The vast expanse of the universe is home to countless unique living beings, each with its own distinct internal and external characteristics. From their intricate body structures to their physical appearances, every being is truly one-of-a-kind. This uniqueness extends to the planets that inhabit the universe, as each one possesses its own special qualities and meanings.
Within the vastness of the universe, the majority of living creatures reside on massive celestial bodies known as planets. These planets vary greatly in their structures, masses, sizes, internal compositions, and overall characteristics. Among them, there is one planet that stands out as the farthest from the Sun. So, what is the name of this planet, and how does it differ from the rest? Let’s delve into the details to find out.
Our planet

Humans and other organisms residing near us inhabit a galaxy known as the solar system. It acquired this name due to its central star, the Sun, which serves as the source of life.
Our galaxy came into existence approximately 4.5 billion years ago through gravitational contraction. In terms of the vast universe, we inhabit a relatively young formation compared to the rest of the known cosmos.
The solar system consists of a limited number of celestial bodies. All of the planets that are presently recognized were discovered prior to the onset of the 20th century.
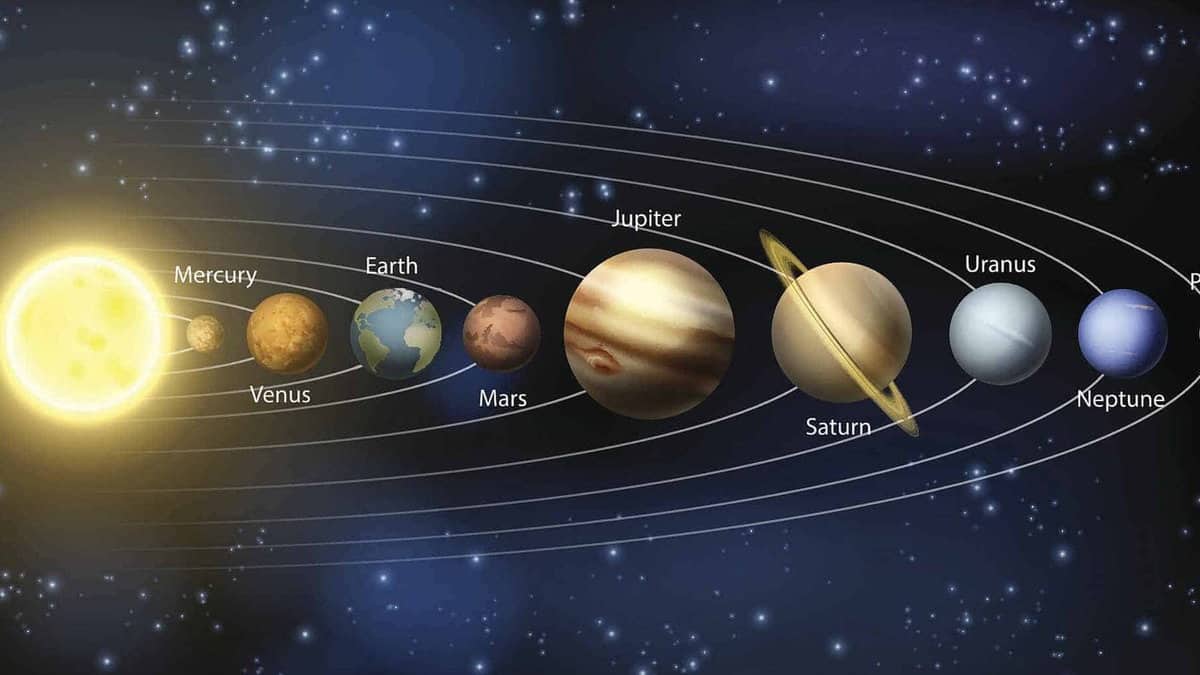
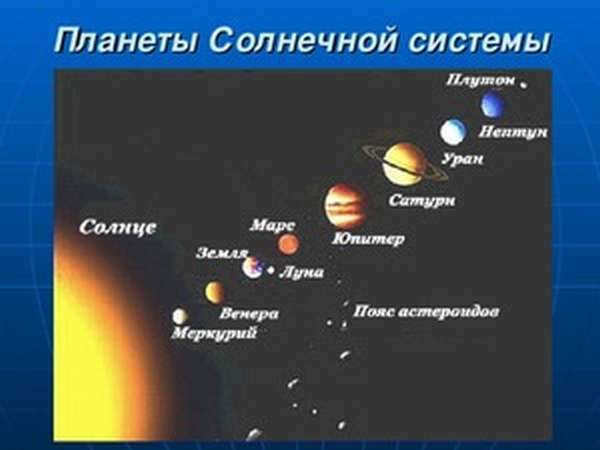
Scientific communities have officially acknowledged the existence of eight celestial bodies positioned at varying distances from the Sun:
- Mercury,
- Venus,
- The planet Earth
- The planet Mars
- The planet Jupiter
- The planet Saturn
- The planet Uranus
- The planet Neptune
Context

Previously, it was believed that Pluto was the most remote celestial object in our galaxy. American astronomer Clyde Tombaugh discovered it in the early 20th century, which earned him recognition from the Royal Astronomical Society of London.
Pluto is a unique cosmic body with an elliptical orbit, which means that it is closer to the Sun than Neptune (hence why it temporarily lost its planet status from 1979 to 1999 when it was inside the orbit of the eighth planet). It is located 7 billion kilometers away from the main star.
Fascinating! Recent astronomical discoveries have provided evidence that Pluto exists within the Kuiper belt, lying a staggering 6,000,000,000,000,000 kilometers away from our planet. It can be confidently stated that Pluto holds the title for being the most distant celestial body from Earth.
The attributes of this cosmic entity are as follows:
- The body has a diameter of 2,300 kilometers.
- Its mass accounts for a mere 0.22% of its Earth equivalent.
- It completes an orbit around the yellow star in a span of 248 years.
- A single day on Pluto lasts for a standard 6.5 Earth days.
- The planetary temperature measures at 223° Celsius.
Read also: Wildlife in Africa: predators and strategies for hunting, exploring the realm of wildlife and rare animal species

Pluto is a rather unique celestial object. On one side, its surface is covered in an everlasting layer of ice, while on the other side it is composed of rocky terrain. Due to the minimal heat provided by the galactic star, it is constantly dark on Pluto, several thousand times colder than Earth.
Pluto’s atmosphere primarily consists of nitrogen, and recent astronomical findings have confirmed that it is gradually evaporating into the vastness of space (similar to what has occurred on our own planet). The surface of Pluto is marked with numerous craters, possibly indicating frequent collisions with other celestial bodies.
Pluto has a total of five moons:
The largest moon is Charon, which shares a similar orbit with Pluto (leading some scientists to consider them a binary system of planets).
Following a lengthy and intense discussion, Pluto has been dethroned as the most distant planet from the Sun. This momentous event occurred in the year 2006, marking a significant turning point in our understanding of the solar system. From that point forward, Pluto was classified as a dwarf planet, relinquishing its status as the final planet in our cosmic neighborhood.
Group of Earth
The group of Earth encompasses celestial entities that bear a striking resemblance to our own planet in terms of their composition and structure. Within this category, we find:

If we examine various cosmogonic hypotheses, we can observe that terrestrial planets with solid surfaces are situated in the inner region of the galaxy, while gas giants are found in the outer region. This is a distinguishing feature of celestial bodies resembling Earth.
- They possess a central metal core.
- They have a silicate mantle.
- They exhibit a solid surface.
Mars is recognized as the farthest planet from the Sun within the Earth group.
Description of Neptune
Following Pluto’s demotion as the most distant planet from the Sun, Neptune took its place as the farthest planet. Named after the god of the seas due to its striking blue hue, Neptune was first observed and described during the Galilean era. However, Galileo mistakenly believed it to be a stationary star, thus missing out on the credit of its discovery.
The distant planet was officially discovered in 1846. However, this was not the result of typical sky observations, but rather a breakthrough in mathematical calculations.
This remarkable achievement was made possible by the French mathematician Urbain Leverrier, who, along with German astronomers Johannes Galle and Heinrich d’Arré, successfully located the elusive celestial body in the vastness of the heavens.
What do we know about Neptune? First and foremost, it is an immense gas planet situated in the outer reaches of our galaxy. This cosmic wanderer is composed primarily of icy substances, containing only a small percentage of hydrogen and helium (approximately 20 percent).
The most distant planet in our solar system receives a significantly lower amount of heat and light compared to Earth, approximately 900 times less. As a result, this gas giant is constantly enveloped in darkness. Powerful storms continuously sweep across the planet, with wind speeds reaching up to 400 meters per second. It is situated a staggering distance of 5,000,000,000,000,000 kilometers away from our planet.
Distinctive features of this celestial body:
- The diameter of this giant is approximately four times larger than that of Earth, and its mass is 17 times greater.
- It possesses a density 1.5 times that of water.
- The temperature on this planet can plummet to minus 214 degrees Celsius.
- Thanks to its rapid rotation on its axis, Neptune experiences shorter days compared to Earth, lasting only 16.11 hours.
- This planet takes 164 years to complete one revolution around its yellow star.
- Additionally, each season on Neptune lasts as long as 40 Earth years.
- Neptune is orbited by a total of 14 satellites, each following a different trajectory. To better categorize them, they have been divided into the following types:
- Outer satellites (yet to be given official names)
- Inner satellites (including Proteus, Larissa, Naiada, Despina, Galatea, and Talasa)
- Individual satellites (Triton and Nereida)
Important! Triton is the largest satellite, with a diameter of 3000 km. Its surface is completely icy and it completes a revolution around Neptune in six Earth days.
