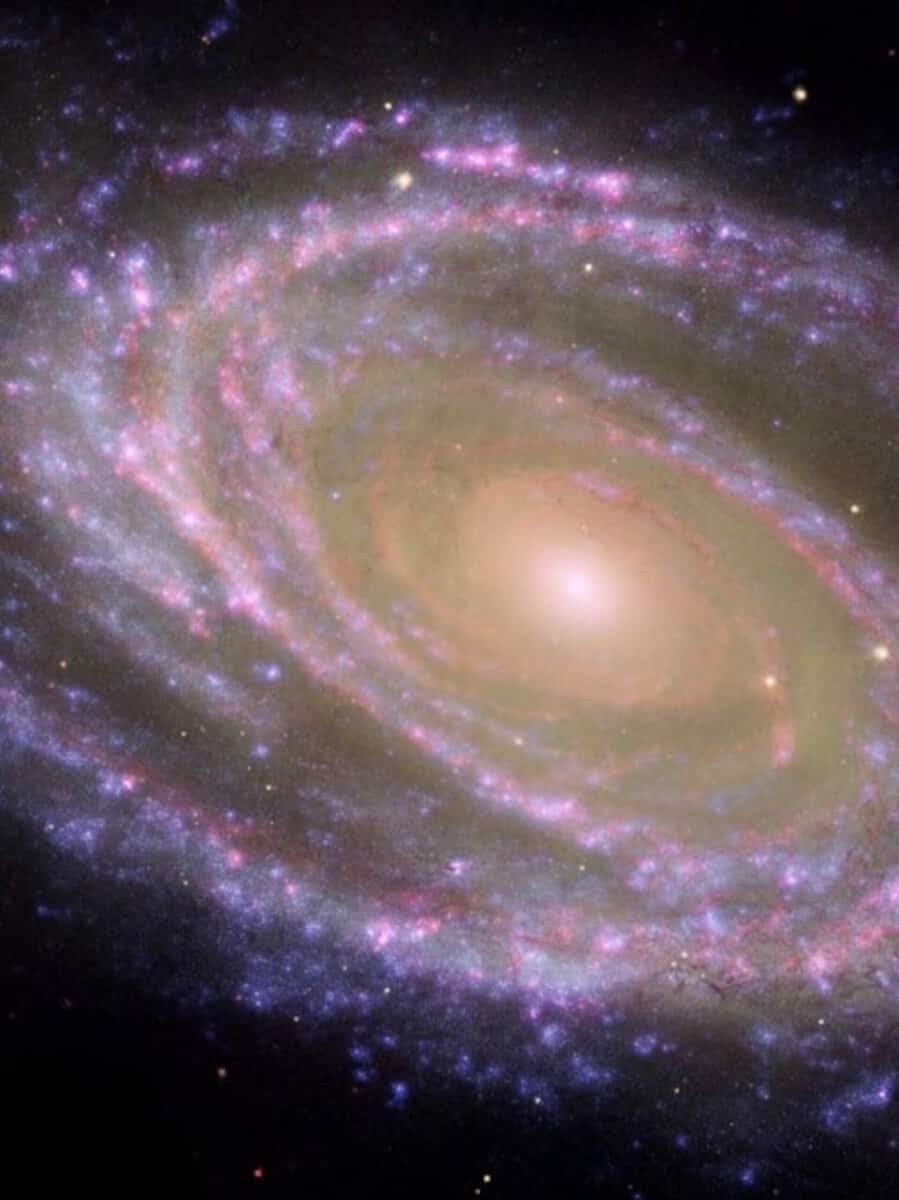
The phenomenon of space is undeniably captivating. The mere notion of the possibility of extraterrestrial life stimulates our curiosity. It allows us to gaze into the infinite expanse and comprehend the immense and uncharted nature of our world. However, space not only captivates our imagination, but it also attracts galaxies. There is a force in the universe that causes galaxies to move in a specific direction. Interestingly, scientists initially believed that groups of galaxies would move haphazardly, unaffected by any discernible pattern. Yet, after analyzing data collected over a span of three years, researchers have discovered an enigmatic pattern. Could it be a technical glitch, or is there truly a mysterious phenomenon at play?


Space exploration is an ongoing endeavor with countless unanswered questions.
What is the concept of dark flow?
The concept of dark flow is a phenomenon in cosmology that has sparked considerable discussion and investigation in the field of astrophysics. It pertains to the enigmatic and consistent movement of clusters of galaxies in a specific direction, which cannot be accounted for by the accepted cosmological model.
The accepted cosmological model posits that the Universe is uniform and symmetrical, meaning that physical characteristics should remain consistent regardless of their orientation on a large scale. However, empirical evidence has demonstrated that galaxy clusters exhibit a preferred motion known as dark flow.

Space is an incredibly dim location, resulting in the use of many terms associated with darkness.
In 2008, a team of researchers led by Alexander Kashlinsky of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center discovered the phenomenon known as dark flow. They utilized data from the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) to examine the movement of galaxy clusters on a large scale.
What is the direction of galaxy movement?
However, there are some fascinating dynamics that can be observed on smaller scales. For instance, our very own Milky Way galaxy is currently heading towards a collision with its closest neighbor, the Andromeda galaxy. This epic encounter is expected to take place in approximately five billion years, and if future generations are fortunate enough to witness it, it will undoubtedly be a remarkable sight.
In addition to this impending collision, both the Milky Way and Andromeda are also moving towards the Virgo cluster, a densely populated cosmic city that boasts around a thousand galaxies.
But that’s not all. The Milky Way, Andromeda, the Virgo cluster, and numerous other galaxies in the vicinity are collectively traveling towards an even larger cluster known as the Norma cluster. Situated in a region of space called the Great Attractor, this massive cluster exerts a gravitational pull that is drawing these galaxies closer together.

For a long time, scientists have had knowledge about the movement of galaxies, our planet, and the overall movement of the universe.
This is where things start to become more complex. As we progress with our observations, it becomes increasingly challenging to precisely determine the movements of galaxies. Additionally, astronomers excel at measuring the motion of galaxies towards or away from us (by analyzing the displacement of light from galaxies), but calculating motions in other directions is considerably more arduous. Therefore, one must depend on computer modeling to make an informed estimate.
While the majority of observations in the vast expanse of the universe support the theory of a “uniformly expanding in all directions” phenomenon, certain inconsistencies have emerged. Some observations have detected a minuscule and almost imperceptible movement, which could easily go unnoticed. It appears that numerous galaxies may be exhibiting a preferred direction of movement, instead of simply expanding uniformly outward.
Hence, the research team has discovered that clusters of galaxies are actually moving towards a specific region in the sky, close to the constellation Centauri, at a velocity of approximately 600 km/sec. This motion cannot be explained by the gravitational influence of neighboring structures or the overall expansion of the Universe. This has led to speculation that some unknown force, different from what is currently understood, could be at play in this scenario.
There have been various proposals to account for the phenomenon known as the dark flow. One theory posits that it arises from the gravitational pull exerted by massive structures located beyond the boundaries of the observable Universe, which in turn causes clusters of galaxies to move in a specific direction. However, this explanation remains a subject of controversy due to the inherent challenges in either proving or disproving the existence of such structures.
Another possibility is that the dark flow represents a trace of the early Universe, a time when it lacked homogeneity and isotropy. According to this hypothesis, the dark flow could be indicative of primordial gravitational waves that may have introduced asymmetry into the initial conditions of the universe.
The differentiation of dark flow, dark matter, and dark energy
The scientific community has a particular interest in the mysterious aspects of the cosmos, which is why these terms have been coined. However, it is crucial to make a clear distinction between them in order to fully comprehend their significance. Dark flow, dark energy, and dark matter are three separate yet interconnected phenomena that currently hold a prominent position in contemporary astrophysical investigations. Despite the common confusion surrounding these concepts, each one represents a distinct facet of the Universe’s structure and evolution.

