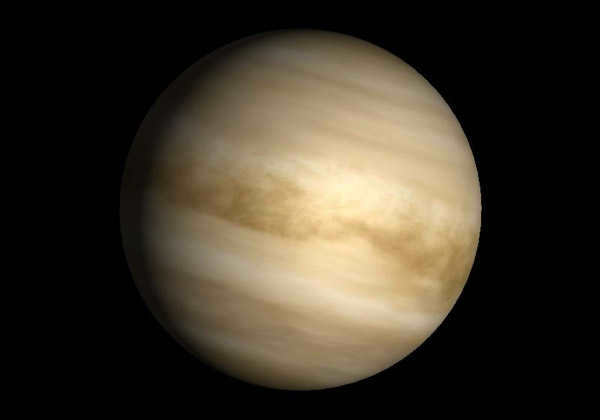

Venus is positioned as the second planet from the Sun. In terms of its dimensions, it is similar to Earth, with a diameter of 12,104 kilometers. However, Venus has several distinctive features compared to our planet. For instance, a day on Venus lasts for 243 Earth days, and a year lasts for 255 days. The atmosphere of Venus consists of 95% carbon dioxide, resulting in a greenhouse effect on its surface. This leads to an average temperature of 475 degrees Celsius on the planet. The atmosphere also contains 5% nitrogen and 0.1% oxygen.
In Venus, there are numerous craters and elevations that bear a resemblance to the continents on Earth. The reason behind the formation of these craters is believed to be the planet’s previous possession of a less dense atmosphere.
One unique characteristic of Venus is that, unlike other planets, its direction of motion is not from west to east, but rather from east to west. This distinctive trait allows it to be visible from Earth without the need for a telescope, particularly after sunset or before sunrise. This visibility is made possible by the atmosphere’s exceptional ability to reflect light.
It is worth noting that Venus does not have any natural satellites.
The planet Earth
Our planet is positioned at a distance of 150 million kilometers away from the Sun, which allows for the creation of a temperature suitable for the existence of liquid water on its surface, thus enabling the possibility of life.
Approximately 70% of the Earth’s surface is covered with water, making it the only planet in the solar system to have such a significant amount of liquid. It is believed that many millennia ago, the presence of water in liquid form on Earth’s surface was made possible by the vapor in the atmosphere, which created the necessary temperature, while solar radiation played a vital role in the process of photosynthesis and the emergence of life on this planet.
The Earth’s diameter measures 12,742 km. A day on Earth lasts for 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds, while a year consists of 365 days, 6 hours, 9 minutes, and 10 seconds. The Earth’s atmosphere is composed of 77% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and a small percentage of other gases. Unlike the atmospheres of other planets in the solar system, none contain as much oxygen.
Scientists estimate the age of the Earth to be 4.5 billion years, approximately the same age as its only satellite, the Moon. The Moon always presents the same face to Earth. Its surface is marked by numerous craters, mountains, and plains. The Moon reflects only a small amount of sunlight, resulting in its pale lunar glow when observed from Earth.
Red Planet
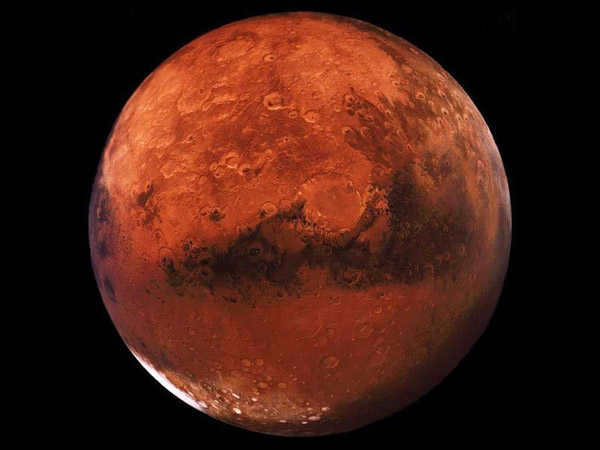

Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, is located 1.5 times further away from the Sun compared to Earth. With a diameter of 6,779 kilometers, Mars is smaller than Earth. The equator region experiences temperatures ranging from -155 degrees Celsius to +20 degrees Celsius. Unlike Earth, Mars has a weaker magnetic field and a rarefied atmosphere, allowing solar radiation to directly impact the surface. This makes it unlikely for life to exist on the Martian surface.
Mars rovers have discovered numerous mountains, dried up riverbeds, and glaciers on the planet’s surface. The surface of Mars is characterized by red-colored sand, which is attributed to the presence of iron oxide.
One of the most common occurrences on Earth are dust storms, which can be extensive and devastating. Although no geological activity has been observed on Mars, it is well-established that significant geological events have taken place in the planet’s history.
The Martian atmosphere is composed of 96% carbon dioxide, 2.7% nitrogen, and 1.6% argon. Oxygen and water vapor are present in minimal quantities.
A Martian day has a duration similar to that of Earth, lasting 24 hours 37 minutes and 23 seconds. However, a Martian year is twice as long as an Earth year, spanning 687 days.
Mars has two moons, Phobos and Deimos. These moons are relatively small and have irregular shapes, resembling asteroids.
Occasionally, Mars is visible to the naked eye from Earth as well.
Jupiter
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. It is a gas giant, composed mostly of hydrogen and helium. With a diameter of about 143,000 kilometers, Jupiter is more than 11 times the size of Earth. It is also one of the brightest objects in the night sky, and can often be seen without a telescope.
Jupiter has a powerful magnetic field, which creates intense radiation belts around the planet. These radiation belts are responsible for Jupiter’s colorful auroras, similar to Earth’s northern and southern lights.
Jupiter is known for its iconic Great Red Spot, a massive storm that has been raging for centuries. This storm is so large that three Earths could fit inside it. Scientists are still studying the Great Red Spot to understand its formation and behavior.
Jupiter has a total of 79 known moons, the largest of which is Ganymede. Ganymede is even larger than the planet Mercury and has its own magnetic field. Other notable moons of Jupiter include Europa, known for its potential subsurface ocean, and Io, known for its active volcanoes.
The exploration of Jupiter began with the Pioneer and Voyager missions in the 1970s and 1980s. More recently, the Juno spacecraft has been studying the planet since 2016, providing valuable insights into its atmosphere, magnetic field, and interior structure.
Jupiter is a fascinating planet that continues to captivate scientists and stargazers alike. Its size, magnetic field, and diverse moons make it a unique and intriguing destination for future exploration.
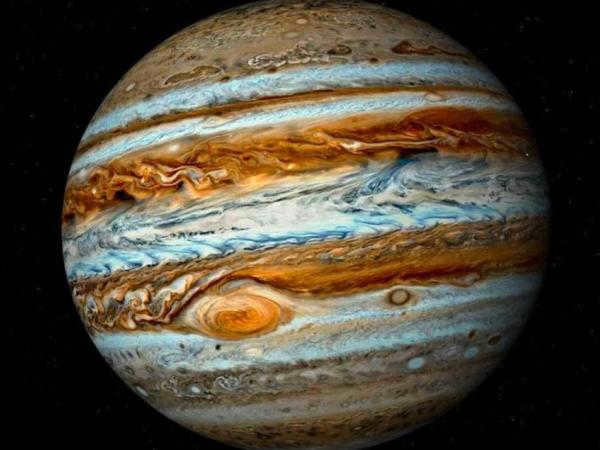

Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, has a diameter of 139,822 km, which is a staggering 19 times larger than Earth. A day on Jupiter lasts a mere 10 hours, while a year on this gas giant is approximately 12 Earth years. Composed mainly of xenon, argon, and krypton, Jupiter’s immense size is just short of becoming a star through a spontaneous thermonuclear reaction, requiring it to be 60 times larger.
Jupiter’s average temperature hovers around -150 degrees Celsius, making it an incredibly cold planet. Its atmosphere is primarily made up of hydrogen and helium, with no traces of oxygen or water on its surface. However, there is a prevailing theory that suggests the presence of ice in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
Jupiter possesses an immense quantity of satellites – 67. Among the most prominent are Io, Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa. Ganymede stands out as being one of the largest satellites within the entire solar system. Its diameter spans an impressive 2,634 kilometers, approximately equal to that of Mercury. Furthermore, its surface exhibits a thick layer of ice, potentially concealing water beneath. Callisto, on the other hand, bears the distinction of being the oldest of Jupiter’s satellites, boasting the highest concentration of craters on its surface.
The planet Saturn