Useful video
Summarizing the Question of the Farthest Planet from the Sun
In today’s discussion, we are confronted with the query regarding the planet that lies at the greatest distance from our Sun. Unquestionably, the answer is Neptune. While present-day technology does not yet permit us to dispatch a colonization fleet to Neptune, or indeed any other celestial body, for comprehensive investigation, it is crucial to bear in mind that the human race never ceases its progress. It is only a matter of time until we break free from the confines of our galaxy.

It is located at a distance of approximately 25,000 light years from our position.
Scientists hypothesize that there is a vast quantity of planets similar to Earth in our galaxy, but their detection presents a significant challenge. Currently, only around one-third of the over 4,000 exoplanets that have been discovered and confirmed are rocky in nature, with the majority of them being situated within a few thousand light-years of Earth.
However, the recently found rocky exoplanet is positioned at a distance of 24,722.65 light-years, making it the farthest known exoplanet within the Milky Way galaxy.
Interestingly, this exoplanet was not detected using the conventional transit method, which involves the planet passing in front of a star and causing a decrease in its brightness. Instead, it was identified using the gravitational microlensing technique, which relies on the predictions of the general theory of relativity.
Imagine a scenario where there are two stars positioned one after the other, as observed from our perspective. Gravitational microlensing occurs when the gravitational field of the star that is closer to us acts like a lens, magnifying the light from the star that is further away. If the nearby star has a planet, the planet’s own gravitational field can also contribute to the lensing effect. This method is particularly effective in detecting planets that are located between Earth and the center of the galaxy, as the galactic center is rich in background stars.
“To understand how rare this detection is, it is worth noting that it took approximately five days to observe the magnification associated with the host star, whereas the planet was only detected during a brief five-hour distortion,” said Antonio Herrera Martin, an astronomer at the University of Canterbury in New Zealand.
Once the scientists confirmed that the distortion was indeed caused by a different celestial body and not an error in the instruments, they proceeded to analyze the star-planet system, known as OGLE-2018-BLG-0677.
It has been discovered by researchers that the exoplanet in question is a super-Earth, with a mass 3.96 times that of our own planet. This finding is significant as it is one of the lightest exoplanets ever detected using gravitational microlensing. The star that the exoplanet orbits has a mass of only 0.12 solar masses. Scientists have not yet determined whether it is a low-mass star or a brown dwarf.
The distance between the exoplanet and its star ranges from 0.63 to 0.72 astronomical units. It takes the exoplanet 617 Earth days to complete one orbit around its host star.
In order to assess the potential habitability of an exoplanet, scientists require knowledge of the star’s temperature and activity level. However, due to its considerable distance and diminutive size, even state-of-the-art instruments are unable to analyze its spectrum.

14.9K posts 45.3K subscribers
Community Guidelines
What regulations can exist here, besides the regulations established by the peekaboo itself 🙂
4 hours, 0 comments, I am unsure what to write. Cool, what. Hallelujah and all that.
It is unfortunate that in the near future we will not witness travel beyond Mars, and according to some, never at all. We need to invent teleportation.)
You journey to it and realize that only the offspring of offspring, and so on, will inhabit it. You arrive. And there is already a five. Well, and if not joking, it would be unfortunate if when you arrive it turns out that it is no longer sustainable for human life.
Aha, and no “Hubble or photoshop” images for added credibility))))))
I am telling you the truth, it is Nibiru.

The Milky Way Galaxy

10 photos, shutter speed 15 sec, ISO 3200
Samsung s20fe
Southern Urals, green zone
The solar system’s most alluring properties.
The Soviet Union launched the first artificial satellite in 1957, which is well-known to us all. Over the years, numerous space agencies, private companies, and research institutes have been establishing their presence in the solar system. The list of frontiers they have conquered is extensive and ever-expanding. While it may appear that there is ample space for everyone in this vast expanse, certain areas of local “real estate” are undeniably more alluring. One such example is the Lagrange points, which capture the attention of all interested parties. These points, named after a mathematician from the 18th century who determined their location, possess immense value as rare havens of stability within our chaotic and ever-evolving cosmic corner.
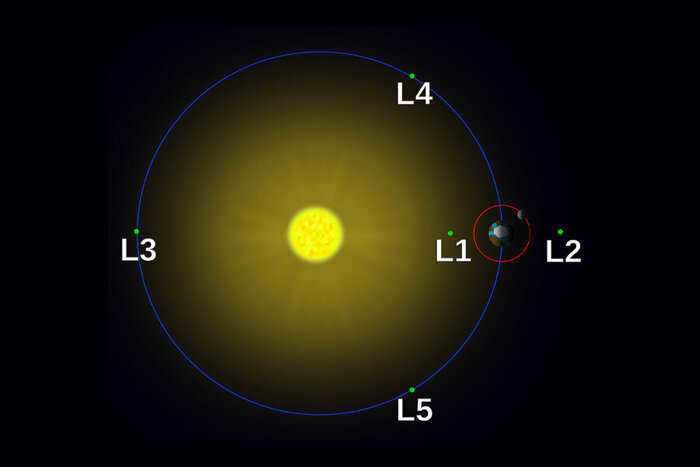
Every celestial object has an influence on each other due to gravity. This influence is particularly noticeable on objects that are close by. In these systems, there are other forces at play that determine the shape of the orbits of the objects in motion. At the Lagrangian points, these forces are perfectly balanced. Therefore, if a small object is placed at one of these points, it will maintain a constant distance from the larger bodies, creating stable areas known as cosmic parking lots. Once an object is in one of these zones, there is no need to expend energy to stay there. This makes it an ideal location for any man-made object intended for long-term space habitation.
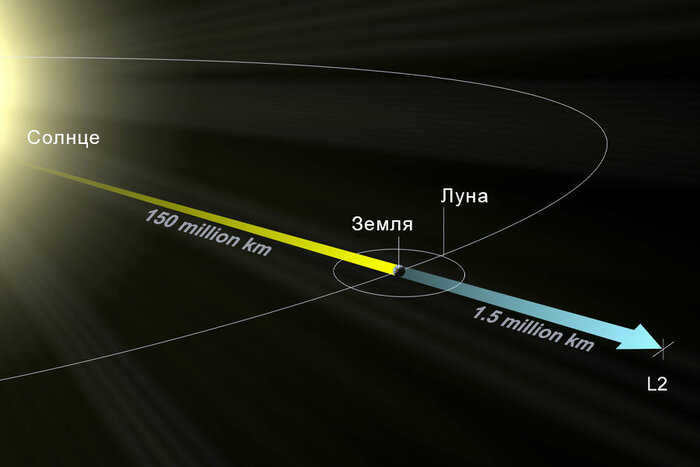
The issue of what can be placed in a specific Lagrange point is quite fascinating. Let’s examine the ones formed by the gravitational interaction between the Sun and Earth. L1 is positioned approximately 1.5 million kilometers from our planet, between these two celestial bodies. It serves as an ideal location for observing the Sun since there is never any obstruction to the view of the star.
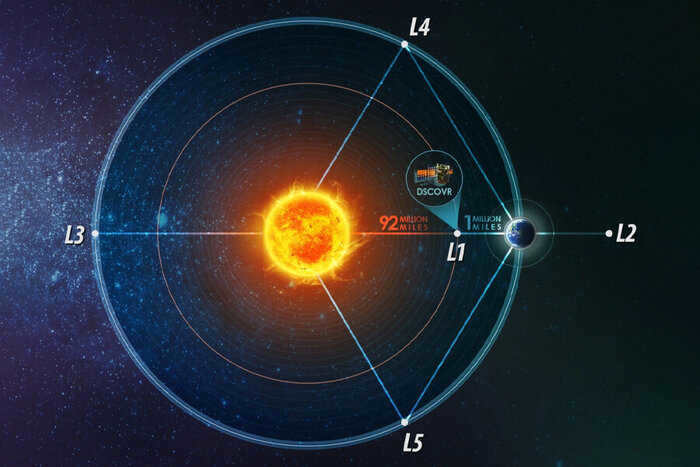
The Deep Space Climate Observatory is an American spacecraft positioned at Lagrangian point 1, which is used for observing the Sun and Earth.
Lagrangian point 2 (L2) is located on the opposite side of the Earth, at the same distance. This strategic position ensures that it is shielded from direct sunlight, offering unique opportunities for observations in the deep cosmos. In 2022, the highly anticipated James Webb telescope, which astronomers have eagerly awaited for two decades, commenced its operations from this vantage point.
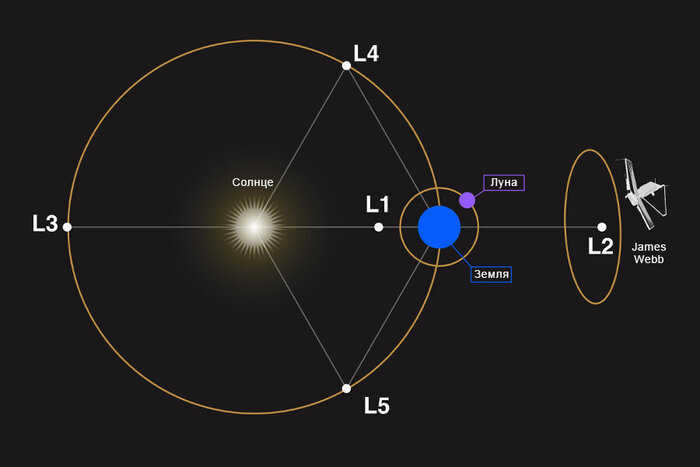
L3, located on the opposite side of Earth’s orbit from the Sun, is a highly enigmatic location. It is the sole point in the entire Universe that remains invisible from the surface of our planet, even in theory. As a result, it has become a popular subject for science fiction authors, although scientists themselves find little practical value in it.