Researchers are continually working on innovative approaches to assist in identifying these phenomena.
Dark energy, on the other hand, is responsible for the rapid expansion of the universe. It functions as a repulsive force that opposes gravity and causes the universe to expand at an increasingly rapid pace. However, the exact nature of dark energy remains unknown.
Earlier, we discussed the concept of the dark flow.
The origins of the dark flow
Various hypotheses have been proposed to explain this phenomenon, but most scientists believe that the dark flow emerged in the early stages of the universe’s formation. Astronomers theorize that it manifested mere moments after the Big Bang, even before the inflationary period when the universe rapidly expanded. Nevertheless, the true nature and origins of the dark flow continue to elude us, as they lie beyond the bounds of our observable universe.

The possibility of the existence of multiple universes, known as the theory of multiverse, continues to be a subject of debate.
One intriguing variation of this theory, based on string theory, suggests that our universe could have a parallel twin universe that emerged after the Big Bang.
To stay updated with the latest scientific news, be sure to subscribe to our Zen and Telegram channel.
Despite extensive investigation, the true essence and genesis of the enigmatic dark flow remain shrouded in ambiguity. A comprehensive grasp of this captivating phenomenon necessitates additional observations and comprehensive studies focused on the vast cosmic framework.

Science
When gazing at the night sky with a telescope, one can witness a multitude of celestial bodies that are beyond the reach of the naked eye. Among these, there are numerous star clusters referred to as galaxies. These galaxies can consist of billions, and even trillions, of stars.
Galaxies comprise of stars, dust, and dark matter, all of which are held together by gravitational forces. It is possible for some galaxies to collide and merge with one another.
There is a wide range of shapes and sizes when it comes to galaxies, and they also come in various ages. Many of these galaxies have black holes located at their center. In certain instances, these black holes found at the center of galaxies can be incredibly large and highly active.
The area surrounding these black holes emits a significant amount of energy that astronomers can detect, even from far distances.
Other galaxies may contain fascinating objects like quasars, which are the cores of galaxies that possess the highest amount of energy in the entire universe.

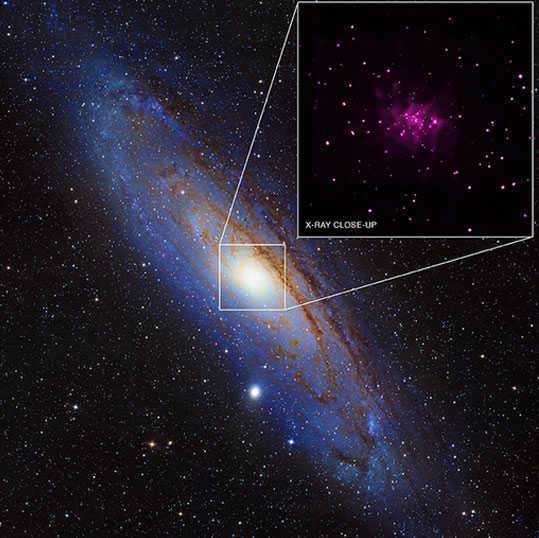
Recently, a group of astronomers made a remarkable discovery in the neighboring galaxy Andromeda – they found a staggering 26 previously unknown black holes. This finding represents the largest known cluster of black holes outside of our own galaxy, the Milky Way.
Unlike stars and other celestial objects, black holes themselves do not emit any visible light. However, their presence can be inferred through the detection of radiation emitted by the matter that is pulled into them. In the past, only 9 black holes were known to exist in the Andromeda galaxy, but now with this new discovery, the total number has increased to 26.

Galaxy Formation: A Mystery Yet to Be Solved
The process of galaxy formation still remains a mystery for astronomers. Following the Big Bang, the universe primarily consisted of hydrogen and helium.
One theory suggests that gravitational forces attracted dust and gas, leading to the formation of individual stars. These stars gradually drew closer, eventually giving rise to star clusters and ultimately galaxies.
On the other hand, some scientists propose that galaxies first emerged from the combination of dust and gas, with stars appearing later within these galactic structures.

Galactic Phenomenon
During the early 1900s, there was a debate among astronomers regarding the nature of the universe. Some believed that it was contained within our galaxy, known as The Milky Way, while others argued that there were separate objects, such as clusters of gas and dust in spiral formations. American astronomer Harlow Shapley referred to these formations as “star islands” or “island universes.”
In 1924, another American astronomer named Edwin Hubble made a significant discovery. He found several unique pulsating stars, known as cepheids, in certain nebulae and concluded that they were located outside of the Milky Way.

Astronomer Edwin Hubble (1889-1953) from the United States of America
It was discovered that certain objects, previously believed to be part of our galaxy, are actually located much further away from our galaxy within other star clusters.
Following Hubble’s measurement of the distance to individual stars, he went on to alter the amount of light emitted by galaxies due to their motion. He determined that the galaxies surrounding the Milky Way were moving away from it at incredibly high velocities..
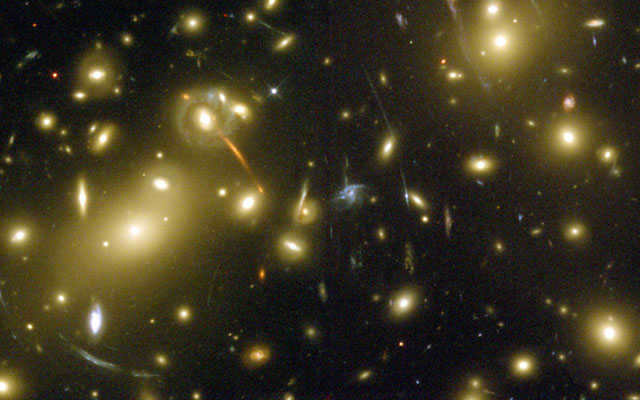