The second largest planet in the solar system has a diameter of 116,464 kilometers. It closely resembles the Sun in terms of composition. It has a considerably long year, lasting nearly 30 Earth years, while a day on this planet is only 10.5 hours. The surface temperature averages at -180 degrees Celsius.
The planet’s atmosphere is primarily made up of hydrogen with a minimal amount of helium. It frequently experiences thunderstorms and auroras in its upper layers.
Uranus
Uranus, also known as the seventh planet from the Sun, is a unique and fascinating celestial body. With its distinctive blue-green color and its unusual sideways rotation, Uranus stands out among the other planets in our solar system.
One of the most intriguing features of Uranus is its atmosphere. Unlike the other gas giants in our solar system, Uranus has a mostly hydrogen and helium atmosphere with a significant amount of methane. This methane gives Uranus its distinctive blue-green color.
Another interesting aspect of Uranus is its rotation. While most planets in our solar system rotate on an axis that is roughly perpendicular to their orbit, Uranus spins on its side. This means that its poles are almost in the plane of its orbit, causing extreme seasonal variations in temperature and sunlight.
Uranus also has a unique system of rings. While not as prominent or well-known as Saturn’s rings, Uranus has a system of thin, dark rings that are made up of small particles of rock and ice. These rings add to the planet’s beauty and mystique.
In addition to its rings, Uranus has a number of moons. The largest and most well-known of these moons is Miranda, which has a highly varied and geologically active surface. Other notable moons include Ariel, Umbriel, Titania, and Oberon.
While Uranus has been visited by spacecraft, such as Voyager 2 in 1986, much of the planet’s mysteries remain unsolved. Scientists continue to study and explore this enigmatic planet, hoping to uncover its secrets and gain a deeper understanding of our solar system.

Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun and the third largest in the solar system. With a diameter of 50,724 kilometers, Uranus is often referred to as the “ice planet” due to its extremely low surface temperature of -224 degrees Celsius. Unlike most planets, Uranus has a unique tilt, with its axis located at a 90-degree angle to its orbit, causing it to appear as if it is “lying on its side.” This unusual tilt also affects the planet’s seasons, with both summer and winter lasting for approximately 42 Earth years. A day on Uranus lasts for 17 hours, while a year is equivalent to 84 Earth years.
Uranus is also home to 27 satellites, including its most well-known moons: Oberon, Titania, Ariel, Miranda, and Umbriel.
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third-largest by mass. Among the gaseous planets in the Solar System, Neptune is the most dense. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times the mass of Earth but not as dense.

Neptune, the eighth planet from the Sun, shares similarities in composition and size with its neighboring planet Uranus. With a diameter of 49,244 kilometers, Neptune has a day that lasts 16 hours and a year that stretches to 164 Earth years. Although previously believed to lack any weather phenomena on its icy surface, recent discoveries have unveiled that Neptune boasts the highest wind speed among all the planets in our solar system, reaching a whopping 700 kilometers per hour.
Accompanied by 14 satellites, the most renowned being Triton, Neptune is confirmed to possess its own atmosphere.
Moreover, Neptune proudly displays six rings, adding to its celestial beauty.
Curious information about the planets in our solar system
When observed from Earth, Mercury appears as a mere speck in the vastness of the sky. This is due to the significant disparity in size between the two celestial bodies within our solar system:

Venus is commonly known as the Morning and Evening Star because it is the first star visible in the sky at sunset and the last star to disappear from view at dawn.
One fascinating fact about Mars is the presence of methane on its surface. The planet’s rarefied atmosphere causes constant vaporization of the gas, suggesting a continuous source, which could potentially be attributed to living organisms within the planet.
Jupiter lacks distinct seasons. The most intriguing phenomenon is the Great Red Spot, a feature on the planet’s surface that remains largely unexplained. Scientists speculate that it is a massive hurricane that has been rotating at high speeds for several centuries.
Did you know that Uranus, just like many other planets in our solar system, has its very own ring system? Interestingly, these rings were not immediately discovered after the planet itself due to the poor light reflection of the particles that compose them.
One fascinating characteristic of Neptune is its deep blue color, which is why it was named after the ancient Roman god of the seas. Because of its remote location, it was one of the last planets to be found. However, its position was actually calculated mathematically, and over time it was observed exactly where it was predicted to be.
Here’s an intriguing fact: it takes approximately 8 minutes for light from the Sun to travel all the way to the surface of our planet.
Despite years of careful study, the solar system still holds many enigmas and undisclosed secrets. One of the most intriguing theories revolves around the existence of extraterrestrial life on other planets, which is currently being actively pursued.
The vast expanse above our heads has always mesmerized humanity and naturally piques the interest of children as well. In the second grade, students delve into the topic of “Planets of the solar system. Stars and constellations” during their lessons on the world around them.
The solar system may be a mere speck in the vast galaxy, but its planets remain partially uncharted territory.
Thanks to cutting-edge technology, scientists can now gather data on celestial bodies situated far away from Earth and the Sun, thus advancing our understanding. The exploration of space is an ongoing journey, with each day bringing new discoveries.
According to the prevailing theory, around 4.5 billion years ago, the current arrangement of planets in our solar system came into existence due to the cataclysmic explosion of one or more stars. At that time, our solar system was comprised of a dense cloud of gas and dust. However, over the course of time, this cloud gradually collapsed under its own gravitational pull, giving rise to the formation of the Sun and the other celestial bodies that make up our planetary system.
Solar system – A collection of planets that revolve around a luminous star, known as the Sun.
The solar system is comprised of 8 recognized planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) as well as 5 dwarf planets that orbit in a similar plane. Based on their physical characteristics, the planets are classified into the terrestrial group and the gas giant planets.
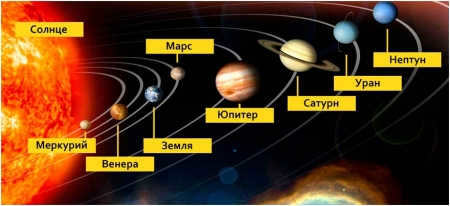
Planetary arrangement within the solar system
The initial four planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars – fall into the category of Earth-group planets, also referred to as terrestrial planets. They share many similarities, including their relatively small size and mass, as well as their chemical and mineral composition. These planets possess a limited number of satellites, with Earth having just one and Mars having two, while Mercury and Venus lack any satellites altogether.
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are identified as gas giant planets. These immense celestial bodies are primarily comprised of hydrogen and helium, enclosed by delicate rings, and possess numerous satellites.
Pluto was part of the solar system as the 9th planet until 2006. However, due to its significant distance from the Sun and small size, it was removed from the list of planets. It is now classified as one of several dwarf planets.
The Sun is the main star
The Sun, a massive ball of gas, serves as the primary source of heat and light in the solar system. While the planets themselves do not produce their own light, they reflect the radiant energy emitted by the Sun.
With a surface temperature exceeding 5,700°C, the Sun’s distance from the Earth is fortunate, preventing everything from burning up. If the Sun were even farther away, all life on our planet would succumb to freezing temperatures.
Life exists on Earth because of the abundance of sunlight and heat. The Sun’s activity fluctuates in cycles of approximately 11 years, either increasing or weakening. Due to the extreme temperatures, it is challenging to study the Sun’s surface, but scientists are working on launching a specialized device to overcome this obstacle.
The Sun is enormous, about 110 times the size of Earth, with a mass 1000 times greater than all the planets combined. The exact number of similar suns in the universe remains a mystery, as astronomers continue to explore the cosmos without finding a definitive answer.
Each planet in our solar system orbits the Sun at varying distances and also rotates on its own axis. This rotation is responsible for the changing seasons and the progression of time throughout the day. In a complete revolution around the Sun, Earth takes 365 days, while it completes one full rotation on its axis in 24 hours. The duration of a planet’s year depends on its distance from the Sun, resulting in varying lengths of time for each planet’s orbital journey.
The Earth: a planet that belongs to a group in the solar system