L4 and L5 exhibit some differences compared to the previous Lagrangian points. The key distinction lies in the fact that the first three points in each set of Lagrangian points possess a slight instability, causing the objects within them to gradually shift sideways. While it is possible to maintain objects in these points if desired, it does require additional effort. In certain celestial body pairings, the stability of L4 and L5 may not be particularly high. For instance, if the masses of the bodies differ by less than a factor of 25. However, in the case of the Sun-Earth system, where the star is significantly heavier than the planet, these points exhibit remarkable stability. Furthermore, they appear to attract various objects, with the Sun-Jupiter system’s L4 and L5 points being particularly captivating as they have accumulated thousands of asteroids.
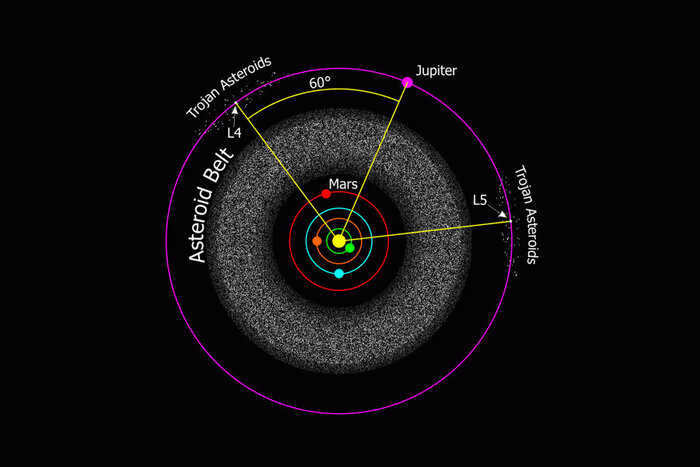
Each Lagrangian point in the solar system has its own unique characteristics. Some of them have the potential to be used for gathering construction materials, if we consider drifting asteroids as such. Others could serve as refueling stations to replenish the fuel for spacecrafts venturing into the vastness of space. It is also conceivable that human colonies could be established in these points. Of course, this is a vision of the distant future, one that we may not witness given the current state of affairs on Earth. However, it is always good to dream, isn’t it?
Thank you for your attention! If you enjoyed the article, you can show your support by giving it a “like” or subscribing to this channel. We would also like to take this opportunity to mention that we have our own Telegram channel where we regularly share fascinating posts about space and astronomy.
We deeply appreciate all of our readers. If you wish to provide financial support (via the button provided below), your name/nickname will be included at the end of our next post. This is our way of expressing our gratitude for your kindness and support!
20 intriguing facts about the most distant planet in our solar system
A visual comparison of the sizes of Neptune and Earth
1. Neptune was first discovered in 1846. It was the initial planet to be identified through mathematical calculations rather than direct observation. [1]
2. With a radius measuring 24,622 kilometers, Neptune is nearly four times larger than Earth. [2]
3. The average distance between Neptune and the Sun is 4.55 billion kilometers. This is equivalent to approximately 30 astronomical units (an astronomical unit refers to the average distance from Earth to the Sun). [2]
4. Neptune is known for having the most powerful winds among all the planets in our solar system. Scientists estimate that these winds can reach speeds of up to 2100 km/h. [1]
5. A Neptunian year, which is the time it takes for Neptune to complete one orbit around the Sun, is equivalent to almost 165 Earth years. [1]
6. Unlike other planets, Neptune does not have a solid surface. Instead, it has a gaseous atmosphere primarily made up of hydrogen, helium, and methane. This atmosphere extends deep into the planet, gradually transitioning into a mantle composed of water, ammonia, and methane ice. Below the mantle is a core made up of rock and ice. [1][2]
7. The blue color of the planet is a result of the methane present in the outer layers of the atmosphere. However, Uranus, which is Neptune’s neighbor, appears blue-green despite having the same amount of methane. This has led scientists to speculate that there may be an unknown component in Neptune’s atmosphere that gives it a bluer hue. [1]
8. Neptune has a total of 14 satellites. Triton, the largest satellite of Neptune, was discovered just 17 days after the discovery of the planet itself. [1]
9. Neptune’s axial tilt is similar to that of Earth’s, resulting in similar seasonal changes on the planet. However, due to Neptune’s significantly longer year compared to Earth’s, each season on Neptune lasts for more than 40 Earth years. [2]
10. Triton, the largest moon of Neptune, possesses its own atmosphere. There is a possibility that beneath its icy shell, a liquid ocean may be concealed. [1]
11. Although Neptune does have rings, they are much less substantial compared to Saturn’s iconic ring system. [1]
12. Voyager 2 is the sole spacecraft that has successfully reached Neptune. Launched in 1977, it was intended to explore the remote planets of our solar system. In 1989, the spacecraft flew within 48,000 kilometers of Neptune, transmitting remarkable images of its surface back to Earth. [3]
13. Due to its elliptical orbit, Pluto (formerly recognized as the ninth planet in our solar system and now classified as a dwarf planet) can sometimes come closer to the Sun than Neptune. [2]
14. The Kuiper belt, located far from Earth, is greatly influenced by Neptune and consists of remnants from the formation of our solar system. Throughout the existence of the solar system, the planet’s gravitational force has caused gaps to form within the belt’s structure. [1]
15. Neptune possesses a significant internal heat source, the exact nature of which remains uncertain. The planet emits 2.6 times more heat into space than it receives from the Sun. [1]
16. Some scientists propose that at a depth of 7,000 kilometers, Neptune experiences conditions that lead to the breakdown of methane into hydrogen and carbon, with the latter subsequently crystallizing into diamond form. This suggests the possibility of a remarkable natural occurrence known as diamond hail within Neptune’s ocean. [1]
17. The temperature in the upper regions of Neptune can reach as low as -221.3 °C. However, as we delve deeper into the layers of gas on the planet, the temperature steadily rises.
18. The images of Neptune captured by Voyager 2 could potentially be the only close-up images we have of the planet for the next few decades. Although NASA had plans to send a Neptune Orbiter in 2016, no official launch date for the spacecraft has been announced yet.
19. Neptune’s core is estimated to have a mass 1.2 times that of the entire Earth. In fact, the total mass of Neptune exceeds that of Earth by a factor of 17.
20. A day on Neptune is equivalent to 16 Earth hours.
Comparison of the sizes of planets in the solar system
1 ru.wikipedia.org
2 solarsystem.nasa.gov
3 ru.wikipedia.org
Rate the article:
Also read us on our channel in Yandex.Zen
Other articles on our website:
Distance from Earth to Venus in kilometers: the smallest and the largest
Drawing of Venus against the Sun
The moment when the planets are at their maximum proximity to one another is referred to as opposition. The distance between the planets can vary even during opposition. The nearest distance from Earth to Venus is 38 million kilometers. And the farthest distance is 261 million kilometers. Although this might seem surprisingly large, it pales in comparison to the distances between other planets. Just try to imagine the vastness of the distance between Earth and Neptune.
The close distance of Venus explains why it is the second most brilliant entity in the nocturnal firmament. With an apparent stellar magnitude of approximately -4.9, it can even vanish altogether from the celestial canvas when it reaches the furthest point in its orbital trajectory from our vantage point.
The apparent stellar magnitude of Venus is also influenced by the reflectivity of its atmosphere, which is predominantly composed of sulfuric acid clouds. These clouds reflect a significant portion of visible light, thereby augmenting the planet’s albedo.
Planetary Transits
Venus periodically crosses the Sun’s disk, which is known as a transit. These transits occur in pairs at intervals of over a century. Throughout history, transits have been observed in 1631, 1639, 1761, 1769, 1874, and 1882. The most recent transits took place on June 8, 2004, and June 6, 2012.
Venus always appears brighter than any star. Its brightness in Earth’s sky is greatest when it is closest to Earth.
It is most easily visible when the Sun is low above the horizon and is always about 47 degrees away from the Sun.
Venus rotates faster than Earth, so it overtakes Earth every 584 days. During this time, it is easier to see Venus in the morning, shortly after sunrise.
comments powered by HyperComments
Enjoyed this post? Share it with your friends!
Which planet is the most distant from Earth?
During my days as a student, I learned in my astronomy classes that Pluto holds the title for being the farthest planet from the sun. However, recent discussions have emerged challenging Pluto’s classification as a planet and suggesting the existence of another planet beyond its orbit. I am not entirely sure about these claims as I have yet to come across any reliable data. 🙂 The distance from Earth, on the other hand, depends on the relative positions of the planets in relation to the sun. It is possible for Neptune to be farther from us than Pluto if it orbits on the opposite side of the sun while Pluto remains on our side. 🙂
Pluto is known to be the farthest planet from the sun.
In the entire solar system, Pluto holds the record for being the most distant planet from Earth.
Neptune is now recognized as the farthest planet from Earth, making it the eighth planet in the solar system. This decision was reached by the III Division of the International Astronomical Union (IAU) during their current general assembly in Prague. The IAU excluded Pluto, which was previously considered the ninth planet for the past 76 years since its discovery in 1930, from the list of “full-fledged” planets in the solar system.
With Pluto no longer being classified as a planet, Neptune now holds that distinction.
A new addition has been made to the solar system with the recent discovery of the tenth planet by astronomers. This latest finding marks the sixth time astronomers have identified a tenth planet in our solar system. Prior to this, Pluto and Neptune held the title of being the ninth or eighth planet, as Pluto’s unique orbit made its classification uncertain. However, with the confirmation of Neptune as the eighth planet, astronomers are now aiming to officially designate Sedna as the new ninth planet in the solar system.
Meet Pluto, the toughest planet, resembling our very own Earth. However, given that Pluto is a staggering 5,899 million kilometers away from us, we cannot definitively assert this claim. It was in the year 1930 when Pluto was first observed, making it the tiniest and lightest planet within our solar system. Its diameter measures a mere 2,400 kilometers (1,491 miles), actually smaller than our very own Moon. Interestingly, Pluto follows an orbit around the Sun that takes on the shape of a flattened circle. Because of this unique trajectory, Pluto currently finds itself closer to the Sun than Neptune. This state of affairs will persist until 1999, at which point Pluto will once again reclaim its status as the farthest planet within our solar system.