As galaxies move farther away from us, they also move at a faster rate. This discovery by Hubble led to the conclusion that the entire universe is expanding. Astronomers later discovered that this expansion is happening at an accelerating rate.
Categories of galaxies
Galaxies are categorized based on their shapes. Each category possesses unique characteristics and undergoes different stages of development.
Some galaxies, including the Milky Way, have spiral arms that extend from their centers. These galaxies are referred to as spiral galaxies and are the most prevalent type.
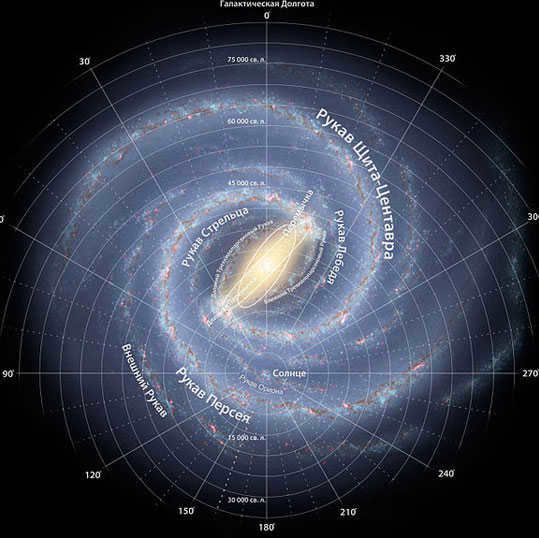
The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy that contains a central junction.
The gas and dust within a spiral galaxy orbit its center at incredibly fast speeds, reaching several hundred kilometers per second. This rapid rotation is what gives a spiral galaxy its distinctive shape.
Some spiral galaxies feature a unique structure in their center, known as a junction, which is composed of gas and dust. This accumulation of material plays a crucial role in the formation of new stars, and can be found in various spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way.

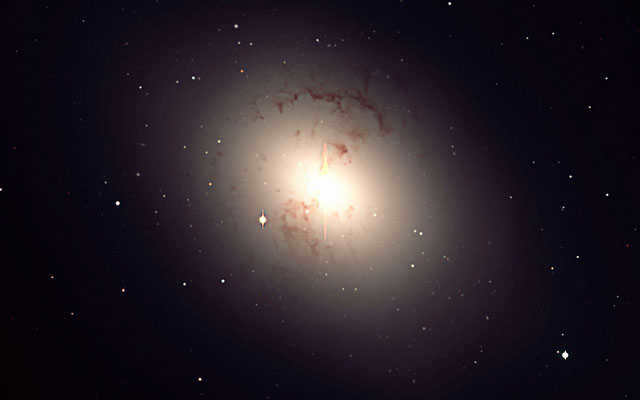
Elliptical galaxies don’t have arms like spiral galaxies. They can either be shaped like an elongated ellipse or a perfect sphere. These types of galaxies contain less dust compared to spiral galaxies, which means that the process of star formation in them is already complete.
The majority of stars found in elliptical galaxies are already old. Astronomers have observed only a small number of elliptical galaxies, but they believe that more than half of the galaxies in the universe fall into this category.

Irregular galaxies make up the remaining 3 percent of galaxies. They lack a distinct shape, whether it be round or spiral, which is why they are called irregular. Their form can be altered by the gravitational forces exerted by other galaxies, causing them to stretch or twist. Additionally, the shape of irregular galaxies can be changed through mergers with other galaxies or their close proximity.
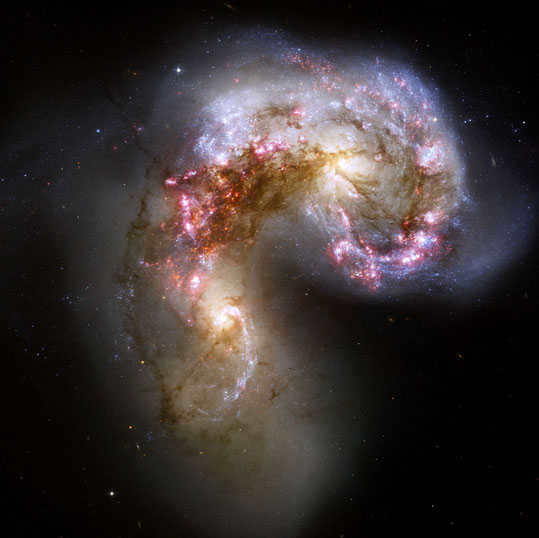

Galaxies in Collision
Galaxies occasionally wander through the vastness of space and clash with one another. At times, they converge to form clusters known as galaxy clusters. These clusters can range from massive conglomerates containing thousands of galaxies to smaller, more intimate gatherings.
Our very own galaxy, the Milky Way, is a member of a cluster called The Local Group, which consists of a whopping 50 galaxies.
Galactic collisions can result in a phenomenon known as mergers, which play a vital role in the growth and evolution of many galaxies. While individual stars typically do not collide during these mergers, the influx of gas and dust can trigger a heightened rate of star formation. In approximately 5 billion years, the Milky Way is slated to collide with the Andromeda galaxy.

The destiny of the Andromeda and Milky Way galaxies
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope “Hubble” has captured a mesmerizing photo of two colliding galaxies. These two galaxies bear a resemblance to a penguin bending over an egg. Both of these galaxies are situated near the Hydra constellation and are approximately 326 million light-years away from Earth.
Referred to as the spiral galaxy NGC 2936, the “Penguin” is currently undergoing star formation. At one point, it had a similar appearance to the Milky Way and took on the shape of a flat spiral disk. However, the orbits of the stars within this galaxy have been disrupted due to the gravitational influence of another egg-shaped galaxy, NGC 2937, causing it to change its shape. NGC 2936.
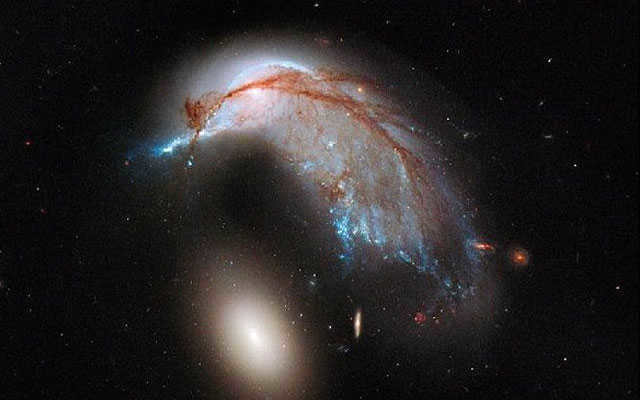