The group of planets that includes Earth is part of the solar system.
The planet closest to the Sun is called Mercury
Mercury is named after the ancient Roman god Mercury, who was associated with trade, cunning, travel, and theft. It is fitting that this small, fast-moving planet bears the name of such a deity. Mercury completes an orbit around the Sun in just 88 days, making it the planet with the shortest year.
Mercury also has the longest day among all the planets, lasting approximately 59 Earth days. This long day contributes to extreme temperature changes on the planet’s surface, with temperatures reaching about +485°C during the day and dropping to as low as -190°C at night. The stark contrast in temperature is due to one side of the planet being intensely heated while the other side has already cooled down.
Mercury, which is smaller than Earth by a factor of 2, is the tiniest among all the planets. Due to its lack of atmosphere, sustaining life on Mercury is impossible. The surface of the planet is covered with meteorite craters and rocks. The first image of Mercury was captured in 1974. In ancient times, observing Mercury was challenging as it was often concealed by the Sun’s rays, earning it the reputation of being an elusive planet.
Mercury can only be observed early in the morning before sunrise or in the evening after sunset. The planet undergoes significant changes in appearance, ranging from a thin sickle to a complete circle. Additionally, Mercury does not have any natural satellites.
Venus, the second planet
Venus is named after the ancient Roman goddess of beauty and love. In ancient times, it was referred to as the “morning” and “evening star” due to its radiant brightness. It can be observed with the naked eye as it appears just before sunrise, when other celestial bodies are no longer visible, and remains visible after sunset, when other cosmic objects have yet to become visible.
Venus is often referred to as Earth’s “twin” due to its similar size and mass. However, the similarities end there. The surface temperature reaches + 450°C degrees (making it the hottest planet), and it is surrounded by a dense atmosphere composed of carbon dioxide clouds that trap heat.
On the dark side of Venus, the temperature drops to approximately -20°C as the sun’s rays are unable to reach this area for an extended period of time. The surface of Venus is composed of mountains and plains, with frequent volcanic eruptions occurring. Due to the intense atmospheric pressure, exploring the planet is challenging, and no research vehicle can remain on Venus for more than two hours.
Venus is known for being one of the slowest planets in our solar system. A day on Venus lasts longer than any other planet, lasting approximately 243 Earth days. In contrast, a year on Venus is slightly shorter than a day, lasting approximately 225 Earth days. Additionally, Venus does not have any natural satellites. Unlike all the other planets in our solar system, Venus rotates in a clockwise direction.
Earth, the third planet from the sun, is our home planet.
Earth is known by various names, but it is interesting to note that it does not have a specific god name, unlike other celestial bodies. This may be because ancient civilizations believed that Earth was the center of the universe and the only planet with life on it. The name itself comes from the Anglo-Saxon term “of the soil” or “dry land”, highlighting its connection to the ground.
Earth is a unique planet in our solar system due to its abundance of water. In fact, approximately 70% of Earth’s surface is covered in water, which gives it a distinct blue appearance when viewed from space.
In addition to water, Earth is also composed of continents, which make up the remaining portion of its surface. Water on Earth exists in three states: liquid, solid (ice), and gas (water vapor). This diversity of states is due to the varying temperatures and conditions present on our planet.
Another fascinating aspect of Earth is its axial tilt, which is responsible for the changing seasons. As Earth orbits the sun, its axis is tilted, resulting in different amounts of sunlight reaching different parts of the planet throughout the year.
Finally, it is worth mentioning that a year on Earth lasts approximately 365 days, while a day is composed of 24 hours. These measurements are the basis for our calendar and timekeeping systems, allowing us to organize and understand the passage of time.
The composition of the Earth’s atmosphere is made up of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% carbon dioxide and other gases. The atmosphere’s ozone layer is responsible for absorbing solar radiation. Oxygen is synthesized by plants on Earth through the process of converting carbon dioxide. The presence of these plants is crucial, as without them, our planet would resemble Venus.
In addition to the Earth, there is one natural satellite orbiting it known as the Moon. The Moon’s gravitational force has an impact on the Earth’s bodies of water, resulting in the occurrence of tides. The Moon’s rotation is in sync with its orbit around the Earth, which means that only one side of the Moon is visible from Earth. Earth is a planet within the solar system that possesses unique conditions that have allowed for the development of life.
Mars is the fourth planet in the solar system.
Mars got its name from the god of war, as it has a distinctive red color due to its high iron content that oxidizes. In terms of size, Mars is about half the size of Earth. Scientists have discovered the presence of water on Mars, leading to the speculation that there might be life on the planet.
However, Mars lacks a magnetic field to shield it from solar wind, causing its atmosphere to escape. The planet is often plagued by dust storms and whirlwinds. Mars is known for its cold temperatures, with daytime averages not exceeding -5 ºC and nighttime temperatures dropping to -87 ºC.
The belief in life on Mars has been debunked. Nonetheless, Mars is considered the most promising planet for exploration, as its weather conditions are relatively suitable for human exploration.
Mars possesses towering mountains and deep cavities, valleys, massive volcanoes, and polar ice caps. Similar to Earth, Mars experiences seasonal variations, with temperatures reaching up to 20 degrees during the warm period and dropping as low as 90 degrees during the cold period. The Martian year lasts 687 days, which is twice as long as an Earth year, while a Martian day is only slightly longer than an Earth day, lasting 24 hours and 37 minutes.
Mars is orbited by two satellites named Deimos and Phobos, which are irregularly-shaped rocky bodies. In Latin, Deimos means “Fear” and Phobos means “Terror”.