Neptune is the eighth and most distant planet in our solar system. It is also the fourth largest in terms of diameter and the third largest in terms of mass. Its mass is 17.2 times that of Earth and its equatorial diameter is 3.9 times that of Earth. The planet was named after the Roman god of the sea. The concept that Pluto is more closely related to asteroids than planets has gained traction among many, although it has not yet been widely accepted. It seemed that the arrangement of planets had finally found harmony, without the need for a “extra” ninth planet. However, the discovery of new dwarf planets continued, and on March 15, 2004, a group of American astronomers led by Michael Brown announced the discovery of the most distant object in the solar system. This object was found to be located 90 times farther from the Sun than Earth and 3 times farther than Pluto, the “most distant” planet at the time. This object, named Sedna after a sea mermaid from Inuit mythology, has a diameter smaller than that of Pluto at about 1,500 km. Sedna’s highly elongated orbit disrupts the harmony of the solar system. It takes 10,500 years for Sedna to complete one revolution around the Sun, and it is no longer considered part of the Kuiper Belt. Sedna is constantly in darkness and experiences extreme cold. Its surface appears intensely red, second only to Mars in terms of “redness.” It is uncertain whether Sedna is alone or if there are other similar objects at such great distances, as telescopes can only detect objects with a similar orbit during a small fraction of their revolution around the Sun. For Sedna, this period lasts about 100 years, after which it moves to a distant region where it cannot be seen by modern telescopes for over 10,000 years.
Another planet with a revolution period of 30,000 years has been recently discovered.
You’re all foolish! Sedna! Apogee = 140 billion kilometers, perigee = 5 billion kilometers.
Which planet is the farthest from Earth?
Scientists from Italy, Russia, and Switzerland have successfully detected a planet in a different galaxy – the Andromeda Nebula. Its distance from Earth is approximately 2.5 million light years.
In our solar system, Pluto used to be considered the farthest planet.
Pluto used to be classified as a planet in the solar system, but it has since lost its planet status, being replaced by Neptune.
Pluto was officially reclassified as not a planet in 2006, so now Neptune holds that position.
As Neptune has become the farthest planet in our solar system, Pluto is now considered a dwarf planet, or specifically a Plutoid.
Neptune is the farthest planet in the solar system, followed by a multitude of dwarf planets.
Pluto lost its status as a planet because Neptune is now recognized as the farthest planet from the sun.
Since Pluto is no longer considered a planet, it is classified as Neptune.
Among Neptune, Saturn, and Venus, which planet is the farthest from Earth?
- Auto and motorcycle
- Motor Sports
- Car Insurance
- Cars
- Service, Maintenance, Tuning
- Service, maintenance and repair
- Choosing a car, motorcycle
- Traffic Police, Training, Licenses
- Registration of auto-motorcycle transactions
- Other auto topics
- Arts and Entertainment
- Concerts, Exhibitions, Plays
- Cinema, Theater
- Painting, Graphics
- Various arts
- Current events and society
- Social gatherings and entertainment industry
- Political matters
- Society in general
- Society, politics, and media
- Potted plants and gardening
- Leisure and entertainment
- Non-computer games
- Illusions and magic tricks
- Mysticism and esoteric practices
- Divination and fortune-telling
- Interpretation of dreams
- Astrology and horoscopes
- Other types of predictions
- Other forms of entertainment
- Video editing and processing
- Photo editing and printing
- Other photo and video-related activities
- Photography and videography
- Hobbies and personal interests
- Sense of humor
- Military service and military-related topics
- Valuable and timeless classics
- Clubs and nightclubs
- Real estate and mortgage-related matters
- Other unknown topics
- Religion and faith
- Tips and ideas
- Gift ideas
- Goods and services
- Other industrial goods
- Other services
- Unclassified
- Business
- Finance
- Health
- Pregnancy, Childbirth
- Diseases, Medicines
- Doctors, Clinics, Insurance
- Children’s Health
- Healthy lifestyle
- Beauty and Health
- First courses
- Second dishes
- Cooking in …
- Cooking for Kids
- Desserts, Sweets, Pastries
- Appetizers and Salads
- Canning
- Quick
- Beverages
- Grocery shopping and selection
- Other culinary
- Feast, Celebration
- Computers
- Web Design
- Hardware
- Internet
- Advertising
- Appetizers and Salads
- Other projects
- Computers, Communications
- Beeline
- Mobile communication
- Mobile devices
- Online shopping
- Software
- Java
- Cooking in the Kitchen
- Cooking for kids
- Desserts, Sweets, Baking
- Appetizers and Salads
- Canning
- Homework
- Schools
- Architecture, Sculpture
- business and finance
- Macroeconomics
- Accounting, Auditing, Taxes
- Universities, Colleges
- Education abroad
- Humanities
- Natural Sciences
- Literature
- Publishing and writing
- Psychology
- Philosophy, unknown
- Philosophy
- Linguistics
- Additional education
- Self-improvement
- Music
- Science and Technology
- Technology
- Choosing and purchasing equipment
- Technics
- Other educational topics
- Science, Technology, and Languages
- Administrative Law
- Criminal Law
- Civil Law
- Financial Law
- Housing Law
- Constitutional Law
- Social Security Law
- Labor Law
- Other legal issues
- Independent vacations
- Travel
- Around the World
- Residency and Real Estate
- Other information about cities and countries
- Wildlife
- Maps, Transportation, and GPS
- Climate, Weather, and Time Zones
- Restaurants, Cafes, and Bars
- Vacationing abroad
- Hunting and Fishing
- Documents
- Other tourist topics
- Work Environment
- CV writing
- Recruitment agencies
- Other sectors of the business world
- Human Resources, HR
- Part-time and temporary employment
- Manufacturing firms
- Advancement in one’s profession
- Other matters related to one’s career
- Jobs and Career
- Transition and
Scientists Discover the Most Distant Galaxy from Earth
A team of astrophysicists at the renowned Keck Observatory in Hawaii have recently made an extraordinary breakthrough, capturing the emissions of the farthest galaxy ever observed from Earth. This extraordinary find is located a staggering distance of over 13 billion light-years away from us, giving us a glimpse of what the universe looked like a mere 585 million years after the Big Bang. The discovery, reported by TASS and confirmed by the observatory’s press service, sheds new light on the early stages of our universe.
Named EGSY8p7, this newly discovered galaxy is situated a mind-boggling 13.1 billion light-years away from our planet. To determine its age, scientists utilized an advanced infrared spectrometer, which allowed them to detect the presence of the Lyman-alpha line within its spectrum. This groundbreaking research opens up exciting possibilities for further exploration and understanding of the cosmos.
“In our observations of nearby objects, we consistently notice the presence of the Lyman-alpha line in their spectra, which serves as a reliable indicator of star formation. However, as we venture deeper into the Universe and observe objects at earlier stages, we have discovered an increasing number of hydrogen clouds filling the gaps between galaxies, causing absorption of this signal,” explains astrophysicist Adi Citrin.
It is notable that scientists have not only successfully detected a new galaxy, but they have also recorded the distinct Lyman-alpha line in its spectrum. According to scientific theories, during the first 400 million years of the Universe’s existence, it was opaque to this radiation due to the abundance of neutral hydrogen. Over time, as the first galaxies emerged, the radiation emitted by stars gradually transformed the neutral hydrogen into protons and electrons.
Earlier, it was reported on the NASA website that the Spitzer telescope’s observations have confirmed the existence of an Earth-like planet closest to us, located 21 light-years away from the Sun. The planet, named HD 219134b, orbits the star Gliese 892 in the Cassiopeia constellation. Gliese 892 is dimmer and cooler than the Sun, but it can still be visible to the naked eye from Earth. However, due to its close proximity to the star, HD 219134b is not capable of supporting life.
The most distant planet from us
Even though Neptune is not the largest planet, it has a greater mass than Uranus. Observing this planet is not easy – you will likely only see a small disk. A telescope is not necessary to observe this planet – you can easily see it with binoculars. The planet’s ring is not visible from Earth. Only one space satellite, Voyager-2, had the privilege of reaching this faraway planet. No one else has been able to replicate the success of this spacecraft.
Neptune is located 30 astronomical units away from the Sun, and its diameter is nearly 50,000 kilometers. In other words, this object weighs the same as 17 Earths! It takes almost 165 years for Neptune to complete one orbit around the Sun, and its average temperature is 55 Kelvin.
According to ancient tales, Neptune received its name due to its distinctive blue color, which is often associated with the vast waters of the seas and oceans. As Neptune is considered the god of the sea, it was fittingly named in his honor.
Upon the discovery of the seventh planet in our solar system, Uranus, scientists became perplexed by its unusual behavior. Its orbit did not adhere to Newton’s laws and exhibited peculiar patterns. This led scientists to propose the existence of an unidentified planet, which they believed was influencing Uranus’ orbit. Utilizing the available data, astronomers calculated the approximate location of this presumed planet. To their astonishment, their deductions proved accurate, and Neptune was revealed to the world. This remarkable feat of astronomical calculation had never before been achieved.
The composition of the planet is very similar to that of uranium, with both being primarily composed of ice and solidified gases, along with a small percentage of hydrogen and helium. The core of Neptune is estimated to have a mass comparable to that of Earth.
Neptune is categorized as a gas giant, experiencing frequent tornadoes, storms, and wind streaks. Wind speeds on the planet can reach up to 650 m/s! In addition to receiving energy from the Sun, Neptune also generates internal heat, which is more than twice the amount of solar energy.