Penguin with an egg: an instance of the convergence of two galaxies (NGC 2936 and NGC 2937).
Andromeda Galaxy (fresh picture)
A fascinating fresh image portrait of the galaxy nearest to the Milky Way reveals the galaxy Andromeda you can observe our neighbor in a totally unique perspective thanks to Japan’s newest telescope instrument Subaru. The fresh images were recently presented at the Hawaii Summit.
The fresh instrument, known as Hyper-Suprime Cam (HSC). permits you to capture crisp pictures of the universe across a broad spectrum.
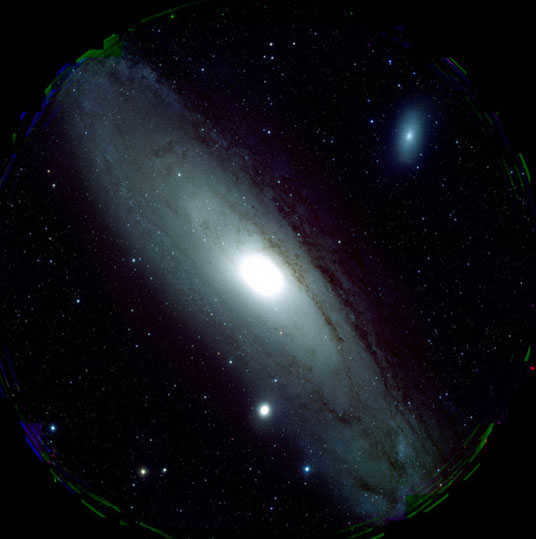

A new high-resolution camera from the Subaru Telescope captures stunning images of the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as M31, is located just 2.52 million light-years away from Earth. This spiral galaxy is considered to be very similar to our own Milky Way.
Even with the naked eye, the Andromeda Galaxy can be seen in the night sky as a faint speck. It was first described in 964 A.D. by the Persian astronomer As-Sufi.
Astronomers have devised a plan to utilize the cutting-edge HSC instrument in order to gather fresh comprehensive data on every single known galaxy. The Andromeda Galaxy, along with its counterparts M32 (located in the center left) and M110 (situated at the bottom), holds the distinction of being the farthest galaxies in existence. In addition to obtaining sharper visuals of the most remote galaxies, researchers also aim to delve into the phenomenon of how colossal entities possess the ability to warp light through their gravitational force.
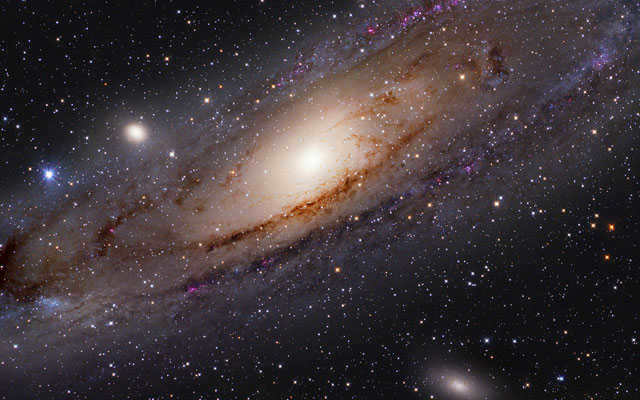

The Andromeda Galaxy, along with M32 (located to the center left) and M110 (found at the bottom)
This information will aid researchers in charting the dispersion of invisible matter.and identifying recently emerged miniature galaxies in the cosmos. Through the examination of galaxies serving as gravitational lenses.scientists will be capable of determining the quantity of matter present in the Universe and gaining further insight into the enigmatic entity – dark matter..
The tiniest galaxy
A remarkably faint agglomeration of 1,000 stars encircling the Milky Way. holds the record for being the lightest galaxy in terms of mass ever identified. This diminutive galaxy was spotted in the constellation of Aries in 2007 and was given the name Segue 2. Its substance is unified by a small assemblage of dark matter.
Spotting a galaxy smaller than Segue 2. Segue 2 – is akin to unearthing an elephant tinier than a mouse according to the researchers. This galaxy is only 900 times more luminous than the Sun, when compared to the Milky Way. the Milky Way is 20 billion times brighter than our star.
The galaxy Segue 2 is not a star cluster because it encompasses dark matter. encompasses dark matter which astronomers theorize functions as cosmic adhesive. It has recently become evident that Segue 2 is 10 times less dense than previously surmised.
There is a possibility that, beside the Milky Way, there exist other small galaxies that astronomers have not yet managed to detect.
When we gaze at the night sky filled with stars, we can observe a vast collection of stars: some bright and barely visible, others white and blue, reddish and green. This group of stars is what the ancient Greeks referred to as the Galaxy, which is known as the Milky Way in Russian.
If you were to view this star system from a distant location, you would notice that it resembles a flattened sphere containing 150 billion stars. The size of our Galaxy is so immense that it is difficult to comprehend. It takes approximately 100,000 Earth years for a beam of light to travel from one end to the other!
The core of our Galaxy is the central point, surrounded by numerous large spiral branches filled with stars. Our Sun is positioned 30,000 light-years away from the nucleus of the Galaxy, residing in one of its spiral arms. Therefore, it is situated on the outskirts of the Galaxy.
Despite the apparent density, stars in the Galaxy are actually quite sparsely distributed. For instance, in the vicinity of the Sun, the average distance between the nearest stars is approximately 10 million times greater than their own sizes.
Consequently, stars in the Universe are not randomly scattered. They are organized into structured systems where gravity (attraction) binds them together. These systems of stars are known as galaxies. In addition to stars, galaxies consist of interstellar dust and gas.
There are multiple galaxies present in the vast expanse of the Universe. The ones closest to our own star system are located approximately 150,000 light years away. When observed from the southern hemisphere sky, they appear as small, hazy dots.
Galaxies exhibit a diverse range of shapes and structures. Among them are globular and elliptical galaxies, as well as disk-shaped and spiral galaxies like our very own Milky Way. Additionally, there are galaxies with irregular shapes.
In the section of the Universe that can be explored using modern astronomical tools, there exist billions of galaxies. Astronomers have referred to this collection of galaxies as a metagalaxy..
Galaxies are vast collections of stars, interstellar dust, and gas. They can be likened to enormous celestial islands adrift in the cosmos.
Galaxies can be categorized into three primary types: spiral (resembling a rotating wheel with bursts of light around its circumference), elliptical (having an oval shape), and irregular (taking on a blob-like form).
The sun and all the stars visible in the nighttime sky belong to the star system known as our Galaxy. This system also includes the multitude of stars that compose the shimmering band known as the Milky Way. Our Galaxy is commonly referred to as the Milky Way. In ancient times, it was referred to as the “heavenly river” or the “heavenly road,” and the ancient Greeks believed that this “road” was formed by droplets of divine milk that had been spilled.
The Milky Way wraps around the entire sky like a vast, shining ribbon. It becomes particularly visible when you are away from the bright lights of the city. If you observe it through binoculars on a clear night, you will see that it is composed of a multitude of radiant stars. The dark patches are actually clouds of gas and dust that obstruct the light emitted by distant stars.
Other galaxies are situated at great distances from our planet. The proximity to the nearest one is usually measured in megaparsecs.
Our galaxy possesses a spiral configuration, with spiral arms extending outward from its core. Its diameter spans an impressive 100,000 light years. This signifies that it takes exactly that many years for light to travel from one edge of the galaxy to the other. Numerous other galaxies in the Universe exhibit spiral shapes. The nearest large spiral galaxy to us is the Andromeda Nebula.
Galaxies – an explanation for kids
Astronomy for kids > Galaxies
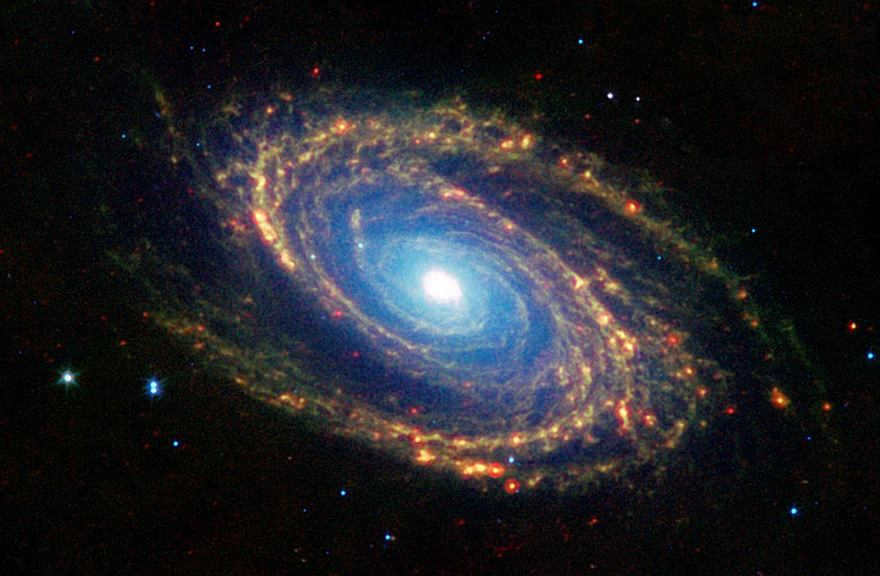