The gas giants planets of our solar system.
Jupiter, the fifth planet.
Jupiter was named after the ruler of the Roman gods. Throughout history, humans have observed it in the sky and associated it with the most powerful deities. Jupiter is the second brightest object after Venus. It is also known as the “king of the heavens”. This gas giant is the largest planet in our solar system.
Jupiter has a mass that is twice the combined mass of all other planets, moons, comets, and asteroids in our solar system. It is 318 times larger than Earth. The planet rotates incredibly fast, completing one rotation on its axis in just 9 hours and 55 minutes. This is the shortest day, while a year on Jupiter lasts for 12 Earth years. The temperature on the planet reaches as low as -160 °C degrees.
Strong winds constantly blow on Jupiter at a speed of 160 m/s, creating storms, hurricanes, and tempests. These whirlwinds are clearly visible in the planet’s photos taken by space instruments, resulting in alternating dark and light stripes that constantly change in color and shape.
Jupiter’s atmosphere is composed of 75% hydrogen and 24% helium. The planet’s structure remains a mystery to scientists as it is impossible to land any equipment on its surface. Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field extends throughout its system, even reaching Saturn’s orbit.
This is one of the reasons why Jupiter has a vast number of satellites. Currently, more than 70 satellites are known to orbit Jupiter. The largest satellites are Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
Saturn is the sixth planet in the solar system.
Saturn was first observed by Galileo in the early 17th century, making it the second largest gas giant in our solar system. It was given its name after the Roman fertility god and is also known as the “lord of the rings”. The planet boasts a system of 7 rings, composed of countless fragments of rock, dust, and ice, which orbit around it at a speed of 10 km/s.
Scientists believe that these rings are remnants of a shattered moon that fell victim to Saturn’s strong gravitational pull. Known since ancient times, Saturn is one of the most prominent celestial objects visible in our night sky.
A year on Saturn lasts nearly 30 Earth years, while a day on the planet is only 10 hours and 33 minutes long. The average surface temperature is a bone-chilling -180°C. Saturn is orbited by more than 60 satellites, with the largest one being Titan, which boasts an atmosphere similar to that of Earth.
Saturn’s atmosphere is predominantly made up of hydrogen (96%) and helium (4%), with trace amounts of other gases. On the surface of Saturn, there are powerful winds blowing at speeds of 500 m/s. These winds, combined with the heat from the planet’s hot core, create the yellow and golden streaks that can be seen in its atmosphere. Saturn also experiences northern lights. Despite being known for centuries, Saturn remains one of the least explored planets in our solar system.
The seventh planet in our solar system is Uranus
On a clear night, Uranus can be observed with the naked eye and was first discovered in 1781. In order to maintain tradition, Uranus was named after the ancient Greek god of the sky, rather than the Roman counterpart. Uranus is often referred to as the blue planet, much like Earth. Its atmosphere is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, with a small amount of methane, which gives the planet its distinctive blue-green color.
The gas giant Uranus is known for being the smallest among its kind. It boasts an impressive collection of 27 satellites and 13 rings, with the largest satellites being Oberon, Titania, Ariel, Miranda, and Umbriel.
Uranus takes a staggering 84 Earth years to complete one orbit around the Sun, while a day on Uranus lasts for 17 Earth hours. One of the most fascinating aspects of Uranus is its extreme tilt of 97 degrees, causing the planet to appear to rotate on its side. This unique characteristic results in seasons that change once every 42 years, with 42 years of summer and sunshine followed by 42 years of prolonged polar night.
Considered the coldest planet in our solar system, Uranus is situated about 20 times farther from the Sun than Earth. Its surface temperature can reach a bone-chilling -218 degrees Celsius. Due to these frigid conditions, Uranus is often referred to as the “ice giant.” In terms of mass, Uranus is nearly 15 times heavier than Earth, making it the fourth most massive planet in our solar system.
Neptune, the eighth planet in our solar system, is another remarkable gas giant worth exploring.
Neptune is a frigid gaseous planet with a set of 5 pale rings orbiting around it. The wind speeds on this celestial body can reach up to an astounding 600 meters per second, while the temperature plunges to a bone-chilling -220°C. The uppermost layer of Neptune’s atmosphere mainly consists of hydrogen (80%), helium (19%), and a minuscule amount of methane (1%). The planet’s mesmerizing blue hue is a result of the plentiful presence of methane. A full rotation of Neptune takes approximately 17 hours to complete, whereas a single orbit around the Sun is equivalent to a staggering 165 Earth years.
Moreover, Neptune possesses a total of 14 natural satellites, with the largest ones being Triton and Nereid. The tilt of Neptune’s axis bears a striking resemblance to that of our own planet Earth, measuring at a close 28°C.
Dwarf planets in the Solar System
In 2006, after the discovery of celestial bodies larger than Pluto, scientists faced the task of categorizing these newly found objects. They decided to assign them the term “dwarf planets.”
There are currently 5 known dwarf planets in our Solar System: Pluto, Ceres, Makemake, Eris, and Haumea. Dwarf planets stand apart from terrestrial planets and gas giants due to their small size, distance from the Sun, and the presence of an icy surface layer.