Neptune has two distinct features on its surface. The first is known as the Great Dark Spot, which was identified in the southern hemisphere. The second spot is slightly smaller and has yet to be named.
As for the presence of the initial entity, its whereabouts remain a mystery – it has either been vaporized or is currently positioned at an angle that renders it invisible to us. Recently, scientists have made a significant revelation regarding Neptune: a fresh spot has emerged. This discovery highlights the dynamic nature of the planet’s atmosphere, with the precise trigger still eluding our understanding.
Which planet is closest to the sun and which is farthest away.
Which planet resides in the closest proximity to the sun? Planets, which have their name derived from the Greek word “wandering,” reflect the light emitted by our sun. This is the reason why we are capable of perceiving them. The planet that is closest to the sun is Mercury. It orbits the sun at a distance of approximately 58 million kilometers. In terms of size, Mercury is just one-twentieth the size of Earth. Its atmosphere is extremely rarefied and consists of helium, argon, and neon. Mercury is not only the planet that is closest to the sun, but it also holds the title for being the fastest planet in our solar system. It travels at a velocity of roughly 170 kilometers per hour. Mercury completes one full revolution around the sun in only 88 days.
The planet that is closest to the sun is Mercury, followed by Venus in second place, Earth in third place, Mars in fourth place, Jupiter in fifth place, Saturn in sixth place, Uranus in seventh place, and Neptune in eighth place (which is also the farthest planet from the sun).
Pluto is no longer classified as a planet.
The planets within our solar system are arranged in the following order in relation to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. (Earth, located approximately 150 million kilometers away from the Sun, follows a slightly elongated circular orbit known as an ellipse.)
Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, while Uranus is the furthest.
Mercury holds the distinction of being the planet closest to the Sun, while Pluto is recognized as the planet located farthest from it.
The Sun takes precedence, followed by Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and finally Neptune. AND THAT CONCLUDES THE LIST.
What is the planet that is nearest to the Sun? Planets (derived from the Greek word “wandering”) reflect sunlight, which allows us to observe them. The planet that is closest to the Sun is Mercury, which orbits the Sun at a distance of 58 million kilometers. Mercury is just one-twentieth the size of Earth. Its atmosphere is very thin and comprises helium, argon, and neon. Mercury not only holds the record for being the nearest to the Sun, but it is also the swiftest among all the planets, traveling at a speed of approximately 170 kilometers per hour. It only takes Mercury 88 days to complete one revolution around the Sun.
What is the nearest planet to Earth in the Solar System?
For many centuries, humans have been fascinated by one of the most enigmatic entities in the galaxy, but Venus continues to captivate scientists worldwide. The closest planet to our own is veiled in secrecy, with only a select few having been able to approach it.
In the past, our ancestors referred to it as both the Morning Star and the Evening Star, mistakenly believing that they were observing two separate celestial bodies. The truth is that the orbit of this celestial dweller surpasses that of Earth every 584 days and becomes prominently visible in both the morning and evening. It took several centuries for us to uncover this secret.
Venus versus Mars
During the mid-20th century, scientists were engaged in a quest to determine which planet was the closest to Earth. It was scientifically proven that as they moved along their respective orbits, the distances between the two planets constantly fluctuated. When Venus is at its closest point to Earth, the distance between them is a mere 38,000,000 kilometers, causing Venus to shine brighter than any other star. Conversely, when they are at their farthest points from each other, the distance stretches to a staggering 261,000,000,000 kilometers. In contrast, Mars has a minimum approach of only 55,000,000 kilometers and a minimum distance of 401,000,000,000 kilometers, providing undeniable evidence that Venus is indeed the planet closest to Earth.
The measurement of the distance between Earth and Mars
Exploration
In ancient times, when it illuminated the sky at dawn and dusk, it shone so brilliantly and exquisitely that astronomers named it Venus, in tribute to the ancient Greek goddess of love. The only celestial body with a feminine moniker, it still evokes notions of romance, femininity, and elegance. Scientists were not mistaken, as the closest planet to our own, it ranks among the top three brightest cosmic entities, surpassed only by the Sun and the Moon. In the early 17th century, Galileo Galilei confirmed this through his trusty telescope. Through his observations, the scientist documented the movement of this celestial object across the heavens, providing the first scientific account of it. Mikhail Lomonosov later discovered its atmosphere, earning it a esteemed position among the eight planets. It would take several centuries to fully comprehend its mysteries.
An unparalleled ambiance
A significant breakthrough in the research was accomplished through the Soviet Union missions conducted in the mid-20th century, during the 1960s. The initial spacecraft were unable to even reach Venus. It was only in 1967 that Venus 4 successfully managed to unveil the mysteries of the closest planet to Earth. Although the craft was ultimately crushed by the immense atmospheric pressure, it managed to gather crucial data on temperature and chemical composition. The atmosphere of Venus consists primarily of carbon dioxide, accounting for 96% of its composition, with nitrogen making up over 3% and traces of sulfur, water, argon, neon, and helium. Recently, scientists discovered the presence of ozone at an altitude of 100 kilometers.
The atmosphere’s upper layer is highly dense, resembling a similar layer found in water at a depth of 900 meters. The planet is ensnared by clouds of sulfur dioxide gas and sulfuric acid, stretching an impressive sixty kilometers high. These clouds possess the ability to reflect back up to 60% of the sunlight that is meant for our planet, resulting in a significant impact. Furthermore, the combination of unprecedented carbon dioxide levels and sulfuric acid has transformed this celestial body into a blazing fireball. This excessive greenhouse effect has caused temperatures to skyrocket, averaging a scorching 467°C. As a result, this planet ranks as the hottest in the solar system, second only to the Sun itself, whose temperature remains constant regardless of day and night.
A hostile goddess
Astronomers have been left frustrated by such research. Until recently, the origin of the serene and uniform brightness of Venus remained uncertain. It was only through the use of radar that scientists were able to study this celestial object. In 1997, the Geological Survey of America succeeded in creating a comprehensive map of Venus’s surface. The closest planet to Earth is completely devoid of water, although it is believed that it was once covered by it before gradually evaporating. This process has left behind enormous basins carved by long channels of volcanic lava. Over 160 large volcanoes have been discovered on the planet’s surface, some of which are truly awe-inspiring, spanning over 100 kilometers in size. Observations have confirmed that these volcanoes are actively erupting and spewing out lava. The Venusian surface lacks the familiar occurrence of precipitation, but the thunderstorms that occur in its atmosphere have the potential to create these massive volcanoes.
Using mathematical calculations to determine the elevations, astronomers have discovered two continents on this planet – Ishtar and Aphrodite. Both of these continents are home to impressive features. Ishtar boasts the planet’s tallest peak, the eleven-kilometer tall Maxwell Mountains, while Aphrodite is home to the majestic Maat volcano.
The American spacecraft Magellan has revealed that none of the craters on this planet exceed a diameter of 2,000 kilometers. This suggests that smaller meteorites are simply incinerated in the planet’s fiery atmosphere. The largest crater discovered so far covers an area of 30 kilometers. Furthermore, researchers unanimously agree that this planet, being the closest to Earth, is relatively young and therefore lacks large potholes.
Sibling Planet Resembling Earth
After conducting observations, researchers have made the fascinating discovery that Venus shares many similarities with Earth. They are often referred to as “sisters” due to their similar composition, structure, mass, size, and density. The only significant difference between them is a mere 638 kilometers in diameter. The closest planet to Earth is comprised of a solid core that stretches for approximately six kilometers, surrounded by a thick mantle that spans over 3,000 kilometers in a molten and viscous state. The outermost layer, known as the crust, reaches a depth of 30 kilometers, mirroring that of our neighboring planet. However, there is ongoing debate among scientists regarding whether Venus possesses a solid or liquid core, and a definitive answer has yet to be reached. Some argue for a liquid core, akin to that of Earth, while others propose the opposite. Interestingly, the closest planet to Earth lacks a magnetic field, which is typically generated by the heat of a liquid core. The mystery surrounding Venus’ core continues to puzzle scientists.
Breaking the Rules
It is commonly believed that all celestial objects rotate in a west-to-east direction on their axis. However, our protagonist defies this convention and rotates in the opposite direction. Interestingly, Uranus also shares this unique trait, rotating from east to west. Venus, on the other hand, takes approximately 225 Earth days to orbit the Sun at a speed of 35 km/s, and completes one rotation on its axis in 243 days. This means that one day on Venus lasts longer than a year. Due to its slow rotation, Venus almost always presents the same side to the Earth. It takes this impregnable sphere 4 Earth days to complete a full revolution, making a Venusian day almost 117 Earth days long.
If you were to travel to the closest point to Venus, it would take at least 100 days to return to Earth. The first flight of the American Mariner 2 spacecraft lasted 153 days.
The Exclusive One
Over the course of nearly six decades, more than forty spacecraft have embarked on journeys to explore the impenetrable orbit and reveal to humanity the identity of the planet that lies closest to Earth. Throughout previous centuries, astronomers were adamant about the existence of rings and satellites encircling Venus. Countless expeditions, however, have confirmed that Venus stands alone in its celestial realm, devoid of any surrounding entities. The only celestial body that comes close to it is the asteroid 2002. In 1976, the American astronomer Flandren proposed the intriguing hypothesis that Mercury might have once been a satellite of Venus, only to be “misplaced” at a later time.
Presently, the planet that lies nearest to our own remains an unattainable and inhospitable aspiration, as comprehending its mysteries still eludes us.
Related news:
Remember to share. Takeaway.
The most distant planet from the Sun – Science
The most distant planet from the Sun
Latest findings in the solar system
We have been accustomed to the belief that there are 9 planets in the solar system, and many are convinced that our solar system has been thoroughly studied and explored for the presence of planets. However, this is far from the truth. It is time to revise the old astronomy textbooks, as every year, astronomical scientists uncover more and more celestial bodies that do not resemble asteroids or planetoids. One of the most surprising pieces of news was the announcement of the discovery of a new planet in our solar system.