All information pertaining to galaxies for children of any age: inclusive of descriptions accompanied by photographs, the definition of what constitutes a galaxy, the various types, the Milky Way, and an explanation of how galaxies come into existence and merge in space.
An introduction suitable for children, whether it be at home or in a classroom setting, can commence by clarifying that galaxies are colossal cosmic systems that are composed of dust, gas, and stars. It’s important for children to grasp the concept that an exact number cannot be calculated, as there may be 100 billion such systems in the observable Universe alone. Some of these systems bear a resemblance to our very own Milky Way, while others exhibit a completely distinct structure.
It is essential to convey to children that small galaxies are characterized by having fewer than a billion stars. In our galaxy, known as the Milky Way, the Sun is just one of 100 billion stars.

Galaxies with a spiral shape
Galaxies with a spiral shape, such as the Milky Way, are characterized by a flat disk with a bulging center and spiral arms. Within this disk, planets, stars, dust, and gas orbit around the central region.
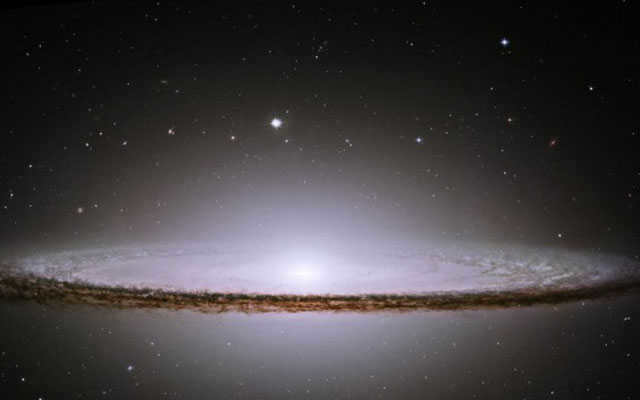
Although we are not aware of it, these galaxies rotate at speeds of hundreds of kilometers per second. This rotation causes the matter in the disk to take on a spiral shape, resembling a cosmic whirlwind. Some spiral galaxies are even more pronounced in their curvature, resembling the Sombrero Galaxy.
Within the bulging center of these galaxies, older stars are typically found, while new stars are constantly forming within the spiral arms. Surrounding the disk is a halo, which intrigues scientists as it may contain a significant amount of enigmatic dark matter.

Elliptical galaxies
Parents or teachers at school can teach young children that elliptical galaxies are named after their shape. They are commonly elongated, circular galaxies. Sometimes, they can even resemble a cigar.
Elliptical galaxies have a large number of old stars, up to a trillion, but not much dust and other interstellar matter. The stars in these galaxies rotate around the center, similar to spiral galaxies, but there are some differences. It is important to explain to children that the directions of rotation in elliptical galaxies are more chaotic and even random. Very few new stars are formed in this type of galaxy.
Giant elliptical galaxies are renowned celestial bodies in the vast expanse of the Universe. These remarkable entities can extend up to a staggering length of 2 million light-years. Nonetheless, amidst their grandeur, one can also encounter diminutive counterparts – dwarf elliptical galaxies.

Irregular galaxies
Any galaxies that do not fit into the aforementioned categories are categorized as irregular galaxies. They possess distorted shapes and lack a consistent and defined form. The reason for this is that they are often subject to the gravitational pull of other galaxies.
In the vast expanse of outer space, one can come across individual galaxies as well as paired galaxies. However, they commonly congregate in groups known as clusters or superclusters. Within these clusters, gravitational interactions and even mergers take place. As a result, gases begin to accumulate at the center of these galaxies, occasionally leading to the rapid formation of new stars.
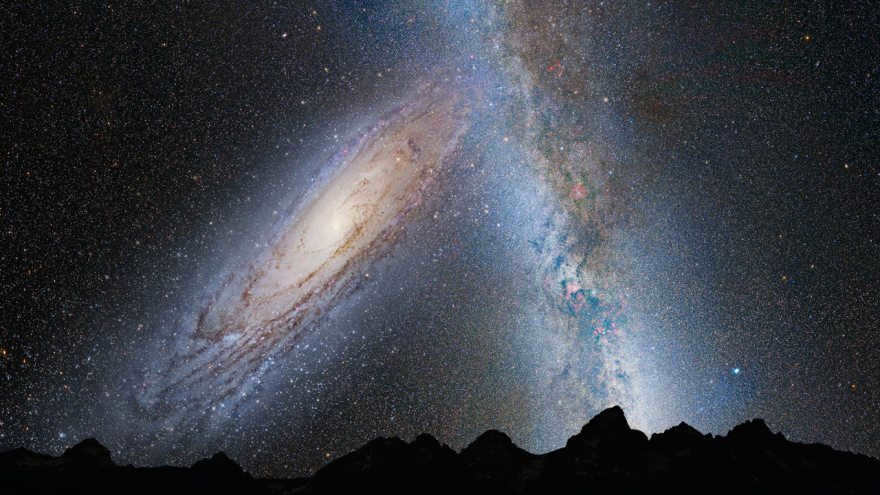