Dwarf planets are an interesting feature of our solar system. One of the most well-known dwarf planets is Pluto, which was first discovered in 1930. With a diameter of approximately 2,377 kilometers, it is smaller than our Moon. Unlike other planets, Pluto has its own atmosphere, ice polar caps, and even satellites. However, in 2006, Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet, losing its previous planet status.
Another notable dwarf planet is Erida, which was discovered in 2005. With a diameter of around 2,326 kilometers, it is smaller than Pluto. Erida is located beyond the orbit of Neptune and has a satellite named Dysnomia.
Makemake is an astronomical object classified as a dwarf planet. Discovered in 2005, it has a size of approximately 1,430 kilometers. Makemake is located in the Kuiper Belt, a region beyond Neptune’s orbit where various dwarf planets and other celestial bodies are found.
Haumea is another dwarf planet, which was first detected in 2004. It has a diameter of about 1,600 kilometers. Haumea also resides beyond Neptune’s orbit and has a distinct elongated shape, resembling a loaf of bread.
Gaumea is a third dwarf planet, also discovered in 2004. It has a diameter of around 1,011 kilometers. Similar to Haumea, Gaumea is located beyond Neptune’s orbit and has a spherical shape, resembling a soccer ball.
Dwarf planets do not possess a gravitational field, resulting in a constant presence of small celestial bodies within their orbit. Due to their considerable distance from Earth, dwarf planets remain relatively unexplored and poorly understood.
Within the vast expanse of the solar system lie countless enigmas and hidden truths, yet humanity finds itself merely at the inception of its quest to explore space and diligently seek out extraterrestrial life.
Slide 3
The Sun is significantly larger than any planet in our solar system. It is an average star, a luminous sphere of gas that emits its own light as a result of its high surface temperature. In terms of size, the Sun is extremely vast, with a radius 109 times greater and a mass 330,000 times greater than that of Earth. Unlike the planets, which derive their shine from reflected sunlight, the Sun shines on its own. The planets are positioned in the following order relative to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, and Jupiter.

Slide 4
Mercury, also known as the closest planet to the Sun, holds the title for being the smallest planet in our solar system, excluding Pluto. Its orbit around the Sun is completed in just 88 days. The surface of Mercury is incredibly hot, reaching temperatures that can melt tin and lead. With barely any atmosphere to speak of, its solid ground is marked by numerous craters. In ancient Roman culture, Mercury was revered as the patron saint of trade and travelers.

Slide 5
Venus, the second planet from the sun and one of the terrestrial group planets, has a unique atmosphere and surface. Its atmosphere is filled with dense layers of clouds, primarily composed of carbon dioxide, a heavy metal substance that traps the planet’s heat. The surface of Venus is characterized by numerous volcanoes, including some very large ones that reach heights of 3 kilometers and stretch up to 500 kilometers wide. Venus comes close to Earth in terms of its characteristics and planetary features.

Slide 6
The planet known as Earth is positioned as the third celestial body in our solar system, revolving around the Sun. When seen from outer space, Earth displays a vibrant blue hue, which is a result of the surrounding atmosphere rich in oxygen and the massive bodies of water, constituting more than two-thirds of its surface. Approximately 4.7 billion years ago, Earth was created from a cloud of gas and dust that was also responsible for the birth of our Sun. Earth is accompanied by a natural satellite called the Moon. As the Earth spins on its axis, different regions of the planet are alternatively exposed to sunlight, resulting in the occurrence of day and night.

Slide 7
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and is known for its distinctive red color, which earned it the name of the god of war in ancient times. The atmosphere of Mars primarily consists of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, with small amounts of water vapor, oxygen, and argon. However, the low surface pressure on Mars prevents the existence of liquid water. The climate on Mars can be described as a cold and dry highland desert.

Slide 8
Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system, is located fifth from the sun. Unlike solid planets, Jupiter is not made up of a single material. Its name was inspired by the king of the Roman gods, and it is known to have 28 satellites. Among these satellites, four of them, namely Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto, were discovered in 1610 by the Italian scientist Galileo. These four satellites stand out due to their significant size and mass. Additionally, Jupiter has 20 outer satellites that are situated at such a great distance from the planet that they cannot be seen from its surface.

Slide 9
Saturn is the sixth planet orbiting the Sun and boasts a remarkable system of rings. This celestial body has been recognized since ancient times and stands out as one of the most luminous objects in our night sky. The composition of Saturn’s atmosphere consists mainly of hydrogen and helium, while its winds are characterized by great strength. Encircling the planet, Saturn’s rings consist of numerous small solid fragments of rock and ice, forming a width of 400,000 kilometers and varying in thickness.

Slide 10
Uranus, also known as the seventh planet from the sun, is often referred to as the blue planet due to its resemblance to Earth. In ancient Greek mythology, Uranus was a celestial deity and the father of Kronos (Saturn), the Cyclopes, and the Titans. Interestingly, Uranus was actually discovered by accident, as it had been previously observed but mistaken for a star. The atmosphere of Uranus is composed of hydrogen, helium, and methane, which gives the planet its distinct blue color. Additionally, Uranus possesses rings that, although faint, are similar to those of Saturn.

Slide 11
Neptune is the fourth largest planet in our solar system and is located eighth from the Sun. Similar to Earth and Uranus, Neptune has a distinctive blue color due to the presence of methane in its atmosphere. This fascinating planet has a total of 8 satellites, with Triton being the largest among them. On the surface of Triton, you can find various geological features such as rocks, craters, and dark volcanic bands. The average distance from the Sun to Neptune is approximately 4.5 billion kilometers.