Located in the Kuiper Belt, Xena is a planet that is three times farther from the Sun than the well-known Pluto. This region of space has also revealed several other sizable celestial bodies that could potentially be classified as planets. Scientists speculate that Xena may not be the last planet to be discovered in our solar system, and they continue to study this enigmatic belt.
Interestingly, Xena was named by accident. Journalists took the name out of context, and it has stuck ever since. There is also a variant spelling – Xena. However, most people are familiar with the warrior princess who inspired the planet’s name. It is worth noting that this name translates to “stranger.” What mysteries will this extraterrestrial entity reveal to our scientists?
Discovered in 2003, it took scientists two years to confirm that this celestial body is indeed a planet. Thus, in 2005, after the discovery of the planet’s moon, it was announced that we have more planets than we previously thought. By the way, the moon started to be called Gabriella, just like Xena’s moon.
In comparison to our Moon, Gabriella is much smaller: the Moon has a diameter of 3.5 thousand kilometers, while Gabriella has a diameter of 248 km. However, Xena is also much smaller compared to Earth. Its exact size is unknown, but it is believed that the planet has a diameter of 2210-3550 km (Earth’s diameter is 12756 km).
Following the discovery of Xena, astronomers have started reevaluating the definition of the term “planet” in order to establish a precise definition. Until a consensus is reached, the number of recognized planets in our Solar System may vary, as if Pluto and Xena are not considered planets due to their small size, there will only be 8 “true” planets.
By the way, the planet closest to the Sun is Mercury.
Ekaterina Chipula, Samogo.Net
Where does the world’s largest pig live? Ranking of baby formula: the most popular manufacturers
The Nearest Planet to Earth
Solar System > Planets of the Solar System > The Nearest Planet to Earth
There is a lot of curiosity among our audience regarding the question “Which planet is the closest to Earth?”. The answer is Venus, without a doubt. It holds the position of being the third most luminous planet in the night sky, with only the Sun and the Moon being brighter. When Venus reaches its closest point in orbit to Earth, the distance between our two planets is a mere 38 million kilometers.
Visual Depiction of the Orbits of Venus and Earth
3D perspective of the Maat Mountains
Although Venus is the closest planet to Earth, its atmosphere is inhospitable for any kind of life. The highest recorded temperature on Earth was in 2005 in Iran’s Lut Desert, where temperatures reached a scorching 70.7° Celsius. This extreme heat is unbearable and destructive to most organisms, while Venus maintains an average surface temperature of approximately 460° C.
While Earth’s atmosphere is predominantly composed of nitrogen and oxygen, Venus’ atmosphere is overwhelmingly carbon dioxide, accounting for as much as 96% of its mass. CO2 acts as a greenhouse gas, trapping heat on the planet’s surface. In addition to the lack of oxygen and high temperatures, the entire circumference of Venus is enveloped in a cloud of sulfuric acid.
A new volcano emerges in the Themis region
Despite being the closest planet to Earth, Venus remains enigmatic due to its impenetrable sulfuric acid clouds that reflect or scatter all light, making it impossible to see its surface below the upper atmosphere. It wasn’t until the late 20th century when scientists were able to gather information about the planet’s surface through radar scanning. The surface of Venus is known to have large volcanoes, potentially even active ones, and over 1000 craters with diameters reaching up to 20 kilometers. However, these findings are limited to one side of the planet that faces Earth.
Venus, the closest planet to Earth, shares similar characteristics such as diameter, weight, and volume. However, what sets our nearest neighbor apart is its eerie and inhospitable nature.
The Venus Express probe is presently gathering data on Venus. In 2014, BepiColumbo was launched, which will soon transmit information back to Earth, providing us with a wealth of knowledge about this celestial body.
Until recently, Pluto, the ninth planet, held the title for the farthest planet from the Sun. However, in 2006, astronomers made the decision to remove it from the planetary lineup after careful observation.
Pluto had previously lost its planetary status from 1979 to 1999 when it traversed Neptune’s orbit. Some suggest that it may not even belong to our solar system. As a result, Neptune is now recognized as the farthest planet from the Sun.
Neptune Description
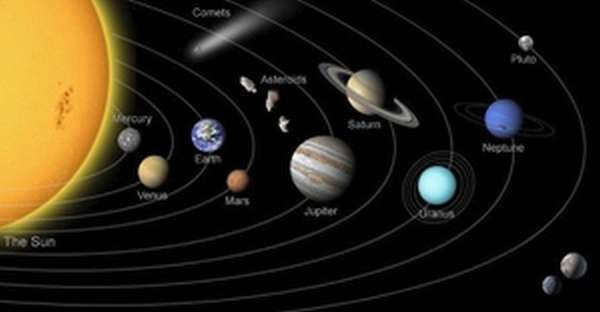
Aside from our home planet, the solar system consists of eight other celestial bodies:
Neptune, the farthest planet from the Sun and Earth, is known for its perpetual twilight due to its illumination being 900 times dimmer than that of Earth. Its distance from Earth is approximately 5 quadrillion kilometers.
This distant planet is also referred to as an icy planet, as it is composed of about 20% helium and hydrogen. A day on Neptune lasts just over 16 hours, while a full revolution around the Sun takes 164 years. The most recent completed revolution occurred in 2011.
Neptune’s Moons
The distant planet of our solar system, Neptune, boasts a plethora of moons. In fact, it is accompanied by a total of fourteen moons.
These moons can be categorized into distinct groups:
- Internal Moons (Talasa, Naiada, Proteus, Galatea, Larissa, Despina)
- Separate Moons (Nereida and Triton)
- External Moons (yet to be named)
The internal moons are characterized by their irregularly shaped rocky forms, with diameters reaching up to 200 kilometers. They swiftly orbit around Neptune, completing their rotations in a matter of hours due to their incredible speed.
Triton, on the other hand, is a notably large moon with a diameter of approximately 3000 kilometers. Covered in ice, it takes around 6 days for Triton to complete a full revolution. Interestingly, it is gradually getting closer to Neptune as it follows a spiral trajectory. Scientists predict that Triton will eventually collide with Neptune, resulting in the formation of a ring.
Nereid has an irregular shape and completes a full orbit around Neptune in one Earth year. The outer satellites of Neptune are located tens of millions of kilometers away. The farthest satellite takes 25 years to complete one orbit around the planet.
Pluto holds the record for being the most distant planet from Earth.
From elementary school, children are taught that Earth is the third planet in our solar system, with Pluto being recognized as the most distant planet from Earth.
Since the discovery of Pluto, the ongoing debate regarding its planetary status has been a topic of discussion. There are several arguments against classifying it as a planet:
- Its small size (Pluto’s mass is only 0.22% of Earth’s).
- Its significant distance from Earth, which hinders thorough study.
- Its constantly changing orbit, causing it to sometimes be positioned in front of or behind Neptune.
Pluto is situated within the Kuiper Belt, approximately 6,000,000,000,000,000 kilometers away from Earth and measures 2,300 kilometers in diameter. It completes a full orbit around the sun in 248 years, while a single day on Pluto lasts for 6.5 Earth days. The surface temperature on this celestial body drops to as low as minus 223 degrees Celsius. What makes Pluto intriguing is its unique composition, with one side covered in ice and the other adorned with rocky formations.
Due to the minimal solar heating, Pluto remains in a perpetual state of darkness. However, scientists have managed to observe a heart-shaped region on the planet’s surface, characterized by towering ice mountains reaching heights of up to 4 meters.
Pluto possesses a nitrogen-based atmosphere, which research has revealed to dissipate into the void of space. This occurrence bears a striking resemblance to a phenomenon that transpired on Earth eons ago: the nitrogen vaporization that resulted in the emergence of carbon, carbon dioxide, and the inception of life.
Pluto’s exterior showcases a multitude of craters brimming with frozen gases, namely nitrogen and methane. These formations can be attributed to collisions with asteroids.
Moons of Pluto
Pluto possesses five satellites: Charon, Hydra, Styx, Nycta, and Kerberus. Charon, being the largest, orbits Pluto synchronously (some astronomers classify them as a binary system), while the other satellites have tilted axes of rotation in relation to Pluto and Charon. These irregularly shaped satellites are bright and potentially covered in water ice.
In spite of Pluto’s reclassification as a dwarf planet, it remains a subject of great interest. Astronomers continue to identify new objects in the Kuiper Belt that exceed Pluto in size, such as Erida and Ceres. It is plausible that one of these objects will soon claim the title of the most distant planet from the Sun within our solar system.
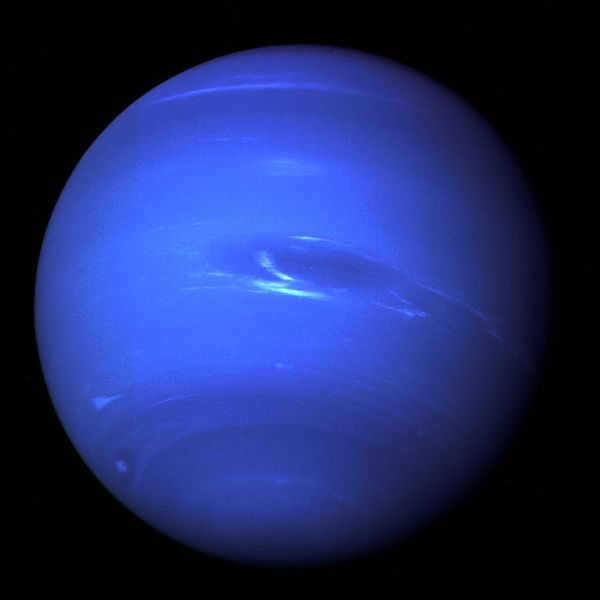

Basic details
Neptune is situated at a distance of 30 astronomical units from the Sun, with a diameter measuring nearly 50,000 kilometers. To put it differently, this celestial body is equivalent to the mass of 17 Earths! Its orbital period around the Sun spans approximately 165 years, and it boasts an average temperature of 55 Kelvin.