After 3.75 billion years, the night sky above us will have a different appearance: the Andromeda galaxy will be getting closer to the Milky Way.
It is important for youngsters to understand that even our own Milky Way may one day be involved in a cosmic collision. The Andromeda galaxy, which is currently separated from us by a distance of two million light-years, is a likely candidate. It can be observed without the need for any special equipment from the northern hemisphere.
There is no reason to be afraid of this event, as it is a natural part of the ongoing intergalactic evolution. Through this process, irregular galaxies can transform into a different shape, while spiral galaxies can turn into elliptical ones.
However, when it comes to the birth stage of galaxies, scientists are divided into distinct factions. One faction posits that small globular clusters, brimming with a million stars, took shape initially and subsequently coalesced to form galaxies. On the other hand, another faction contends that galaxies materialized first and within them stars began to congregate into clusters.
Project “The World of Galaxies” for senior preschool children
IRINA LYKOVA
Project “The World of Galaxies” for children of senior preschool age.
RELEVANCE OF THE PROJECT The project is relevant because space is a vast and fascinating topic that sparks children’s interest and promotes their overall development. It also helps children understand the world around them by encouraging them to discover scientific truths on their own, rather than simply memorizing them.
ISSUES TO ADDRESS The project aims to increase preschoolers’ cognitive interest and motivation during lessons.
What exactly is a galaxy? What types of galaxies exist? And in which galaxy is our Earth located?
GOAL: To introduce children of senior preschool age to the concept of outer space and galaxies through a research-based project activity.
OBJECTIVES (for children, teachers, parents)
– To help children understand that a galaxy is a collection of numerous stars, and that the Earth is located in a spiral galaxy known as the Milky Way.
– To foster a sense of curiosity and interest in scientific research by conducting engaging experiments and involving children in hands-on activities.
For teachers
– To develop project-based learning activities that encourage research and inquiry. This includes organizing project presentations and helping children understand their role as contributors to the project.
– To enhance students’ critical thinking skills by teaching them how to evaluate the effectiveness and reliability of different sources of information. Encourage peer discussions and collaboration throughout the project.
For parents
– To promote a collaborative and supportive partnership between parents and teachers.
To enhance the relationship between children and their parents, we will engage in experiments, play activities, and reading encyclopedias.
Our goal is to actively involve parents in the upbringing and education of children in the group.
PROJECT PARTICIPANTS: Children aged 6-7, teachers, parents
DATES: November-December
We aim to help children understand what galaxies are and increase their motivation for learning.
This project also focuses on fostering the development of children’s independent and creative personalities.
Furthermore, we aim to involve parents in joint activities with their children both at home and in the kindergarten.
PROJECT CONTENT:
Stage 1: Project Development
1. Discuss the principles of working with the project participants.
3. To select materials for visual and practical, experimental activities.
4. Choose materials and attributes for game and cognitive activities.
1. Examination of images of galaxies, planets, stars, illustrations, encyclopedias on the topic: Galaxies.
2. Discussions: “What are Galaxies?”
“Galaxies have names”, “Small and large Galaxies”. 3.
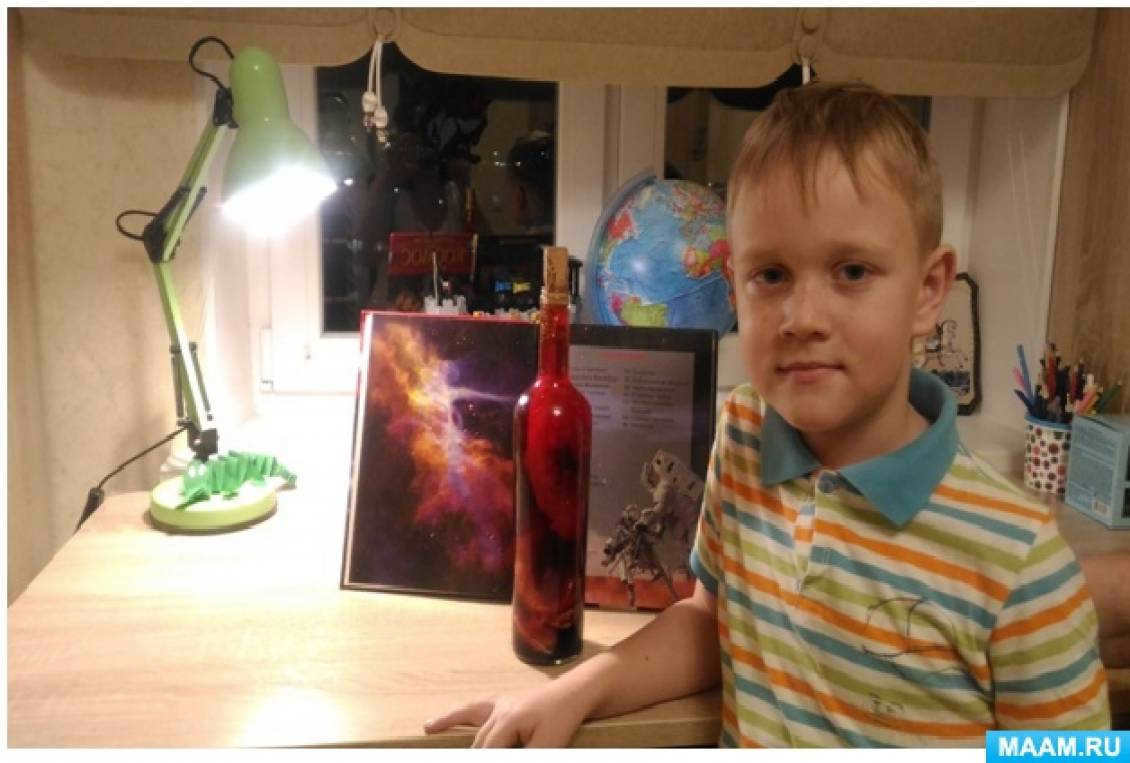
3. Experimental activities: “Galaxy in a bottle”, “Andromeda Nebula”.
4. Meeting with astronomy enthusiast E. G. Draganov. G. Draganov, the leader of the astronomy club at school No. 56.
5. Creative work – creating thematic posters: “Galaxy – Milky Way”, “Galaxy – Andromeda”, “Galaxy – Tadpole”.
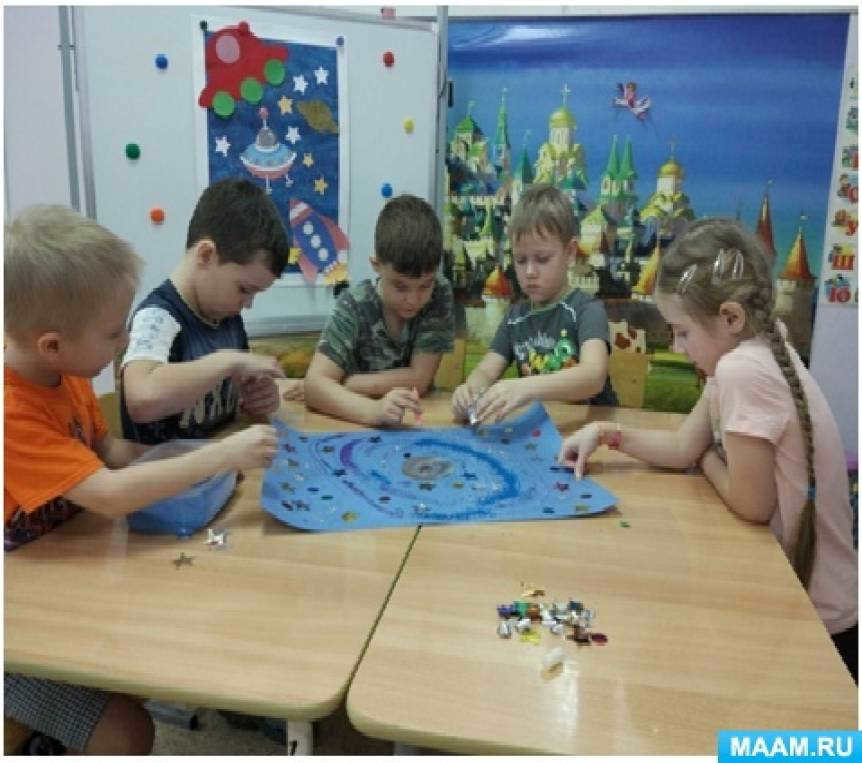
7. Board games: “Universe”, “Journey to distant galaxies”
8. Sports entertainment: “Space journey to the galaxy”.
Revised:
Hosting the galaxy-themed space week.
Establishment of a children’s astronomy club.
EQUIPMENT AND RESOURCES: Illustrative material on the topic of “Galaxies”, telescope, projector, presentations.
INTERNET RESOURCES: E. Levitan “To Kids about the stars”.
Г. Yurmin, A Dietrich. Whychka. Fun encyclopedia.
Л. Petranovskaya “Starry Sky”.
“Fascinating astronomy” E. Kachur from the series “Children’s Encyclopedias with Chevostik”.
Encyclopedias: “Everything about everything”, “From A to Z”, “What is it, who is who?”, Encyclopedia “My first book about space”.