Slide 12
The complete content of the material Presentation “Planets of the solar system”; 2 class can be found in the downloadable file.
This page contains a portion of the content.
Thank you for your assessment. If you wish for the author to know your name,
please log in as a user
and click Thank you once more. Your name will be displayed on this page.

Do you have any thoughts on this? Feel free to share your comment.
What are the options for payment for ZOOM from Russia in 2023? How can we pay for other international services that are currently unavailable due to “sanctions”?
Practice your reading skills and improve your reading comprehension with these exercises
The intricacies and concealed techniques of operating in Yandex.Mail
How to effectively engage with children who have ADHD in a conventional classroom?
Testimonials
Elena Egorova 5.0
I would like to express my immense gratitude on behalf of the primary school educators at Pushchino gymnasium to the skilled programmers responsible for developing this remarkable software! What we used to handle manually can now be organized in a structured manner and receive individual student analysis and class reports. This is absolutely fantastic and brings us immense joy! We immediately recognized the advantages and will actively utilize it starting from the upcoming academic year. At the moment, we have no requests, only gratitude. The instructions provided are very straightforward and easy to understand, which is crucial! Many thanks to you and your colleagues for this invaluable work. It is truly heartwarming when fellow educators comprehend how to streamline the tasks of a teacher.
Nagovitsina Olga Vitalyevna 5.0
Chemistry and Biology Teacher at Chapaevka Village School, Novoorsky Raion, Orenburg Oblast
Review of Sha Template Excel Template Analyzer results for OGE Chemistry
Thank you for the excellent analytical report on OGE chemistry and biology. The analytical work was greatly simplified and helped identify areas needing improvement for the exam. As a teacher with a heavy workload, your template has saved me a lot of time. I have also shared your template with my colleagues and they have found it very useful. Thank you.
Alexandra Chazova 5.0
This template is fantastic and easy to use. It only took me a few minutes to analyze a practice test. I did encounter some issues when printing the report, but I will figure it out. Thank you for providing such a high-quality analyzer.
Tatyana Loseeva 5.0
Thank you so much for the timely issuance of certificates! Everything looks absolutely amazing. My student is thrilled and has already added his certificate to his portfolio. We will definitely continue our collaboration with you!
Yazenina Olga Anatolievna 4.0
Teacher of elementary grades, OGBOU “Center of Education for Children with Special Educational Needs of Smolensk”.
Review of the Webinar: How to create an engaging lesson:
Tools and techniques
I attended the webinar and I was extremely pleased with the valuable information I received. The presentation was concise and to the point. Everything that was discussed and demonstrated is highly applicable to any teacher’s practice. I will definitely make use of the valuable materials provided in the webinar. Thank you to the presenter for sharing her expertise!
Arapkhanova Ashat 5.0
Thank you so much for your assistance. I greatly appreciate it. I quickly figured everything out and found it to be very organized and efficient. There is absolutely no flaw in it. I am extremely satisfied with my decision to trust and purchase this report card from you. Thanks to your help, I was able to save time and now I am able to prepare the time sheets for my employees. I wish you all the best and continued success in the future!
Dambaa Aisuu 5.0
Thank you very much, it saves a lot of time because the analysis is already prepared. I am particularly pleased that there are options available with an essay, without an essay, and just the analysis of the essay! This is excellent!
2007-2023 “Pedagogical Community of Ekaterina Pashkova – PEDSOVET.SU”.
12+ Certificate of Media Registration: El No. FS77-41726 of 20.08.2010. Issued by the Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Media.
Located at: 603111, Nizhny Novgorod, 15-45 Raevskogo Street.
Founder’s address: 15-45 Raevskogo Street, Nizhny Novgorod, 603111.
Founder and Editor-in-Chief: Ekaterina Pashkova
Contact us at: +7-920-0-777-397, [email protected]
Visit our website: https://pedsovet.su/
Copying any materials from the site is strictly prohibited and will be closely monitored and prosecuted.
When material is submitted to the site, the author agrees to transfer the rights to use the material to the editorial office. These rights include both commercial and non-commercial purposes, such as reproduction, public display, translation, and revision of the work. The material can also be made available to the public, all in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Art. 1270, etc.). Please refer to the Rules of Publication for specific types of material. It is important to note that the opinions of the editorial board may differ from those of the authors.
If you need to verify the authenticity of any documents issued by the site, please contact the editorial office for assistance.
- Publish a lesson
- Publish an article
- Make an announcement
- Subscribe to news
- Find answers to Frequently Asked Questions
webinar service –>