According to folklore, Neptune acquired its designation due to its distinct blue hue. It is widely believed that blue is closely associated with the water found in the seas and oceans. As Neptune is the god ruling over the sea, the planet was given its name as a tribute to him.
The discovery of Neptune
When astronomers made the groundbreaking discovery of the planet Uranus, they were puzzled by its unusual behavior. Uranus seemed to defy Newton’s laws of motion and its orbit exhibited strange deviations.
Scientists postulated that these anomalies could be attributed to the gravitational pull of another celestial body, a new planet lurking beyond Uranus and affecting its orbital trajectory. Based on the available data, astronomers made calculations to estimate the approximate location of this hypothetical planet.
To everyone’s astonishment, the assumptions turned out to be correct, and Neptune was unveiled to the world. This triumph of astronomical calculation had never been achieved before, marking a significant milestone in the field.
Composition and conditions
The composition of the planet is remarkably similar to that of uranium, with both planets being predominantly covered in ice and solidified gases, and containing a small percentage of hydrogen and helium. The core of Neptune is estimated to have a similar mass to that of Earth.
Neptune is categorized as a gas giant, resulting in the frequent occurrence of tornadoes, storms, and wind streaks. The winds on Neptune can reach astonishing speeds of up to 650 m/s! Furthermore, Neptune receives internal heat in addition to its energy from the Sun, with this internal energy being more than twice that of the Sun.

Neptune has two distinct spots on its surface. One of these spots is known as the Great Dark Spot, which was initially found in the southern hemisphere. The second spot is slightly smaller and is currently unnamed.
As for the first spot, its current status remains unknown. It is possible that it has either dissipated or is positioned in such a way that it is not visible to us. Recently, scientists have discovered the formation of a new spot on Neptune. This indicates that the planet’s atmosphere undergoes frequent changes, although the exact cause behind these changes is still uncertain.
Discovering the Most Distant Planet from Earth: Characteristics and Information

Which planet is considered to be the farthest from the Sun? That would be Neptune – the eighth largest celestial body in the solar system and the planet that is the most distant from Earth. However, it is also the smallest of the gas giants.
Neptune is more than 17 times more massive than Earth and slightly larger than its twin, Uranus. This giant gas planet revolves around the Sun at a distance of about 4.5 billion kilometers. The planet itself is extremely cold and dark, receiving very little sunlight. On Neptune’s surface, powerful winds rage, sometimes reaching speeds of up to 2,100 kilometers per hour.
Discovered by Leverrier and Galle on September 23, 1846, the planet Neptune is unique among the other celestial bodies in our solar system. Unlike Mars and other planets that can be observed directly from Earth, Neptune’s existence was confirmed not through visual sightings but through meticulous mathematical calculations.
Composition of Neptune
Neptune shares a similar composition with Uranus. Due to its great distance from the Sun, Neptune has one of the coldest outer atmospheres in the solar system, making it the farthest planet from Earth. The temperature of the visible “surface” of the planet is approximately -226.5°C. A single year on Neptune lasts about 165 Earth years. The planet’s gravity is 17 times stronger than that of Earth. The surface of Neptune is liquid, and in theory, it could pull in an astronaut standing on it.
However, at the center of the planet, the temperature is around 5100°C. Additionally, Neptune possesses rings, with one of them being more distinct and the others appearing more vague. Despite this, the overall structure of the rings is quite substantial.
Certainly, the rings of Neptune are distinct from those of Saturn and are likely composed of ice particles, silicate molecules potentially containing carbon. Scientists anticipate that the rings may vanish within the next few centuries.
Atmosphere
The atmosphere of the outermost planet in the solar system, Neptune, primarily consists of two gases: hydrogen (50%) and helium (19%). It also contains a small amount of methane. The lower atmosphere of Neptune is rich in ammonia, hydrogen, and water.
Neptune’s atmosphere can be categorized into two regions: the troposphere, where the temperature decreases as altitude increases, and the stratosphere, where the opposite effect takes place.
There is a tropopause that separates the two zones in the planet’s atmosphere. Additionally, the composition of the clouds in the atmosphere varies based on altitude. These clouds can consist of either ammonia and hydrogen sulfide or hydrogen sulfide and water.
The mantle of Neptune contains a significant amount of water, ammonia, and methane due to the composition of the atmosphere. It also exhibits a remarkably high electrical conductivity. It is theorized by scientists that diamond crystals are formed through the decomposition of methane at a depth of approximately 7,000 kilometers.
Neptune experiences powerful winds in its atmosphere, with speeds exceeding 2,000 kilometers per hour. Dark oval-shaped areas can be observed on the planet’s surface, which astronomers believe to be storms.
The composition of the core
The core of Neptune is made up of iron, nickel, and silicon, similar to the composition of other planets. The planet’s distinctive blue color is caused by the presence of methane, which absorbs the red part of the light spectrum.
Rings around Neptune
Neptune is surrounded by rings, although they are not as extensive as Saturn’s rings. These rings consist primarily of ice particles, silicates, and carbon-based materials. Scientists have identified three main rings around Neptune – the Adams, Leverrier, and Halle rings. In total, there are six rings around the planet.
There are 14 moons orbiting around Neptune, and each of them bears the name of a water-related ancient Greek god or nymph. The most prominent among these is Triton, which is located in close proximity to both the Moon and Earth.
Similar to the other planets in our solar system, Neptune’s name is derived from Greek and Roman mythology. In Roman mythology, Neptune is the ruler of the seas and the water element, while his Greek counterpart is known as Poseidon.
Observing Neptune
Unlike many other celestial bodies, Neptune cannot be seen with the naked eye from Earth. However, with the help of a telescope or powerful binoculars, you can catch a glimpse of Neptune as a small blue disk, similar in appearance to Uranus.
But appearances can be deceiving, as a distant planet may be much closer than it appears. Discover the wonders of Neptune with a unique t-shirt or sweatshirt from our Shining Space collection.
Could life exist on Neptune?
Life as we know it on Earth is not possible on Neptune. The emergence of any form of life requires a source of energy, such as water, which exists mostly in liquid form and undergoes structural changes in extreme conditions.
- Water on Neptune is permanently in crystalline form due to temperatures below 218 degrees Celsius, lack of oxygen, and permafrost, making it impossible for any form of life, including bacteria, to exist.
- Now you have learned which planet is the farthest from Earth, and you can practically touch it with your hand.
- The innovative clothing and accessories from the Cosmomurch brand allow you to create a stylish space-inspired look, transporting you to the most distant corners of the universe. They also provide you with information about new discoveries and interesting facts from the world of astronomy and astronautics.
Which planet is the farthest in the solar system?
Aside from Earth, there exists another celestial body in the solar system known as Neptune. Its discovery in 1846 was made through mathematical calculations rather than direct observations.
Which planet in the Solar System is the most distant from the Sun?
Pluto, which was discovered in 1930, used to be considered the ninth and farthest planet in the solar system until 2006. In contrast, Neptune was recognized as the eighth planet.
However, in 2006, the International Astronomical Union redefined the term “planet” and Pluto no longer met the criteria. Some even propose that it does not belong to the solar system and is instead part of the Kuiper belt.
- Pluto also lost its planet status from 1979 to 1999 when it was located inside Neptune’s orbit.
- When asked to name the farthest planet in the solar system, you may hear both names as an answer.
- In Roman mythology, Neptune is known as the god of the sea.
Discovery
Officially, the most distant planet in the solar system, Neptune, was discovered in 1846. However, as early as 1612, Galileo described it. At that time, he believed it to be a fixed star and was not recognized as its discoverer.
In 1821, when the data on the orbit of Uranus were published, it became apparent that there might be a new planet in existence. The values in the tables differed from the observed configuration.
However, it was only on September 23, 1846, after a two-month search, that Neptune was discovered thanks to mathematical calculations of its orbit. The planet was named after the mathematician who discovered it, Wu. Liverier, who had initially wanted to name it after himself.
Neptune experiences perpetual twilight, with a luminosity that is 900 times dimmer than our own planet. From its orbit, the sun appears as a mere brilliant star.
This colossal planet is situated at a distance of 4.55 billion kilometers, approximately 30 astronomical units away. It possesses a mass that is 17.15 times greater than Earth, and its diameter is four times larger. The average density of Neptune is only one and a half times that of water (1.6 g/cc). Therefore, Neptune is classified as a giant planet, alongside Saturn, Jupiter, and Uranus.
Furthermore, this remote celestial body is also known as an icy planet, as helium and hydrogen make up no more than 15-20% of its composition.
Similar to other colossal celestial bodies, Neptune rotates rapidly on its axis. Its diurnal cycle is a mere 16.11 hours in duration. Furthermore, it gracefully orbits the Sun in an orbit that is nearly circular, taking approximately 164.8 years to complete one revolution. In the year 2011, Neptune accomplished its initial full rotation since its initial discovery.
The surface of Neptune is dominated by fierce winds, boasting an average velocity of 400 m/sec. Interestingly, the planet’s temperature measures at -214°C, a surprisingly higher value than expected.
Evidently, the outermost planet in our solar system possesses an internal heat source, as it emits 2.7 times more energy into space than it absorbs from the Sun. This celestial body experiences constant shifts in its seasons, with each season spanning approximately 40 Earth years.