There is a short-term project called “Wide Shrovetide” that is designed for children in their senior preschool years. This project will run from February 18 to March 4 and aims to promote spiritual and moral growth among the participants.

Project for children in the last year of preschool “Seven Troublesome Onions” Project Objective: To establish a vegetable garden on the windowsill in the children’s home group. Project Challenge: What is the method to cultivate green onions on the windowsill?

The research and cognitive project called “Path to the Stars” is designed for senior preschool children. It has a duration of one week and involves children of senior preschool age, as well as teachers.
I would like to share the details of another project called “Autumn Baskets” which is also intended for children of senior preschool age. In a previous publication, I shared the script for the “Autumn Baskets” holiday, which was the result of this project.

The ecological project “Earth – our shared home” is designed for children in their final year of preschool. It aims to raise awareness about the environment and the importance of taking care of our planet. This project is a combination of creative and research activities, allowing children to explore various aspects of the earth and its ecosystems. Through this project, children will learn about different ways to protect the environment and make a positive impact on the world around them.

Project “Easter Holiday” for senior preschool children Type of project: cognitive and creative; Type of project: group; Duration: medium-term (29.03 – 13.04.2018); Project participants:.
Project “Journalists” for older preschool children on the theme “Health and safety of preschool children” Purpose: Formation of the fundamentals of safe behavior in everyday life, society, nature. Objectives: To strengthen the ability to adhere to the rules of staying in the nursery.

The project “Winter Wonderland” is designed for children in their final year of preschool. Its purpose is to explore the wonders of winter and encourage children to think about the changing seasons, the well-being of everyone during the winter, and the potential consequences if winter didn’t exist.
The project “Russian Matryoshka” is specifically designed for older preschool children. It aims to educate them about the iconic Russian nesting dolls and their cultural significance. The project also includes a protection aspect, promoting the preservation of this traditional art form.
As part of the “Russian Matryoshka” project, there is a holiday celebration called “Ah, Matryoshechka-Matryoshka.” This event showcases the beauty and charm of these dolls. Please enjoy slide 1 of the presentation, which highlights the essence of the Russian Matryoshka.
What is a Galaxy? Explained Simply for Kids

The term “galaxy” is derived from the Greek word galaxias, which means “milky”. This refers specifically to our own galaxy, the Milky Way.
It is estimated that there may be more than 170 billion galaxies in the observable universe. Some of these galaxies, known as dwarf galaxies, are relatively small and contain around 10 million stars, while others are massive and can have as many as 100 trillion stars.
Astronomers have identified different types of galaxies based on their shape, including elliptical galaxies, spiral galaxies, lenticular galaxies, and irregular galaxies.
The spiral arms of spiral galaxies contain dense molecular clouds of hydrogen gas and dust, which are areas of intense star formation.
Interlaced spiral galaxies, such as our Milky Way, feature a lengthy band in the middle, accompanied by spiral arms that extend from the ends. Roughly two-thirds of spiral galaxies possess a shaded structure at their core.
The classification scheme of the Hubble Telescope categorizes spiral galaxies as type S, with ‘a’, ‘b’, or ‘c’ based on the density of the spiral arms and the size of the central bulge. Spiral galaxies with a junction are labeled as SB.
Spiral galaxies are believed to be younger compared to elliptical galaxies. As spiral galaxies consume gas and dust, the process of formation slows down, causing them to lose their spiral shape and gradually transform into elliptical galaxies.
Elliptical galaxies consist of a mass of stars gathered in the form of an elliptical disk.
Elliptical galaxies are often larger, extremely old, and contain minimal amounts of gas and dust, resulting in the formation of very few new stars.
The classification system known as Hubble’s scheme identifies elliptical galaxies by using the letter E followed by a numerical value that represents the level of ellipticity.
Lenticular galaxies, indicated by the symbol S0, are characterized by a prominent central bulge and a disk-like structure. However, unlike spiral galaxies, lenticular galaxies lack a spiral structure and do not actively generate numerous stars.
Galaxies that lack a distinct spiral or elliptical structure are referred to as irregular galaxies. Some irregular galaxies form naturally in this manner, while others are the result of collisions between different types of galaxies.
Our solar system is situated within the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 27,000 light-years away from the Galactic Center.
It is believed that supermassive black holes are present at the core of most galaxies.
About Us
Our Blog
Our Applications
Our Platform
Just a friendly reminder that I will be hosting a master class on April 23 at 3:00 PM Moscow time. During the class, I will be sharing simple yet effective techniques for locating significant locations on our planet.
This will be my final reminder as I am now fully focused on preparing for the class. If you haven’t already, you can sign up for the class by following this link: https://spica-club.ru/space.
Announcement has been made for the registration of my unique course on the astrology of space (astrogeography). You have the opportunity to register by visiting the following link: https://school.akviloncenter.ru/astrogeo
Alexander Kolesnikov offers you an exclusive course on the astrology of space (astrogeography), which is unparalleled in Russia or any other country.
During my visit to St. Petersburg in June 2022, I had the privilege of being interviewed by my esteemed colleague, Anton Mayorov. The interview proved to be a profound and comprehensive exchange, with a multitude of thought-provoking questions that led to a highly engaging conversation.
Astrogeography: The Final Call
The second session of my course is about to begin in an hour. The introduction and the first class have been recorded and are available for viewing. Additionally, there are accompanying materials, including slides packed with information. In a private group, there is an ongoing and lively discussion about the course material, and I am actively addressing any questions that may arise.
Here is the agenda for today’s lesson:
1. Q&A session
2. Showcasing relocation examples on classroom maps
3. Exploring the actual course material on astrosurfing
4. Analyzing the cards from the classroom in terms of relocation during reversal/semi-reversal/quarter reversal
5. Addressing any additional questions
To join the course, simply click here.
A unique opportunity is presented to you to enroll in Alexander Kolesnikov’s exclusive astrology of space course (astrogeography), which offers unparalleled coverage and depth of study not found anywhere else in Russia or abroad.
A video illustration of my ongoing space astrology course has been released.
This topic is one of the subjects covered in my space astrology course. The course can be accessed here:
The concept is that a prenatal eclipse may indicate the locations on Earth where an individual was incarnated in a previous lifetime. This concept …
🔥Attention, colleagues! I am pleased to announce that registration is now open for the incredible conference “Infinitum Destiny” taking place from June 21st to June 23rd, 2023.
I am thrilled to be one of the speakers at this highly anticipated event. Alongside me, there will be 33 distinguished experts in the fields of astrology and psychology.
The main focus of the conference revolves around the intriguing concept of Destiny.
Mark your calendars for the Big Astrological Conference “Infinitum – Destiny,” happening from June 21st to June 24th, 2023.
1️⃣ Don’t miss out on 3 complimentary days of the conference2️⃣ Benefit from insightful presentations by 30 exceptional astrologers
3️⃣ On day 4, indulge in 4 master classes featuring the renowned astrologer ⭐️ V.V. Gorbatsevich …
Created a brief video tutorial for individuals interested in getting ready for my presentation at the upcoming conference (in order to maximize the advantages and enhance the overall experience).
On June 24th, I will be delivering a speech at the renowned Astrological Conference “Infinitum – DESTINY” in Moscow (https://bit.ly/infinity-moscow). The focal point of my presentation will be the evolution of aspects in the Local Space. This subject may appear perplexing at first, but in reality, I will be discussing…
Now you can access my unique course on tape called Astrology of Space (Astrogeography):
Experience the unparalleled coverage and depth of study in Alexander Kolesnikov’s author course Astrology of Space (Astrogeography), which has no parallels in both Russia and abroad.
Today’s new moon is intriguing because the Moon is mostly forbidding, having reached its highest declination of 27° 52′ north just under two days before the new moon. As a result, two crucial points in the Moon’s cycles are closely aligned in time: maximum declination (intensified by the forbidden) and the new moon. This convergence of critical points often leads to significant disruptions on Earth, both in the natural world and in human society.
Another interesting aspect of this New Moon is its opposition to Pluto. In the chart for Moscow, this opposition is concealed in the descending houses, giving it a somewhat subdued appearance.
However, let’s create an astrological chart to determine the location on Earth where the new moon’s opposition to Pluto will be most prominent. To do this, we will utilize the In Mundo display mode, which I discuss in my video on astrocartography (you can watch it here: https://bit.ly/in-mundo).
In the third session of my space astrology course, I provided a thorough explanation of the two different modes for displaying lines (zodiacal and In Mundo). However, it seems that my explanations may have been too complex for some students. In this brief video, I present a simplified…
In the astrocartogram, it can be observed that the lines of the Moon and Pluto are in proximity to both Moscow and Kiev, while the line of the Sun is situated much further to the west. This serves as a noteworthy demonstration for the lines in In Mundo mode: due to the considerable ecliptic latitude of both the Moon and Pluto, their lines deviate from the expected positions on the angular cuspids of the relocation charts.
It appears that the tension brought about by the New Moon has the ability to extend into areas that are already experiencing tension.
However, there are other factors contributing to the tension in the New Moon chart aside from the opposition to Pluto. One of the most notable aspects is the counter-parallel between Mars and Saturn, which is accompanied by their opposition. This means that there is a strong opposition between these planets. The lines of these planets intersect in Transcaucasia, further intensifying the tension in this region. For instance, in Tbilisi, the Mars-Saturn opposition occurs on the Horizon. Additionally, in the New Moon chart for Moscow, as I will demonstrate once again, this opposition falls on the axis of the Equatorial Ascendant and Descendant. I interpret this as a sign of increasing tension between Moscow and the Transcaucasian countries.
If you don’t know about planetary declination and prohibited planets, I have a small book for you: https://www.galactica.ru/books/#declination.
These books were written throughout the years, with the initial one being published in the mid-1990s. Currently, they are being published and reprinted by renowned Russian publishers.
🔥There is an updated edition of the iLuna app for iPhone 🔥
This is the original and most successful of my mobile apps, initially released in 2009. I have spent nearly a year and a half working on the new version, facing numerous distractions, and it is now finally complete. This edition has been fully localized for Russian users. You can find it on the Apple App Store at this link:
My goal is to launch a new version for the Android platform by the end of this year.
iLuna is an interactive astrological calendar.
Below is a video that showcases the app’s features: https://bit.ly/iluna-video-ru
iLuna enables you to effortlessly determine the lunar phase, the Moon’s position in zodiac signs and risings, the Moon’s off-course and retrograde periods…
Shared a video story showcasing the latest update of the iLuna application
Click here to access the app: https://bit.ly/iluna-ios-ru
iLuna is an interactive calendar designed specifically for astrology enthusiasts.
With iLuna, you can effortlessly track the lunar phase, the Moon’s position in the zodiac signs and risings, as well as the periods of the Moon off-course and Mercury retrograde for any day starting from 2005…
🌟The iLuna application is currently available in version 3.1.🌟
As is customary after the release of a new application or a significant update, there are various issues that can range from minor to major.
One user reached out to inform me that the font utilized in the application is too large for his screen size. To address this concern, I have added a special “slider” to the settings page, allowing users to adjust the font size to a comfortable level.
In addition, I have also included a section on the help page for individuals who are interested in enhancing their understanding of astrology.
Furthermore, I have diligently worked on identifying and resolving a few programming errors or flaws commonly referred to as “bugs”.
The link to access the new version remains unchanged: https://bit.ly/iluna-ios-ru.
iLuna represents an interactive astrological calendar.
iLuna enables users to effortlessly determine the lunar phase, the Moon’s location in zodiac signs and constellations, the Moon’s deviations from its predicted course, and periods of retrograde movement…