Satellites
The most distant planet in our solar system has a total of 14 satellites. These satellites are typically categorized into three distinct groups:
- The first group consists of inner satellites including Talasa, Naiad, Galatea, Despina, Larissa, and Proteus. These satellites are characterized by their dark clumps, which can reach sizes of 100-200 km and have irregular shapes. They orbit the planet in a circular path that is almost aligned with the equator, completing a revolution in just a few hours.
- The second group is comprised of Nereid and Triton.
- The remaining five outer satellites have yet to be named.
Each group of satellites plays a unique role in the planet’s orbit and exploration.
Triton belongs to the second category. It is a rather large moon. It has a diameter of about 2,700 kilometers and completes a full orbit around Neptune in 6 days. Its trajectory is in a spiral pattern, gradually approaching the planet. Eventually, it will collide with Neptune and, due to tidal forces, transform into another ring. Triton’s surface is extremely cold, and there is a belief that beneath its icy crust lies a turbulent ocean.
Nereid orbits Neptune once every 360 days. It has an irregular shape. The outer moons are located at a considerable distance (tens of millions of kilometers) from Neptune.
The farthest moon takes 25 years to complete one orbit around the planet. Considering their orbits, inclination to the equatorial plane, and retrograde motion, scientists have concluded that these moons are objects that were captured by Neptune from the Kuiper belt. In July 2013, the discovery of the final moon was made.
Neptune boasts a set of five rings comprised of icy particles. These rings are unique in that some of them contain carbon, resulting in a striking red hue. They are considered to be relatively young and have a short lifespan. Neptune’s rings are known for their instability and significant variability.
Interesting Tidbits
When considering the distant planets in our solar system that the renowned Voyager 2 spacecraft was initially launched to explore, it is worth noting that it was primarily sent on a mission to investigate Saturn and Jupiter. However, its trajectory also allowed for exploration of Uranus and Neptune. The spacecraft was launched in 1977.
On August 24, 1989, Voyager 2 flew an impressive 48,000 km in proximity to Neptune, capturing and transmitting stunning images of the planet and its moon Triton back to Earth. There were plans to send another spacecraft to Neptune in 2016, although specific launch dates have not yet been determined.
Neptune holds the title for being the farthest planet from the Sun
Unquestionably, Neptune is worthy of our attention. As we are aware, it is positioned as the eighth planet in our solar system, making it the most remote planet from the Sun. This gas giant possesses a plethora of captivating and distinctive characteristics. However, let us delve into each of them systematically.
Distinctive Features of the Planet
It should be noted that the makeup of Neptune bears resemblance to its neighboring planet Uranus, setting them apart from the other gas giants. In fact, these two planets are often classified as a separate group known as ice giants. By the way, Neptune’s mass is equal to 1.02×10²⁶kg..
Therefore, it surpasses that of Earth by 17.2 times, ranking it third in this category. However, in terms of size, it comes in fourth place with an equatorial radius of 24,764 km. That’s four times the size of our Earth.
In addition, its internal structure is also comparable to that of Uranus:
- the atmosphere is divided into upper clouds and lower layers of hydrogen, helium, and methane;
- an icy mantle, a dark and heated zone;
Rotation and orbit
Scientists state that the average distance of Neptune from the Sun is 4.55 billion km, and from Earth it is between 4.3 and 4.6 billion km. Recently, on July 12, 2011, one Neptunian year has passed since the planet’s discovery, which lasted 165 Earth years. The planet rotates on its axis every 16 hours.
Interestingly, a complete revolution at the equator takes 18 hours, while at the poles it is slightly faster at 12 hours. It has been discovered that Neptune’s orbit is elliptical and has an inclination of 1.77 degrees in relation to Earth. Additionally, its eccentricity is 0.011.
Due to these orbital characteristics, Neptune experiences seasonal changes similar to those on Earth and Mars. However, each season on Neptune lasts approximately forty years, given its long orbital period.
Neptune’s Atmosphere and Temperature
Similar to Saturn and Jupiter, Neptune’s atmosphere is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, along with hydrocarbons, methane, and potentially nitrogen. However, Neptune’s atmosphere also contains a significant amount of ice, specifically in the form of water, ammonia, and methane. Additionally, the planet’s subsurface is predominantly composed of rock and ice.
Interestingly, the blue hue of Neptune is a result of the presence of methane in the upper layers of its atmosphere. The atmosphere itself can be divided into several regions, including the troposphere, tropopause, stratosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. However, it is commonly divided into the troposphere (lower region) and the stratosphere (upper region).
There is a clear trend here – as the temperature decreases, so does the temperature. According to certain approximations, the temperature in the upper layers is around -220 degrees Celsius, while the core of the planet is scorching hot at 7000-7100 degrees.
Until now, scientists have struggled to explain why the thermosphere is so hot. The sun cannot heat it up to such extremes. Naturally, there are several theories regarding this phenomenon. Firstly, ions from the magnetic field may interact with atmospheric particles, causing them to heat up. Secondly, when gravitational waves from the planet’s depths dissipate, they raise the temperature.
In addition to this, Neptune emits more energy than it receives from the Sun. Therefore, it must have an internal source that contributes an additional 161% to its heat.
Climate
Neptune exhibits unique cloud shadows, distinguishing it from other giant planets. Moreover, it boasts the most powerful winds in its atmosphere, reaching speeds of 600 km/s.
Despite its considerable distance from its host star, the planet possesses enough energy to generate the swiftest winds within the entire system. However, the exact cause of this phenomenon remains uncertain, and it is anticipated that scientists will eventually unravel this enigma.
In contrast to Uranus, Neptune displays meteorological activity. Notably, its weather undergoes frequent changes, owing to the significant variability of its winds and storms. As previously mentioned, the atmosphere experiences vigorous winds, primarily blowing in the opposite direction of the planet’s rotation.
Even though it’s the same in the highest latitudes, this phenomenon is actually a characteristic of air flow activity on the surface. The tilt of the axis leads to the formation of hot areas.
Cloud bands are also influenced by seasonal changes. For instance, in one season, there is an increase in cloud bands in the southern hemisphere of the planet. Additionally, multiple cloud movements have been documented. Storms such as Scooter, Large, and Small dark spots are particularly noteworthy.
Furthermore, dark spots have been observed primarily in the troposphere at low altitudes, as opposed to bright and visible clouds.
Surface of Neptune
Here are the key points to consider:
- It covers an expanse of 7.6 billion square kilometers.
- The density is measured at 1.6 grams per cubic centimeter.
- The free-fall acceleration is approximately 11.15 meters per second squared. However, it’s important to note that Neptune’s surface is not solid, making it impossible to land any type of vehicle on it.
Neptune’s Moons and Rings
At present, there are a total of 14 known moons orbiting Neptune. Interestingly, only one of these moons, known as Triton, has enough mass to have a spherical shape. It is worth noting that Triton was actually discovered 17 days after the planet Neptune itself was discovered.
What makes Triton particularly fascinating is that it has a retrograde orbit and possesses an atmosphere, similar to the moons Io and Titan. Scientists speculate that beneath its icy surface, Triton may harbor an ocean. It is predicted that in the future, Neptune’s gravitational forces will cause Triton to eventually be destroyed. Due to tidal acceleration, Triton is gradually spiraling towards its parent planet, and it is believed that when these two bodies collide, a massive ring will be formed.
It is worth mentioning that the other satellites of Neptune were actually discovered thanks to the Voyager 2 spacecraft. These satellites have been characterized by their irregular shapes and relatively small masses.
There is another noteworthy satellite to mention, Nereid. Unlike all other known objects in the Solar System, it has the highest orbital eccentricity, which is 0.75. It is important to mention that in addition to what was mentioned above, there are also these natural satellites: Naiad, Thalassa, Despina, Galatea, Larissa, Hippocampus, Proteus, Galimeda, Psamapha, Sao, Laomedea, and Neso. They are listed in the order of their discovery.
Neptune also possesses a ring system. Of course, it cannot be compared to Saturn’s rings. However, it does have rings, most likely composed of ice particles that are covering silicates or carbon matter.
Did you know?
- Neptune received its name in tribute to the Roman god of the sea.
- The magnetosphere and magnetic field of Neptune are noticeably tilted at an angle of 47 degrees in relation to the planet’s axis. This could be due to tidal forces within the planet. Additionally, the tail of the magnetosphere extends over 72 times the radius of Neptune.
- Similar to Jupiter’s famous Great Red Spot, Neptune has its own notable feature called the Great Dark Spot.
- Neptune possesses a faint and fragmented ring system.
- Despite being far apart, Neptune exerts a strong gravitational influence on the objects within the Kuiper belt.
- Neptune holds a significant number of Trojan asteroids at its Lagrange points. These asteroids likely formed around the same time as the planet.
- During terrestrial observations, the planet undergoes a visible retrograde motion approximately once every 367 days.
- When exoplanets with a similar mass to Neptune are discovered, Neptune is often used as a succinct description.
Lagrange point – a location in a two-body system where a third body with low mass experiences gravitational force solely from the first two bodies, resulting in it remaining stationary in relation to them. In simpler terms, it is an area of gravitational stability.
The exploration and examination
Interestingly, the naked eye cannot detect Neptune at all from Earth. However, if you utilize a powerful telescope, it can be observed as a small star due to its magnitude of +8. Surprisingly, these telescope observations have not contributed significantly to the investigation of the planet. Nevertheless, thanks to the utilization of spacecraft and the development of adaptive optics, scientists have managed to gather a certain amount of data and materials.
Neptune holds the distinction of being the first planet to be discovered through mathematical calculations. Its discovery occurred on September 23, 1846, as a result of unexpected deviations in Uranus’ orbit. Initially, scientists hypothesized that these deviations were caused by the gravitational influence of an unknown planet, which led to the eventual discovery of Neptune itself. Subsequently, its moons, most notably Triton, were also identified.